Attack Process of APT Group Actor240524 | Image: NSFOCUS
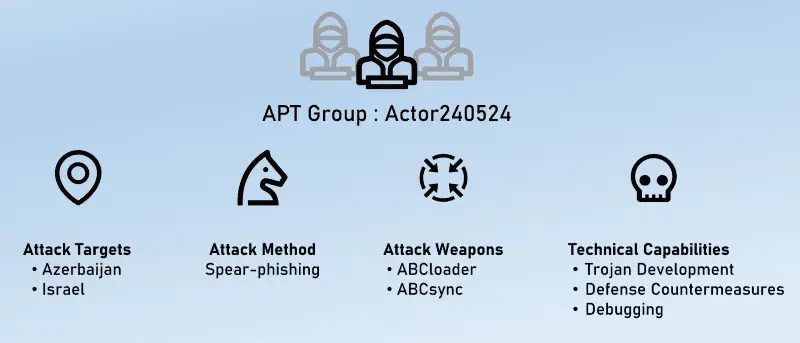
A sophisticated cyber espionage campaign targeting Azerbaijan and Israel has been linked to a previously unidentified advanced persistent threat (APT) group, designated as ‘Actor240524’ by NSFOCUS Security Labs.
Actor240524 distinguishes itself from established APT groups by its unique tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs). The group has demonstrated advanced capabilities in both data theft and the manipulation of file data, all while employing a range of countermeasures designed to evade detection and analysis. The tools of choice for this campaign include two newly identified Trojan programs, named “ABCloader” and “ABCsync” by NSFOCUS researchers.
The attack campaign appears to be politically motivated, targeting Azerbaijani and Israeli diplomats. Given the close economic and political ties between Azerbaijan and Israel, it is likely that Actor240524’s operation is aimed at undermining the cooperative relationship between the two nations.
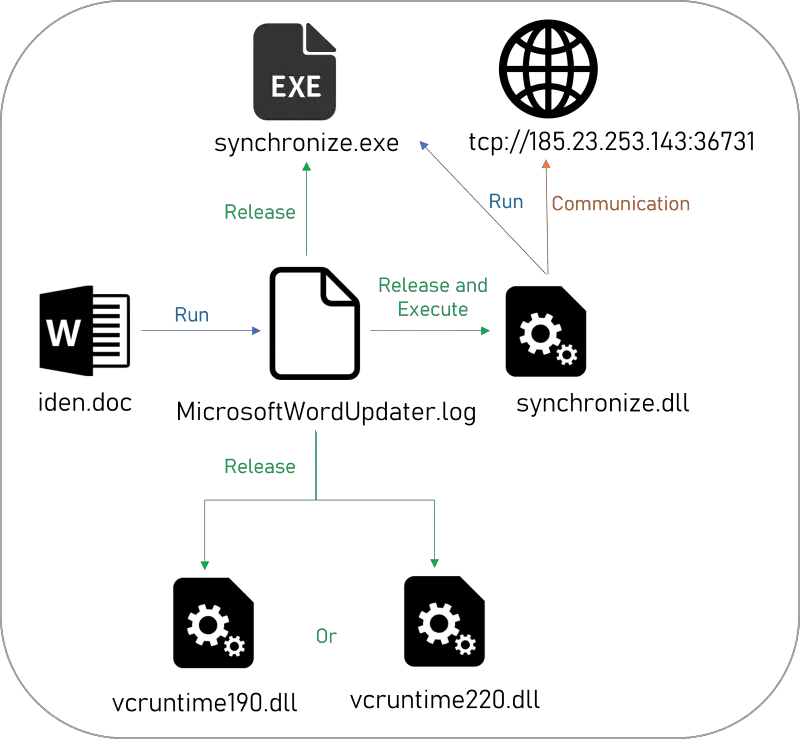
The attack began with carefully crafted spear-phishing emails, which were sent to selected Azerbaijani and Israeli diplomatic personnel. The emails contained a Word document named “iden.doc,” embedded with malicious macro code. Upon opening the document, the recipient was prompted to click “Enable Content,” triggering the execution of the macro code and setting the stage for a multi-stage attack.
The malicious document, upon execution, reads encrypted data embedded within itself, releasing three executable files, including the primary payload “ABCsync.” The macro code decodes the malicious payload and stores it at a specified location under a deceptive filename “MicrosoftWordUpdater.log,” masking its true nature as an executable file.
The payload “ABCloader” (disguised as “MicrosoftWordUpdater.log”) decrypts and releases additional executable files, including the critical “synchronize.dll” (ABCsync). ABCsync establishes communication with a Command and Control (C2) server, enabling the attackers to remotely execute commands and perform malicious operations on the compromised systems.
Actor240524 employed a variety of adversarial techniques to evade detection, including API encryption, PEB detection, hardware breakpoint detection, and screen resolution checks. The Trojan programs also implemented COM component hijacking to achieve persistence, allowing them to remain undetected and active on the targeted systems.
NSFOCUS’s analysis provides a detailed breakdown of the adversarial techniques used by Actor240524. These techniques include:
- API Encryption: Critical strings and API functions are encrypted to thwart static analysis and sandbox detection.
- PEB Detection: The group checks the BeingDebugged field and NtGlobalFlag to detect debugging attempts.
- Hardware Breakpoint Detection: Monitors for the presence of hardware breakpoints to identify potential debugging activities.
- Screen Resolution Detection: Uses screen resolution checks to determine if the environment is a virtual machine or sandbox.
- Process Count Detection: Exits the process if the number of running processes is less than 200, a common characteristic of sandbox environments.
For further information and to access the full analysis, visit the NSFOCUS Security Labs website.
Related Posts:
- Kaspersky Uncovers 10,000 Cyberattacks: Global Organizations Targeted
- APT29 Strikes German Politics with WINELOADER Malware Assault
- Operation ShadowCat Targets Indian Political Observers
- Israel filed a suit against Apple on the iPhone