In the evolving landscape of cyber threats, a new trend has emerged that challenges the conventional understanding of online security. Microsoft’s latest Threat Intelligence report unveils a revelation: threat actors are now exploiting OAuth applications, an open standard for token-based authentication and authorization, to orchestrate financially driven attacks. This innovation in cyber warfare marks a significant shift in how attackers operate, making it more challenging to detect and prevent these intrusions.
OAuth applications, designed to provide secure access to data and resources based on user permissions, have been subverted by attackers. By compromising user accounts, these actors create, modify, and grant high privileges to OAuth applications, using them to mask their malicious activities. A concerning aspect of this misuse is its persistence: even if attackers lose access to the initial compromised account, they can maintain control over the applications.
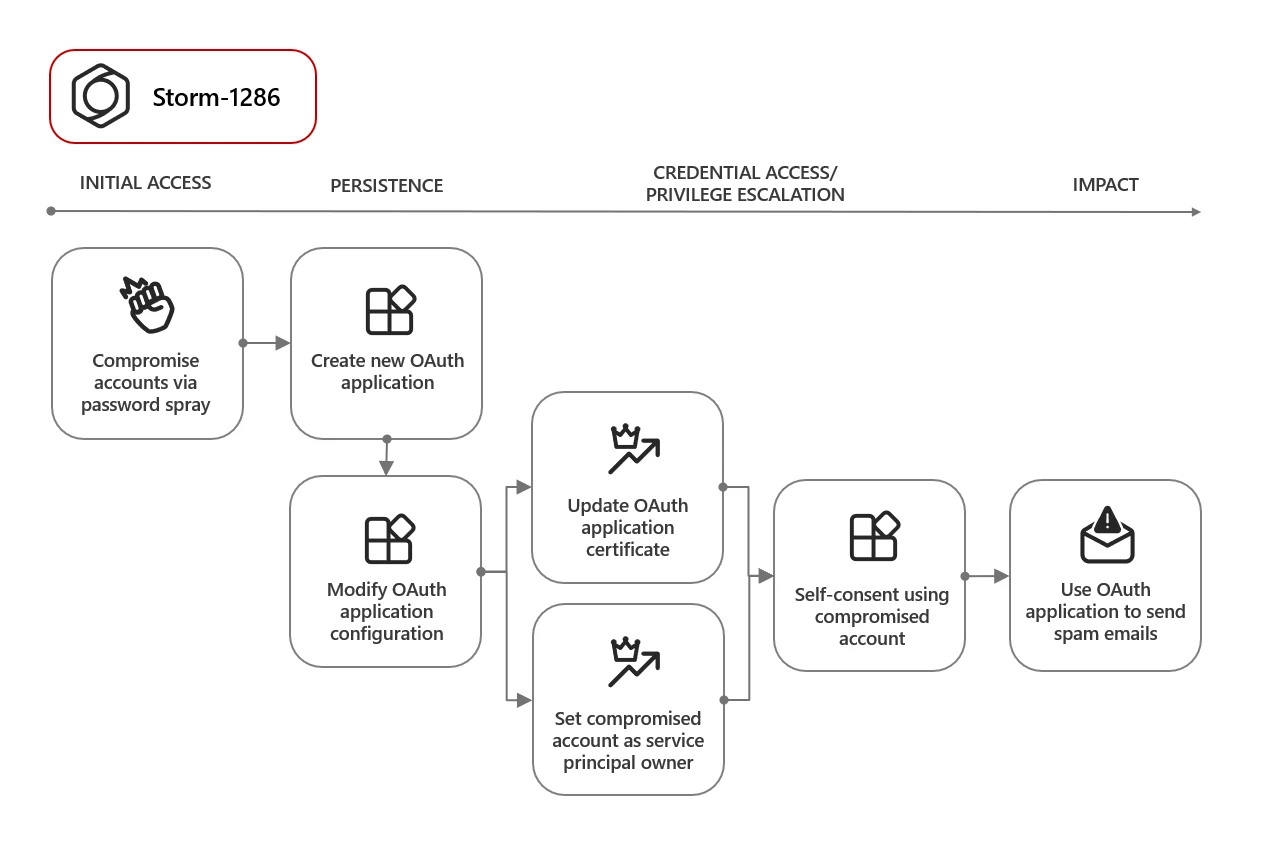
Microsoft has observed various tactics employed by these threat actors:
1. Cryptocurrency Mining: By creating OAuth applications, attackers deploy virtual machines for cryptomining, causing substantial financial losses. An identified actor, Storm-1283, exemplifies this tactic, generating compute fees ranging from $10,000 to $1.5 million.

2. Business Email Compromise (BEC) and Phishing: Attackers create OAuth applications to maintain persistence after gaining initial access through phishing. These applications are then used to orchestrate email phishing activities and facilitate BEC scams.

3. Spamming Activities: Leveraging compromised accounts, attackers set up OAuth applications to control mailboxes and send thousands of spam emails, using legitimate domains to evade detection systems.

Microsoft’s response to these threats is multi-faceted. They employ tools like Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps, Microsoft Defender XDR, and Microsoft Entra Identity Protection to detect and prevent the misuse of OAuth applications. Furthermore, they recommend several mitigation steps for organizations, including strengthening authentication mechanisms, monitoring unusual activities, and regularly auditing OAuth applications.
This report serves as a critical reminder of the ever-changing nature of cyber threats. The misuse of OAuth applications represents a new frontier in cyber warfare, one where traditional security measures might not suffice. Organizations must remain vigilant, adapt their security postures, and stay informed about the latest threat tactics to protect their digital assets effectively.