openedr
We at OpenEDR believe in creating a cybersecurity platform with its source code openly available to the public, where products and services can be provisioned and managed together. EDR is our starting point. OpenEDR is a full-blown EDR capability. It is one of the most sophisticated, effective EDR codebases in the world, and with the community’s help, it will become even better.
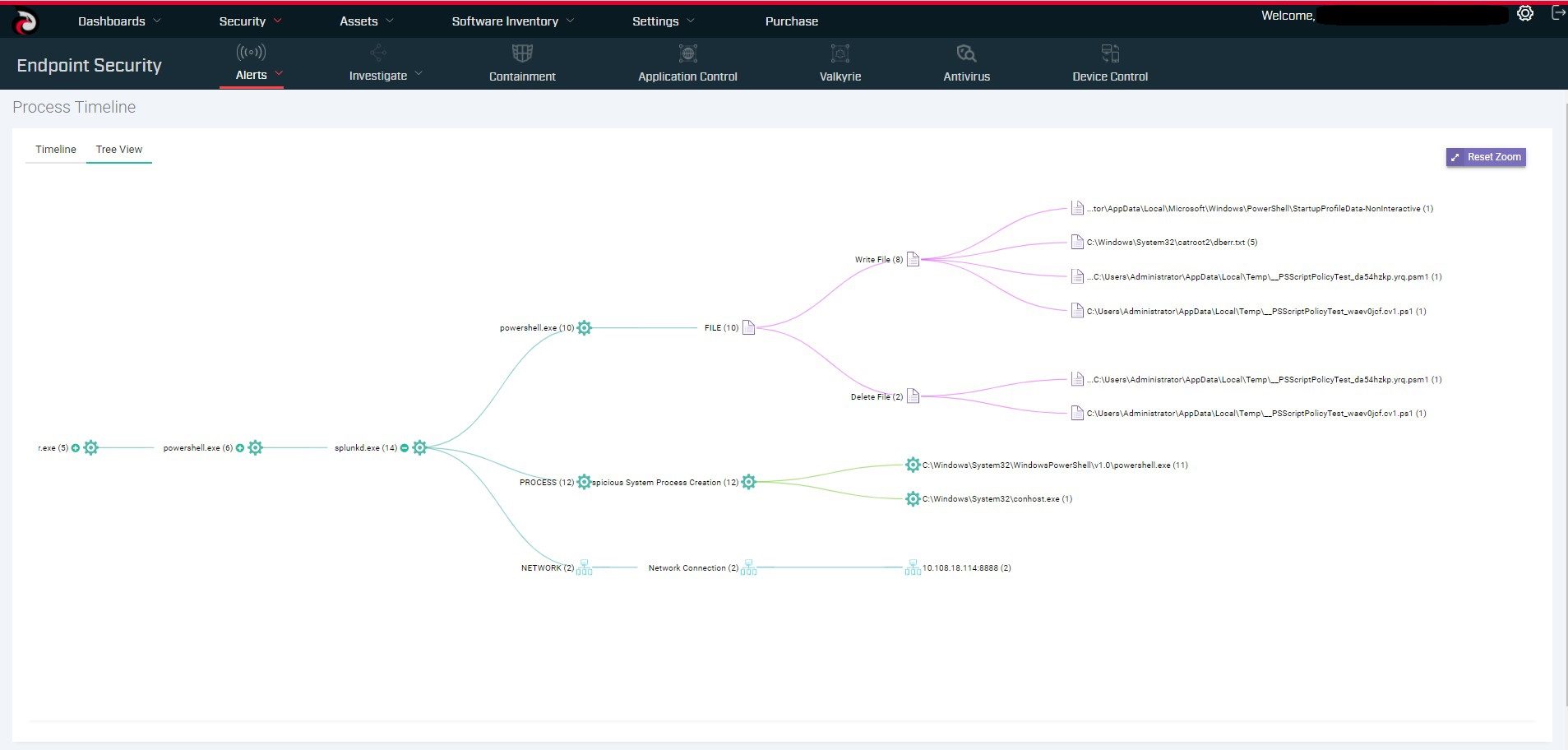
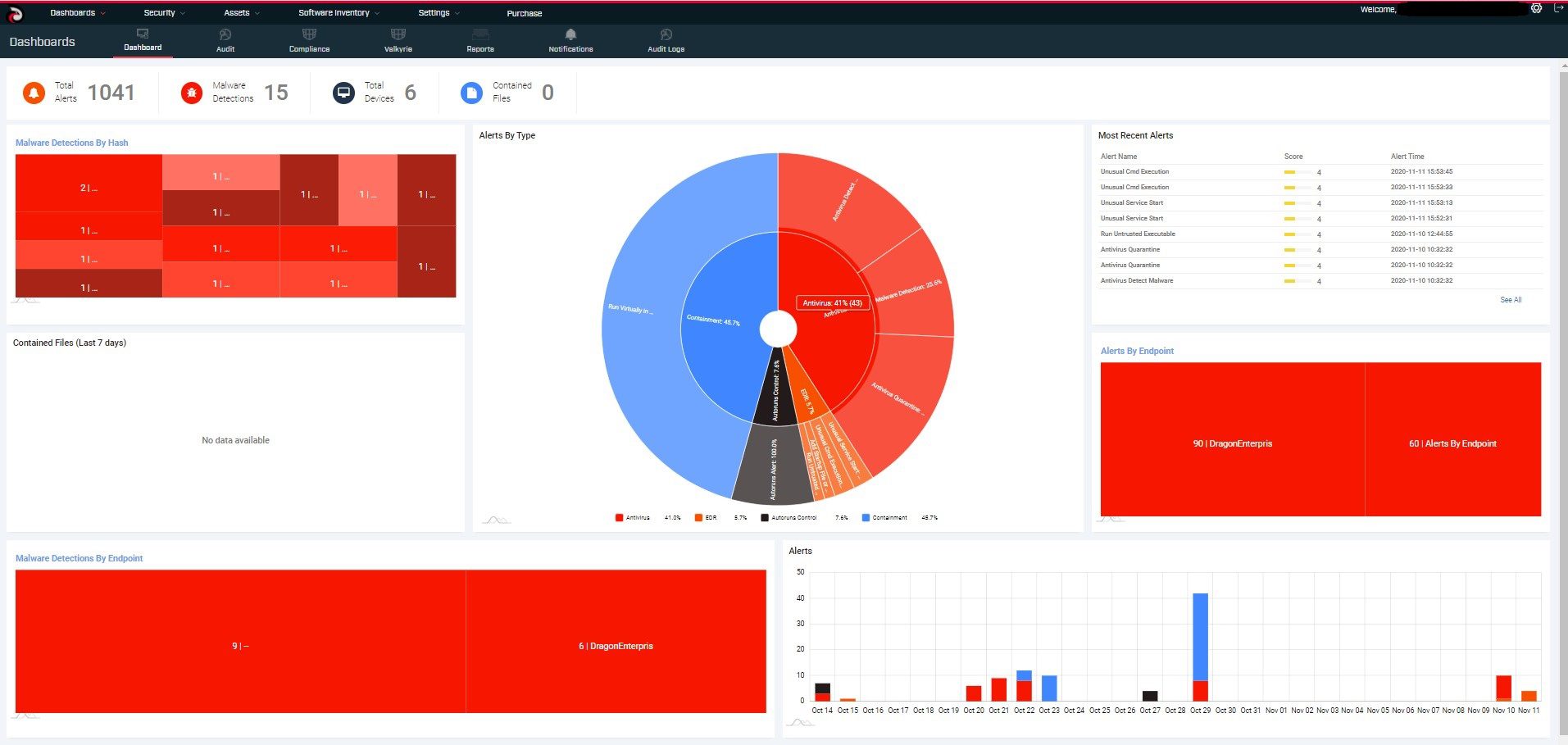
OpenEDR is free and its source code is open to the public. OpenEDR allows you to analyze what’s happening across your entire environment at the base-security-event level. This granularity enables accurate root-causes analysis needed for faster and more effective remediation. Proven to be the best way to convey this type of information, process hierarchy tracking provides more than just data, they offer actionable knowledge. It collects all the details on endpoints, hashes, and base and advanced events. You get detailed file and device trajectory information and can navigate single events to uncover a larger issue that may be compromising your system.
OpenEDR’s security architecture simplifies breach detection, protection, and visibility by working for all threat vectors without requiring any other agent or solution. The agent records all telemetry information locally and then will send the data to locally hosted or cloud-hosted ElasticSeach deployments. Real-time visibility and continuous analysis are the vital elements of the entire endpoint security concept. OpenEDR enables you to perform analysis into what’s happening across your environment at base event-level granularity. This allows accurate root cause analysis leading to better remediation of your compromises. Integrated Security Architecture of OpenEDR delivers Full Attack Vector Visibility including MITRE Framework.
Components
The Open EDR consists of the following components:
- Runtime components
- Core Library – the basic framework;
- Service – service application;
- Process Monitor – components for per-process monitoring;
- Injected DLL – the library which is injected into different processes and hooks API calls;
- Loader for Injected DLL – the driver component which loads injected DLL into each new process
- Controller for Injected DLL – service component for interaction with Injected DLL;
- System Monitor – the genetic container for different kernel-mode components;
- File-system mini-filter – the kernel component that hooks I/O requests file system;
- Low-level process monitoring component – monitors processes creation/deletion using system callbacks
- Low-level registry monitoring component – monitors registry access using system callbacks
- Self-protection provider – prevents EDR components and configuration from unauthorized changes
- Network monitor – network filter for monitoring the network activity;
- Installer
Generic high-level interaction diagram for runtime components 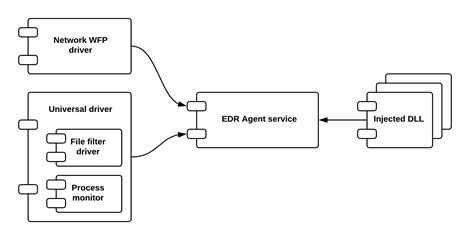 Install & Use
Install & Use
Copyright (C) 2020 ComodoSecurity