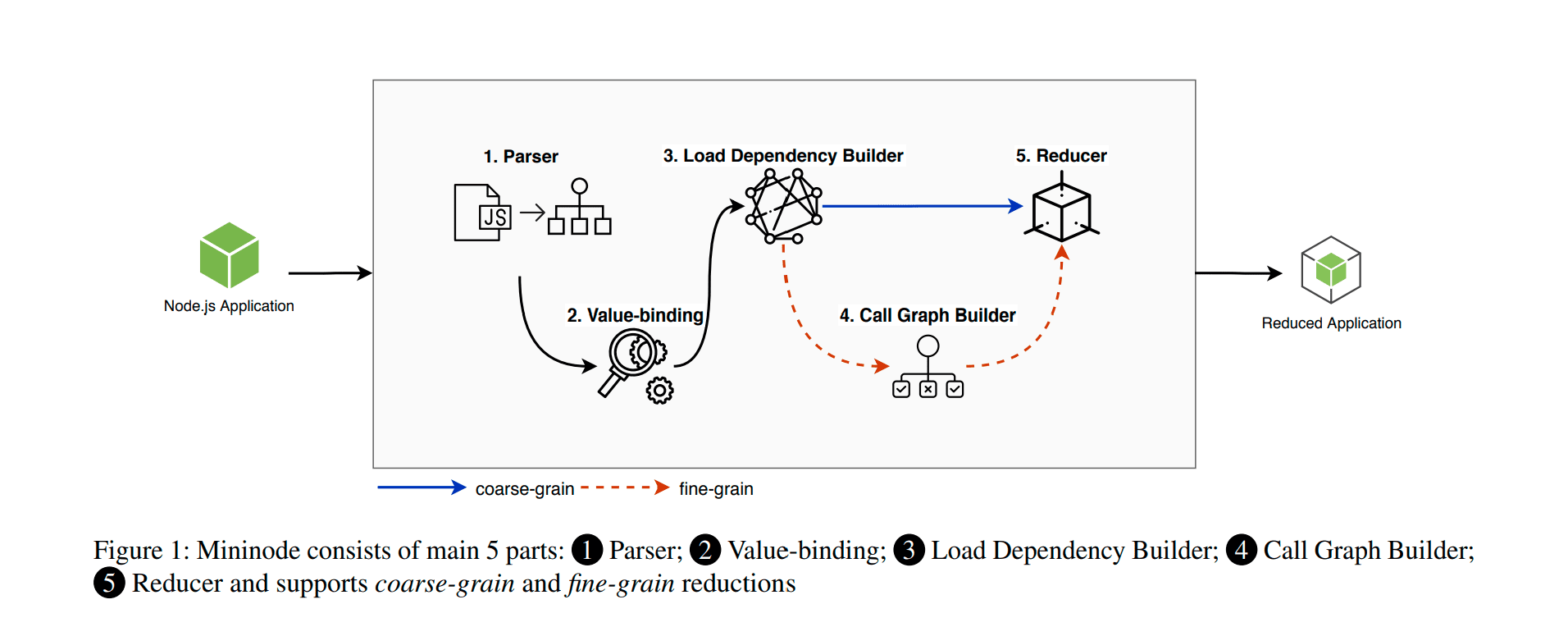
Mininode
Mininode is a CLI tool to reduce the attack surface of the Node.js applications by using static analysis of source code. It supports two modes of reduction (1) coarse, (2) fine.
Mininode constructs the dependency graph (modules and functions used) of the application starting from the main file, i.e. entry point of the application. Mininode initializes the entry point to the package.json file’s main field if it exists. Otherwise, default to index.js.

Download
git clone https://github.com/wspr-ncsu/mininode.git
Use
Example usage: node index.js <path to Node application root folder> –mode=(coarse|fine). Below is the list of options that can be passed to Mininode.
Options
List of command-line options that can be passed to mininode.
--destination, -d: the path where mininode will save the reduced Node.js application. The default value:mininode.--dry-run: just generates mininode.json without modifying the initial application.--mode, -m: reduction mode. The value can be eithercoarseorfine. Incoarsemode mininode will perform the only coarse-grained reduction. While infinemode mininode will perform the fine-grained reduction. In general coarse-grained reduction is more reliable, because mininode will not try to reduce unused functions inside the module. Default value:coarse.--silent: console output is disabled. This will improve the performance of the mininode.--verbose: outputs additional information to the console. The default value:false--log: mininode will generate log file inside, which contains dependency graph of the application in json format. The default value:true.--log-output: the name of the log file generated by mininode. The default value:mininode.json.--compress-log: compresses the final log file. By default it will dump everything into log file. In production it is advised to pass the--compress-logflag to save space.--seeds: seed files from where mininode will start building dependency graph. You can provide many seed files by separating them with colon.--skip-stat: skips calculating the statistics--skip-reduction: if passed mininode will not reduce the JavaScript files. The default value:false.--skip-remove: if passed mininode will not remove unused JavaScript files. The default value:false.
Limitations
- Mininode uses static analysis, which means it can not reduce the attack surface of the Node.js application which uses dynamic behaviour, such as
eval. If Mininode detects dynamic behaviour in the application it exits with errorDYNAMIC_BEHAVOUR_DETECTED.
Copyright (c) 2019, North Carolina State University
Source: https://github.com/wspr-ncsu/