
The AhnLab Security Intelligence Center (ASEC) warns a novel malware distribution tactic involving the use of Microsoft Windows CAB header batch files (*.cmd) to deploy the ModiLoader (DBatLoader) malware. This sophisticated evasion technique targets victims through phishing emails disguised as purchase orders (POs).
The ModiLoader campaign leverages a unique file structure that combines a CAB header (magic header MSCF), command-line instructions, and a portable executable (PE). Despite the *.cmd extension, the file exploits the CAB compression header format to bypass traditional email security and file inspection tools.
ASEC noted, “The threat actor altered the header of the attached file to bypass email security products,” and in some cases, even added a PNG file header to further evade detection.
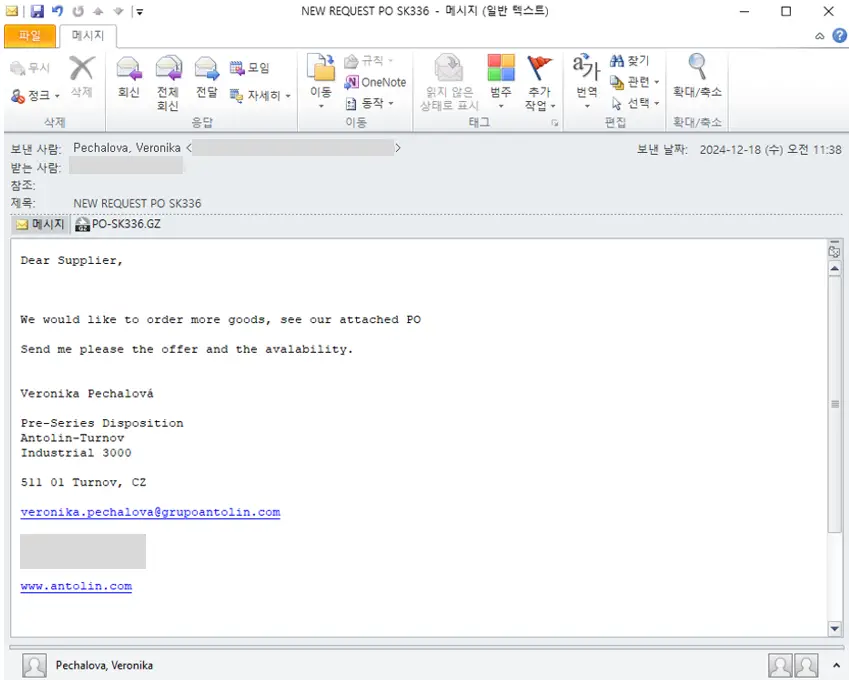
The distribution file, such as PO_SK336.cmd, follows a three-step execution process:
- Executes a command-line script, ignoring the initial header.
- Decompresses itself using extrac32.
- Creates and runs an executable file in the system’s %temp% directory.
The batch file employs the following command for execution:
This technique transforms the *.cmd file into a loader, delivering the malware while bypassing typical security mechanisms. Once executed, ModiLoader drops its payload in the %temp% folder and launches it.
The emergence of CAB-header-based loaders marks an escalation in malware evasion tactics. ASEC emphasizes, “Users should be particularly cautious regarding attached files,” as these methods are specifically designed to exploit human error and technical vulnerabilities.
Related Posts:
- Beyond HTML: The Hidden Danger of Phishing in HTTP Response Headers
- libcurl exists some bugs that leak authentication data to third parties