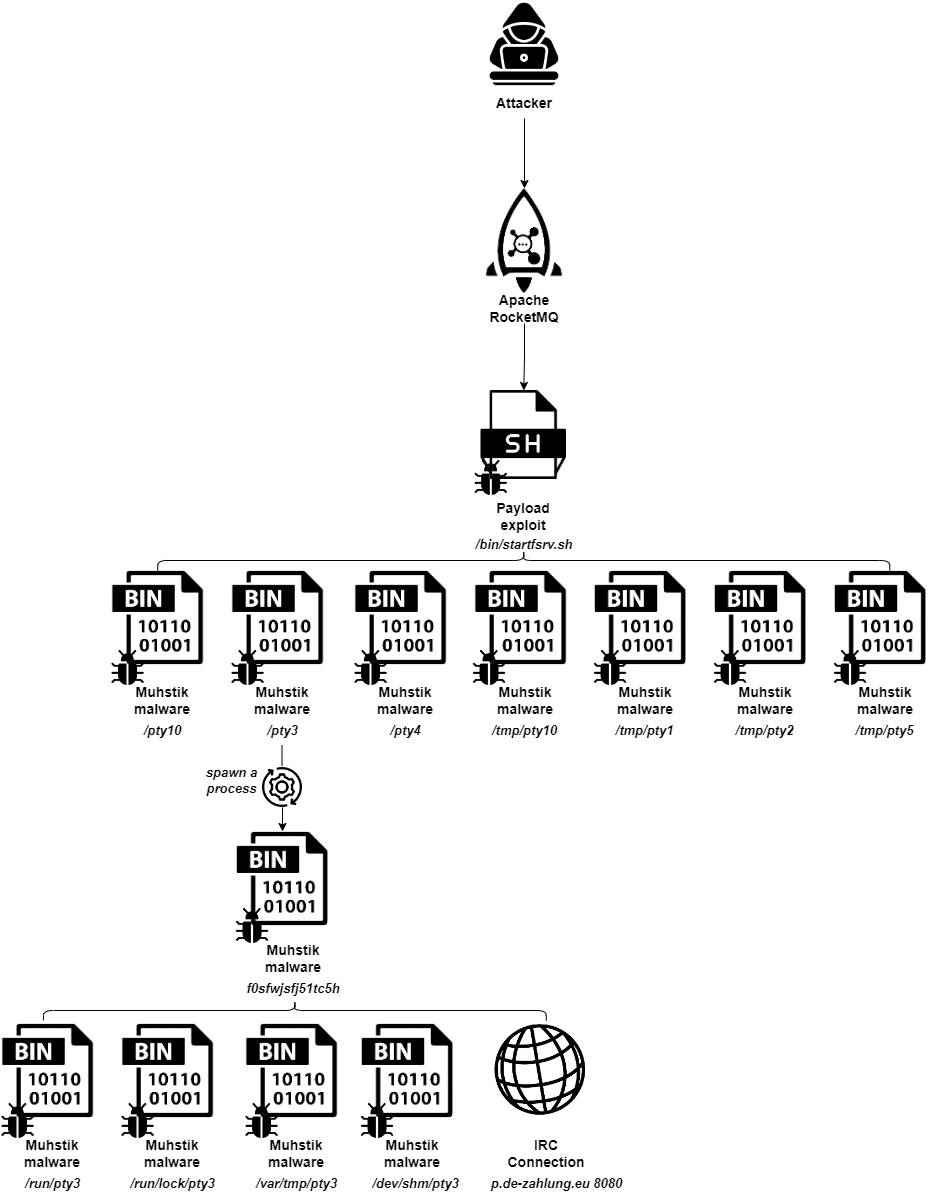
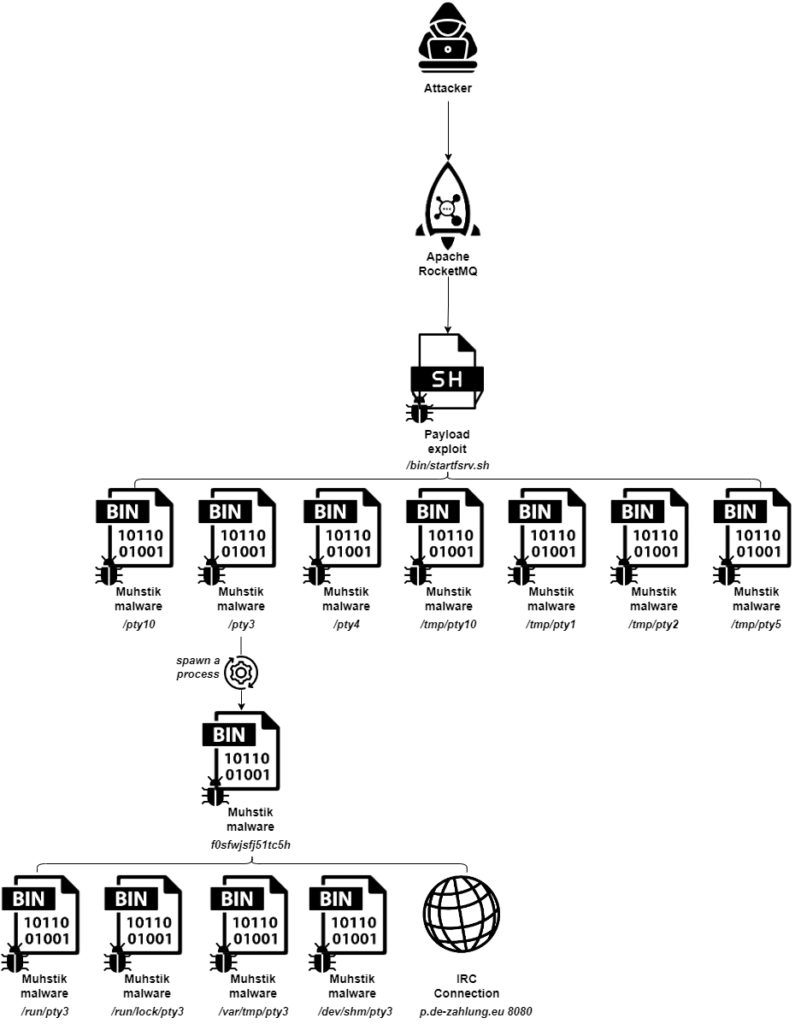
Attack Flow
Cybersecurity researchers at Aqua Nautilus have uncovered a concerning campaign where the Muhstik malware is actively targeting Apache RocketMQ installations. This new wave of attacks leverages a known vulnerability (CVE-2023-33246) in RocketMQ versions 5.1.0 and below, allowing attackers to remotely execute code and download the notorious Muhstik malware onto compromised systems.
The vulnerability in RocketMQ stems from insecure design elements, particularly within its broker component, which is typically not intended for public internet exposure. Attackers can exploit this flaw by manipulating the update configuration function, granting them the ability to execute commands with the same privileges as RocketMQ.
Muhstik, a well-known threat targeting IoT devices and Linux servers, has a history of using infected systems for cryptocurrency mining and launching disruptive DDoS attacks. Recent attacks observed by Aqua Nautilus demonstrate a familiar pattern:
- Initial Access: Attackers scan for vulnerable RocketMQ instances and exploit CVE-2023-33246 to upload malicious payloads. The attackers modified the
filterServerNumsandrocketmqHomevariables to exploit the vulnerability and set up their malicious payload. - Execution: The attackers used the FilterServerManager class to execute the malicious shell command via the CallShell method. The curl command downloaded a shell script containing several binaries from a remote server. These binaries were provided with execution permissions and executed, including the Muhstik malware.
- Persistence: Muhstik malware employs several persistence techniques, such as copying itself to multiple directories (
/dev/shm/pty3,/var/tmp/pty3,/run/lock/pty3,/run/pty3) and editing the inittab file to restart the process automatically. This ensures continuous access to the compromised machine. - Defense Evasion: The malware avoids detection by using techniques like fileless operation, changing file signatures, and using legitimate-looking names (e.g., pty3) to evade security tools. Muhstik malware runs from memory, bypassing traditional file system scans.
- Discovery and Lateral Movement: Attackers use the uname command to gather system information and check for network monitoring tools like strace and tcpdump. Muhstik malware scans for SSH services and attempts to authenticate, allowing attackers to move laterally across the network.
- Command and Control: Muhstik malware establishes communication with a command-and-control server via the IRC protocol. The server issues commands to the compromised machine, including commands to clean up competing malware processes.
The widespread adoption of RocketMQ, a popular message queuing service used in cloud-native applications, amplifies the potential impact of this campaign. Shodan scans reveal over 5,216 vulnerable RocketMQ instances worldwide, highlighting the urgency for organizations to patch their systems immediately.
To safeguard your systems from this threat, it’s crucial to:
- Update RocketMQ: If you are using Apache RocketMQ, ensure you are running version 5.1.1 or later, as these versions contain the fix for CVE-2023-33246.
- Implement Network Security: Employ firewalls and intrusion detection systems to monitor and block suspicious traffic.
- Regularly Scan for Vulnerabilities: Conduct routine vulnerability scans to identify and address any potential weaknesses in your systems.
- Monitor System Activity: Utilize security tools to detect unusual processes and network activity that may indicate an ongoing attack.