OWASP WAP – Web Application Protection Project
Web Application Protection (WAP) is a tool to detect and correct input validation vulnerabilities in web applications written in PHP and predicts false positives. The tool combines source code static analysis and data mining to detect vulnerabilities and predict false positives. Then, corrects the source code to remove the real vulnerabilities inserting fixes (small functions) in the right places of the source code.
- OWASP WAP is a security tool to detect and remove input validation vulnerabilities in web applications and predict false positives.
- Uses source code static analysis to detect vulnerabilities, data mining to predict false positives and inserts fixes to correct the source code.
- Detects and corrects 8 types of input validation vulnerabilities.
- Teaches the user to build secure software.
- Works on Linux, Macintosh, and Windows.
- Requires JRE to run.
- Portable, ready to run and no installation required.
Web Application Protection (WAP) is a source code static analysis and data mining tool to detect and correct input validation vulnerabilities in web applications written in PHP (version 4.0 or higher) with a low rate of false positives.
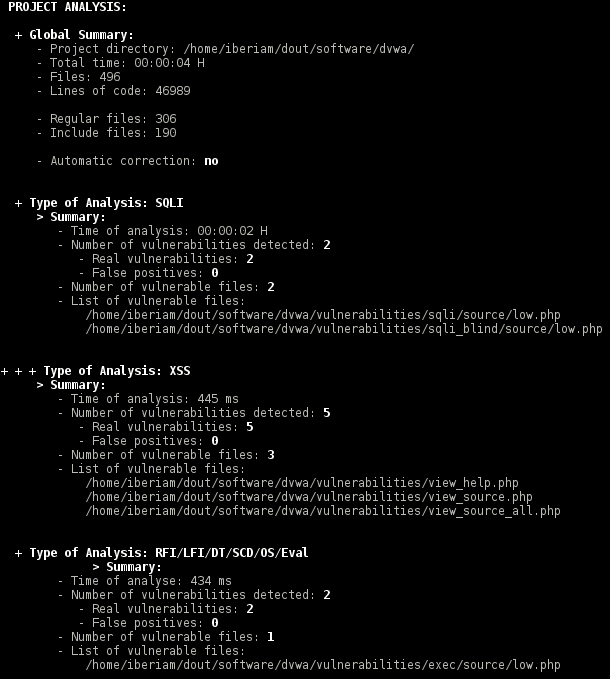
WAP detects and corrects the following vulnerabilities:
- SQL Injection (SQLI)
- Cross-site scripting (XSS)
- Remote File Inclusion (RFI)
- Local File Inclusion (LFI)
- Directory Traversal or Path Traversal (DT/PT)
- Source Code Disclosure (SCD)
- OS Command Injection (OSCI)
- PHP Code Injection
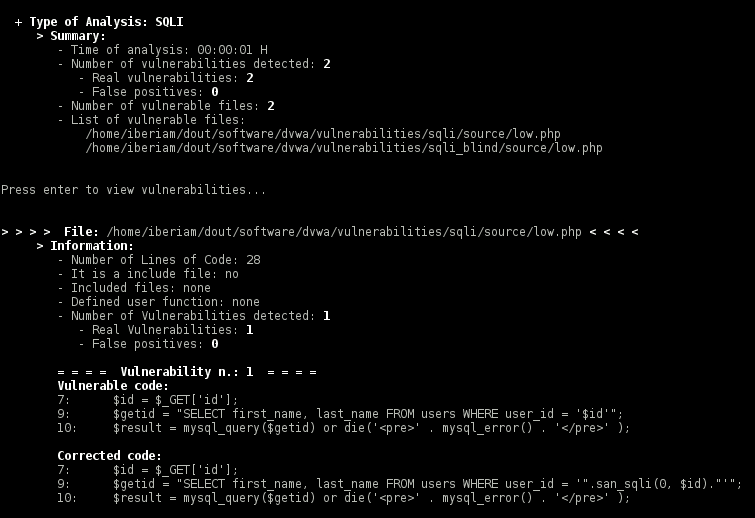
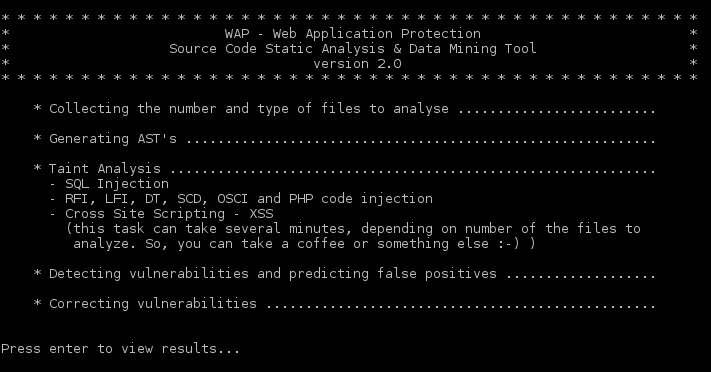
This tool semantically analyses the source code. More precisely, it does taint analysis (data-flow analysis) to detect the input validation vulnerabilities. The aim of the taint analysis is to track malicious inputs inserted by entry points ($_GET, $_POST arrays) and to verify if they reach some sensitive sink (PHP functions that can be exploited by malicious input, such as mysql_query). After the detection, the tool uses data mining to confirm if the vulnerabilities are real or false positives. At the end, the real vulnerabilities are corrected by the insertion of the fixes (small pieces of code) in the source code.
Web Application Protection (WAP) is constituted by three modules:
- Code Analyzer: composed by tree generator and taint analyzer. The tool has integrated a lexer and a parser generated by ANTLR, and based on a grammar and a tree grammar written in PHP language. The tree generator uses the lexer and the parser to build the AST (Abstract Syntactic Tree) to each PHP file. The taint analyzer performs the taint analysis navigating through the AST to detect potentials vulnerabilities.
- False Positives Predictor: composed of a supervised trained data set with instances classified as being vulnerabilities and false positives and by the Logistic Regression machine learning algorithm. For each potential vulnerability detected by code analyzer, this module collects the presence of the attributes that define a false positive and creates with them an instance. Then, the Logistic Regression algorithm receives the instances and classifies them as being a false positive or not (real vulnerability).
- Code Corrector: each real vulnerability is removed by correction of its source code. This module for the type of vulnerability selects the fix that removes the vulnerability and signalizes the places in the source code where the fix will be inserted. Then, the code is corrected with the insertion of the fixes and new files are created. Fixes are small pieces of the code (small PHP functions developed to the effect) that performing sanitization or validation of the user inputs, depending on the vulnerability type.
Installation:
Requirements:
– JRE (www.oracle.com)
1. Download here the latest version of WAP package.
2. Extract the package to your local computer into a directory.
3. At a terminal go to the directory where the package was extracted.
4. Run the script wap to use the tool. See here how you can use the tool.
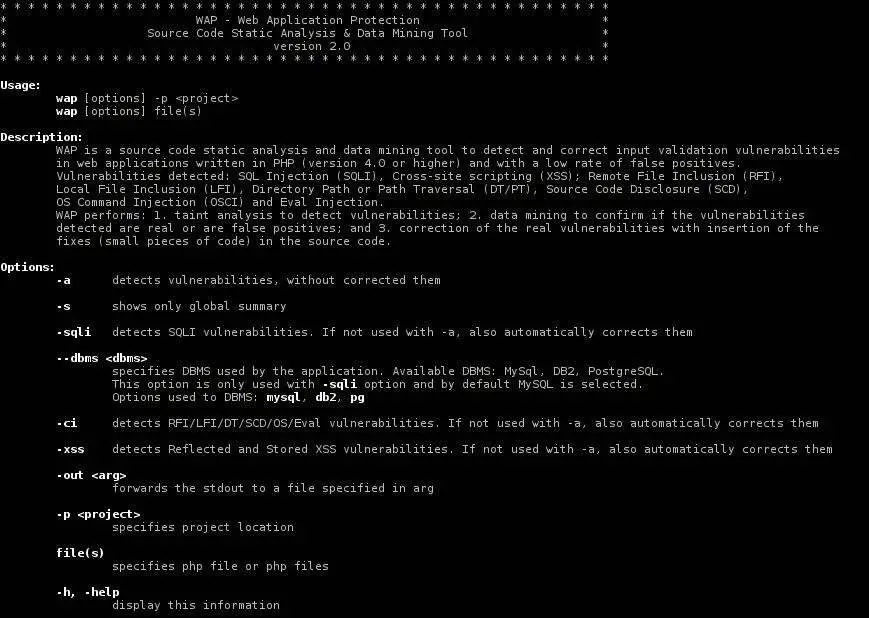
Usage

Author
Ibéria Medeiros
Source: sourceforge



