Image: Eclypsium
A recent investigation by Eclypsium, a prominent supply chain security firm, has unveiled a series of critical vulnerabilities in F5’s BIG-IP Next Central Manager, which could potentially allow attackers to gain control over the network infrastructure.
BIG-IP is a well-known line of products from F5 that includes software and hardware designed to manage, secure, and optimize applications running across various networks. The Next Central Manager is described by F5 as a unified point of control for lifecycle tasks across the BIG-IP Next fleet, aiming to provide improved performance and management capabilities. This central management hub is crucial for organizations as it oversees numerous network operations essential for business continuity and security.

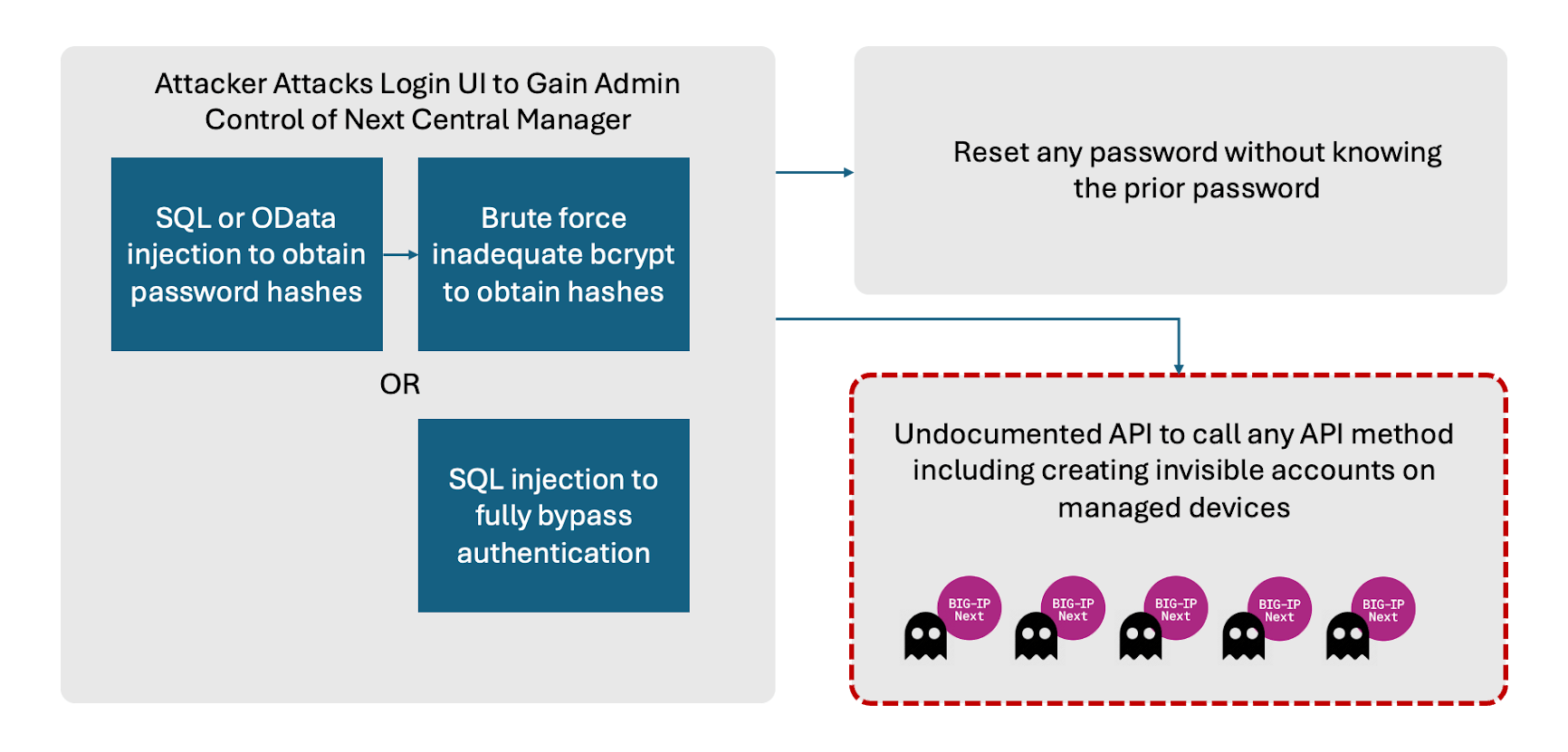
Eclypsium’s report has pinpointed several vulnerabilities, with two major ones assigned CVE identifiers due to their severity and ease of exploitation:
- CVE-2024-21793 (Unauthenticated OData Injection): This vulnerability exists in the handling of OData queries by the Central Manager. If LDAP is enabled, it allows an attacker to manipulate query parameters to extract sensitive information, such as administrator password hashes.
- CVE-2024-26026 (Unauthenticated SQL Injection): A more severe SQL injection flaw, this vulnerability can be exploited to bypass authentication mechanisms and potentially access administrative user password hashes.
These vulnerabilities, if exploited, grant attackers full administrative control of the Central Manager, enabling them to create accounts on any managed BIG-IP Next assets. Alarmingly, these accounts would not be visible from the Central Manager, allowing attackers to maintain hidden, persistent access within the network.
While only two CVEs were officially assigned, Eclypsium reported a total of five vulnerabilities, including three without CVEs that pose significant risks:
- Undocumented API Exploitation for SSRF Attacks: Attackers can manipulate server-side request forgery (SSRF) to invoke any API method on BIG-IP Next devices, potentially creating unauthorized accounts directly on these devices.
- Weak Bcrypt Implementation: The bcrypt cost parameter set to 6, used for hashing admin passwords, does not meet modern security standards, making it easier for attackers to brute-force these passwords.
- Admin Password Self-Reset Flaw: An authenticated administrator can reset their password without needing to know the previous one, complicating efforts to secure the system once compromised.
Eclypsium, which reported the flaws and shared the proof-of-concept exploit for these vulnerabilities.
Given the potential for these vulnerabilities to be exploited in malicious campaigns, Eclypsium and F5 urge all users of BIG-IP Next Central Manager to upgrade their systems to the patched version (20.2.0) immediately. Furthermore, organizations should consider adopting additional security measures such as:
- Enforcing Zero Trust Access Controls: Implement strict access control policies that verify who is attempting to access the network before granting access, regardless of where the request originates.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct thorough audits and penetration testing to identify and remediate vulnerabilities proactively.
- Educating Users and Administrators: Ensure that all users are aware of the potential threats and follow best practices for cybersecurity.