Principal Mapper
A project to speed up the process of reviewing an AWS account’s IAM configuration.

Purpose
The goal of the AWS IAM auth system is to apply and enforce access controls on actions and resources in AWS. This tool helps to identify if the policies in place will accomplish the intents of the account’s owners.
AWS already has tooling in place to check if policies attached to a resource will permit an action. This tool builds on that functionality to identify other potential paths for a user to get access to a resource. This means checking for access to other users, roles, and services as ways to pivot.
How to Use
- Download this repository (git clone https://github.com/nccgroup/PMapper.git) and install its dependencies with pip install -r requirements.txt.
- Ensure you have graphviz installed on your host.
- Setup an IAM user in your AWS account with a policy that grants the necessary permission to run this tool (see the file mapper-policy.json for an example). The ReadOnlyAccess managed policy works for this purpose. Grab the access keys created for this user.
- In the AWS CLI, set up a profile for that IAM user with the command: aws configure –profile <profile_name> where <profile_name> is a unique name.
- Run the command python pmapper.py –profile <profile_name> graph to begin pulling data about your account down to your computer.
Graphing
Principal Mapper has a graph subcommand, which does the heavy work of going through each principal in an account and finding any other principals it can access. The results are stored at ~/.principalmap and used by other subcommands.
esteringer@ubuntu:~/Documents/projects/Skywalker$ python pmapper.py graph
Using profile: default
Pulling data for account [REDACTED]
Using principal with ARN arn:aws:iam::[REDACTED]:user/TestingSkywalker
[+] Pulling info on IAM users and roles, finding admins.
Principals Checked: 100%|##############################################################| 43/43 [00:24<00:00, 1.72it/s]
[+] Finished finding admins.
[+] Started EC2 checks.
Principals Checked: 100%|##############################################################| 43/43 [00:24<00:00, 1.78it/s]
[+] Finished EC2 checks.
[+] Started IAM checks.
Principals Checked: 100%|##############################################################| 43/43 [05:34<00:00, 7.77s/it]
[+] Finished IAM checks.
[+] Starting Lambda checks.
Regions Checked for Lambda Functions: 100%|############################################| 15/15 [00:15<00:00, 1.02s/it]
Principals Checked: 100%|##############################################################| 43/43 [01:44<00:00, 2.44s/it]
[+] Finished Lambda checks.
[+] Starting CloudFormation checks.
CloudFormation Regions Checked: 100%|##################################################| 15/15 [00:16<00:00, 1.07s/it]
Principals Checked: 100%|##############################################################| 43/43 [00:20<00:00, 2.13it/s]
[+] Finished CloudFormation checks.
Created an AWS Graph with 43 nodes and 258 edges
Querying
Principal Mapper has a query subcommand that runs a user-defined query. The queries can check if one or more principals can do a given action with a given resource. The supported queries are:
"can <Principal> do <Action> [with <Resource>]"
"who can do <Action> [with <Resource>]"
"preset <preset_query_name> <preset_query_args>"
The first form checks if a principal, or any other principal accessible to it, could perform an action with a resource (default wildcard). The second form enumerates all principals that are able to perform an action with a resource.
Note the quotes around the full query, that’s so the argument parser knows to take the whole string.
Note that <Principal> can either be the full ARN of a principal or the last part of that ARN (user/… or role/…).
esteringer@ubuntu:~/Documents/projects/Skywalker$ ./pmapper.py --profile skywalker query "who can do s3:GetObject with *"
user/AdminUser can do s3:GetObject with *
user/EC2Manager can do s3:GetObject with * through role/EC2Role-Admin
user/EC2Manager can create an EC2 instance and use an existing instance profile to access role/EC2Role-Admin
role/EC2Role-Admin can do s3:GetObject with *
user/LambdaFullAccess can do s3:GetObject with *
user/PowerUser can do s3:GetObject with *
user/S3ManagementUser can do s3:GetObject with *
user/S3ReadOnly can do s3:GetObject with *
user/TestingSkywalker can do s3:GetObject with *
role/EC2-Fleet-Manager can do s3:GetObject with * through role/EC2Role-Admin
role/EC2-Fleet-Manager can create an EC2 instance and use an existing instance profile to access role/EC2Role-Admin
role/EC2Role-Admin can do s3:GetObject with *
role/EC2Role-Admin can do s3:GetObject with *
role/EC2WithS3ReadOnly can do s3:GetObject with *
role/EMR-Service-Role can do s3:GetObject with *
role/LambdaRole-S3ReadOnly can do s3:GetObject with *
role/UpdateCredentials can do s3:GetObject with * through user/AdminUser
role/UpdateCredentials can create access keys with IAM to access user/AdminUser
user/AdminUser can do s3:GetObject with *
Presets
The existing preset is priv_esc or change_perms, which have the same function. They describe which principals have the ability to change their own permissions. If a principal is able to change their own perms, then it effectively has unlimited perms.
esteringer@ubuntu:~/Documents/projects/Skywalker$ ./pmapper.py --profile skywalker query "preset priv_esc user/PowerUser"
Discovered a potential path to change privileges:
user/PowerUser can change privileges because:
user/PowerUser can access role/EC2Role-Admin because:
user/PowerUser can create an EC2 instance and use an existing instance profile to access role/EC2Role-Admin
and role/EC2Role-Admin can change its own privileges.
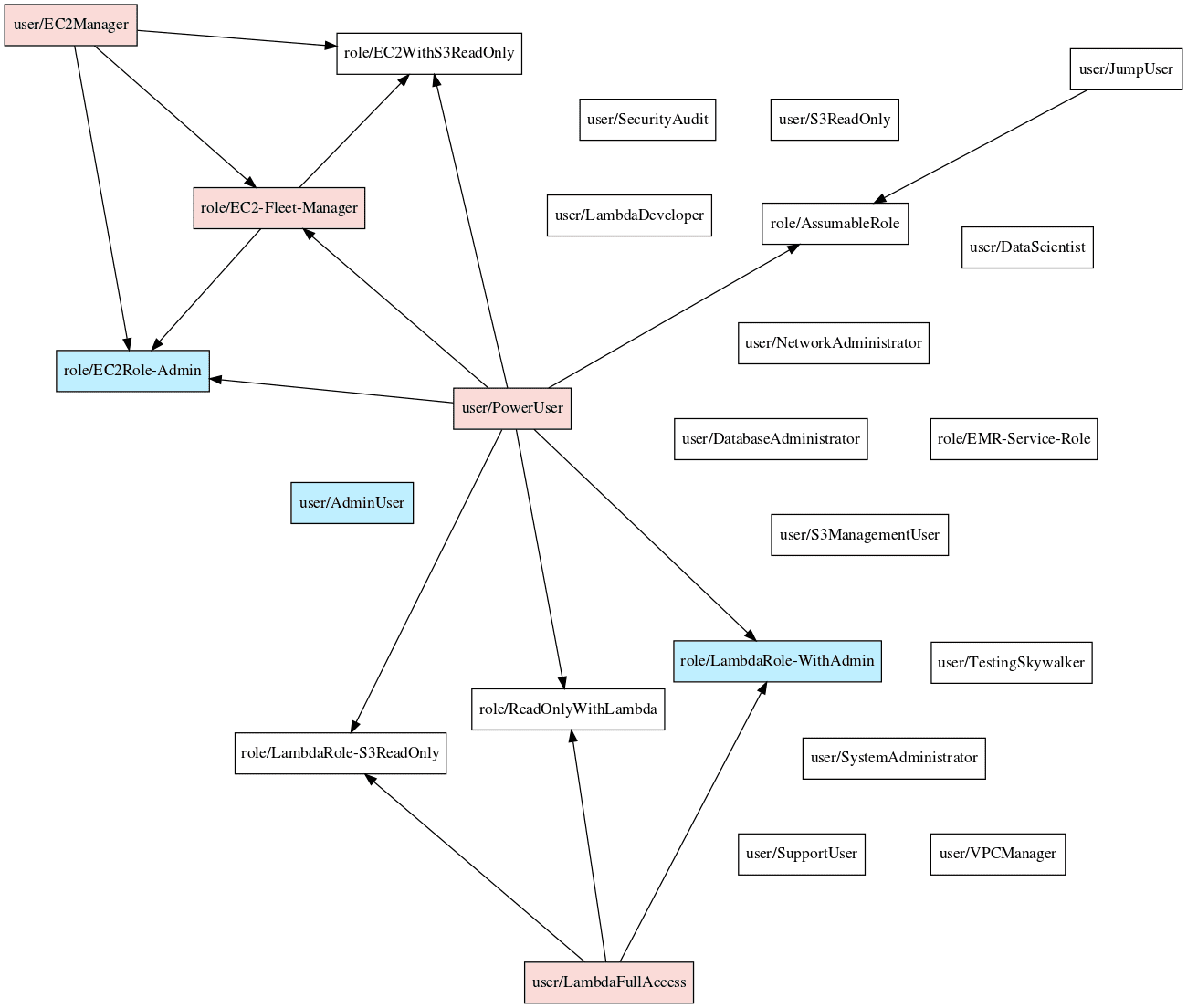
Visualizing
The visualize subcommand produces a DOT and SVG file that represent the nodes and edges that were graphed.
To create the DOT and SVG files, run the command: python pmapper.py visualize
Currently, the output is a directed graph, which collates all the edges with the same source and destination nodes. It does not draw edges where the source is an admin. Nodes for admins are coloured blue. Nodes for users with the ability to access admins are coloured red (potential priv-esc risk).
Copyright (C) 2018 ncc-erik-steringer
Source: https://github.com/nccgroup/