Cisco Talos, the threat intelligence division of Cisco Systems, has published a comprehensive report detailing a long-running cyber espionage campaign dubbed “Operation Celestial Force.” This operation, attributed with high confidence to a nexus of Pakistani threat actors known as Cosmic Leopard, has been systematically targeting Indian government, defense, and technology organizations since at least 2018.
The campaign employs a sophisticated suite of malware, including GravityRAT and HeavyLift, to compromise both mobile and desktop devices. GravityRAT, a multi-platform remote access trojan, enables attackers to exfiltrate sensitive data, monitor communications, and execute arbitrary code on infected devices. HeavyLift, an Electron-based loader, facilitates the deployment of additional malicious payloads, further expanding the attackers’ capabilities.
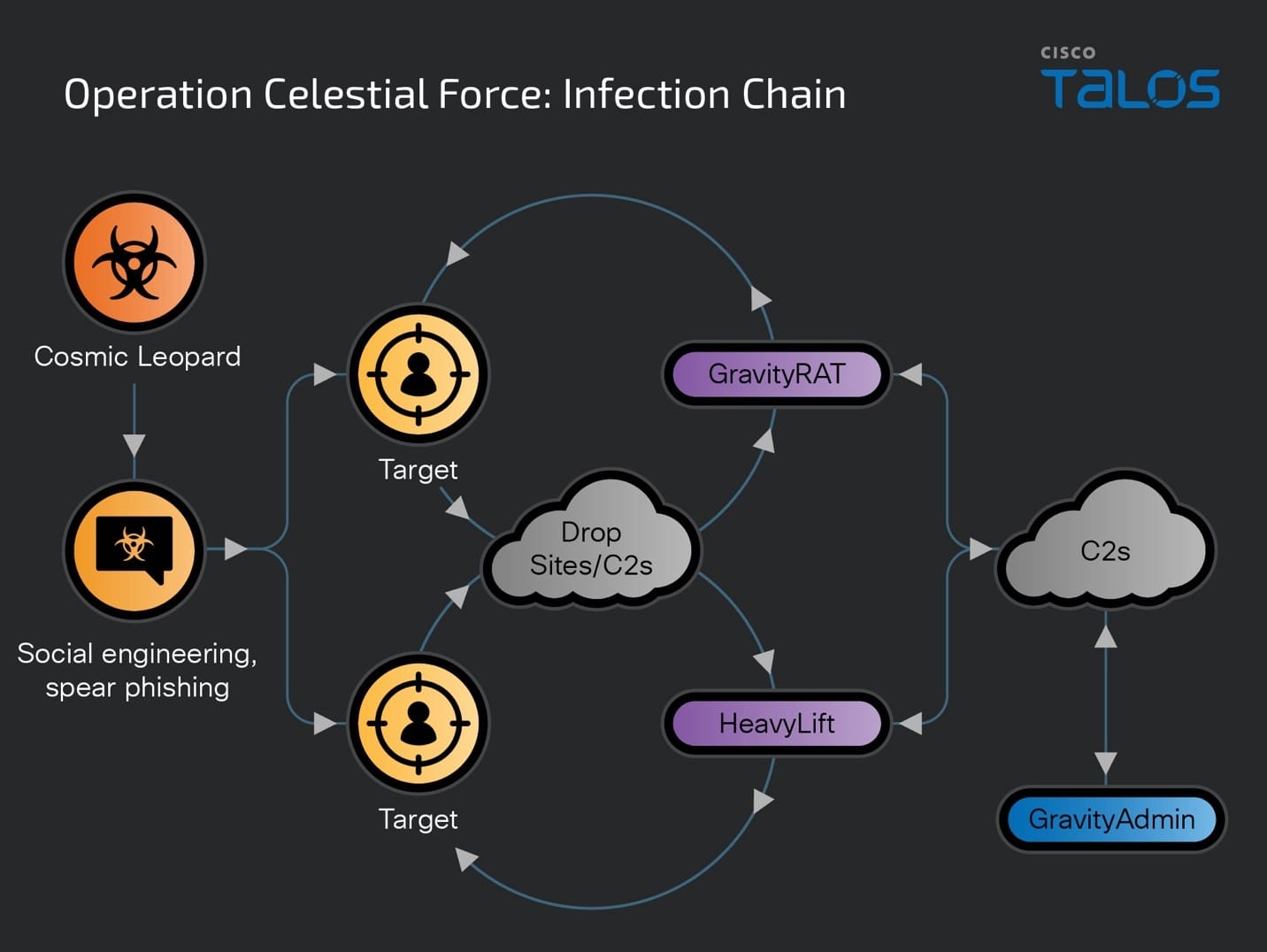
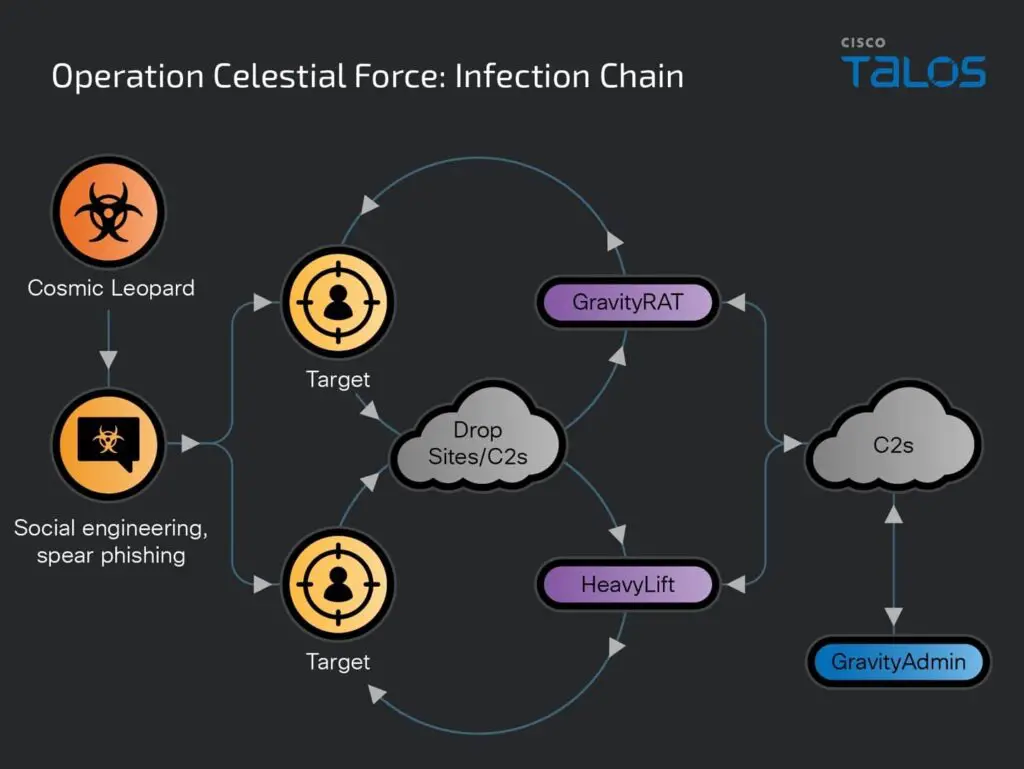
Initially, Cosmic Leopard’s operations centered around the GravityRAT malware family, which targeted Windows systems via malicious documents (maldocs). By 2019, the group expanded its arsenal to include Android versions of GravityRAT, broadening its infection vectors to mobile devices. That same year saw the introduction of HeavyLift, an Electron-based malware loader distributed via malicious installers. These developments indicate a methodical expansion and sophistication of their attack methods.
Cosmic Leopard employs two primary infection vectors: spear phishing and social engineering. Spear phishing campaigns involve sending malicious documents to targets, while social engineering tactics leverage social media platforms to establish trust with targets before sending malicious links. These links lead to the download of either the Windows-based GravityRAT, Android-based GravityRAT, or the Windows-based HeavyLift loader.
Key Components of Operation Celestial Force
- GravityRAT: A versatile remote access trojan (RAT) targeting both Windows and Android systems. It has been in use since at least 2016 and continues to evolve, with the latest variants distributed through malicious websites posing as legitimate Android applications.
- HeavyLift: An Electron-based malware loader that targets Windows systems. It begins with an installer masquerading as legitimate software, which then sets up a malicious application to carry out further attacks.
- GravityAdmin: A tool used to administer infected systems, connecting to GravityRAT’s and HeavyLift’s C2 servers. It features multiple user interfaces (UIs) tailored to specific campaigns.
The findings of this report underscore the growing threat of state-sponsored cyber espionage and the importance of robust cybersecurity measures. Organizations and individuals in India, particularly those associated with critical infrastructure and sensitive information, must remain vigilant and adopt a proactive approach to cybersecurity.