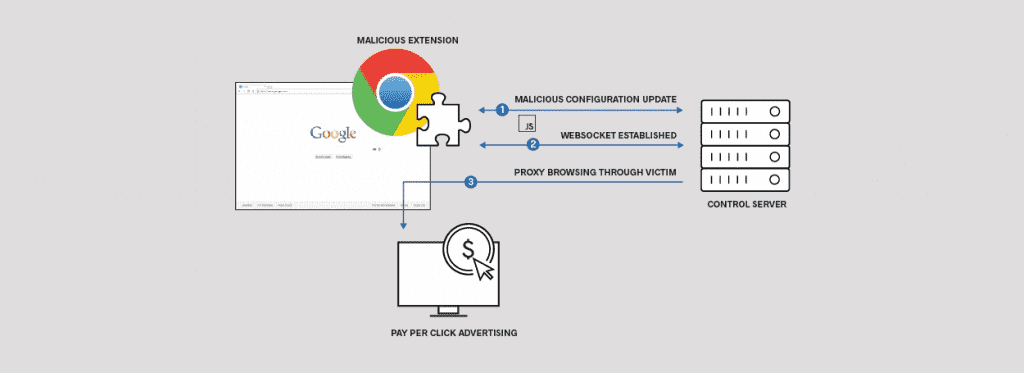
Foreign media reported on January 16, the US network security company ICEBRG found four malicious Chrome extensions for the implementation of click fraud or search engine optimization. The number of affected users has now exceeded 500,000, and attackers may use the extension to further access corporate networks and user information. ICEBRG informs NCSC-NL, US-CERT and Google’s Safe Browsing operations team in preparation for safeguards.
Recently, ICEBRG found an extraordinary surge of outbound traffic from customer workstations to European VPS providers, including workstations from some of the world’s major organizations. Therefore, ICEBRG investigated the situation. According to the survey, the names of the four malicious Chrome extensions are:
1, Change HTTP Request Header (ppmibgfeefcglejjlpeihfdimbkfbbnm)
2, Nyoogle – Custom Logo for Google (ginfoagmgomhccdaclfbbbhfjgmphkph)
3, Lite Bookmarks (mpneoicaochhlckfkackiigepakdgapj)
4, Stickies – Chrome’s Post-it Notes (djffibmpaakodnbmcdemmmjmeolcmbae)
The researchers said the four Chrome extensions allow attackers to send malicious commands to user browsers in the form of JavaScript code, but attackers can only perform click fraud by loading a website in the background and clicking ads.
When the media covered the incident, three other malicious extensions besides Nyoogle were removed from the Chrome Web Store. However, many users still load these malicious extensions in their browsers.
Note: Although the Chrome Web Store removes this malicious extension, it may not be removed from the affected host. In addition, using third-party Chrome Extensions may still allow extensions to be installed.
Currently, ICEBRG has released a detailed report on four malicious Chrome extensions and advised users to check browsers and remove malicious extensions to their computers.
The full report:
Source: BleepingComputer