PoC Exploit for CVE-2023-27524 in Apache Superset Leads to RCE Released
Apache Superset is a popular open-source tool for data visualization and exploration. However, a recent vulnerability has been discovered that could allow attackers to bypass authentication and gain unauthorized access to Superset servers.
The newly identified CVE-2023-27524 has a CVSS score of 9.8. Its primary peril? An authentication bypass that can be a gateway to the dreaded remote code execution (RCE).
If exploited, malevolent actors could easily acquire administrative privileges on targeted servers. The potential consequences are dire: unauthorized access to user credentials and possibly compromising invaluable data.

In a meticulously detailed report by Horizon3, the root cause of the vulnerability was unearthed. Apache Superset, for reasons unbeknownst to many, made use of a default Flask Secret Key for signing authentication session cookies. The implications of such an oversight are massive: any attacker armed with the default key can craft session cookies, paving their way into a server with administrator privileges—especially if the key was left unchanged.
Horizon3’s investigation went further to unearth a staggering statistic: approximately 2,000 internet-facing servers—spanning universities, corporations, governmental bodies, and beyond—had detectable configurations using this perilous default key.
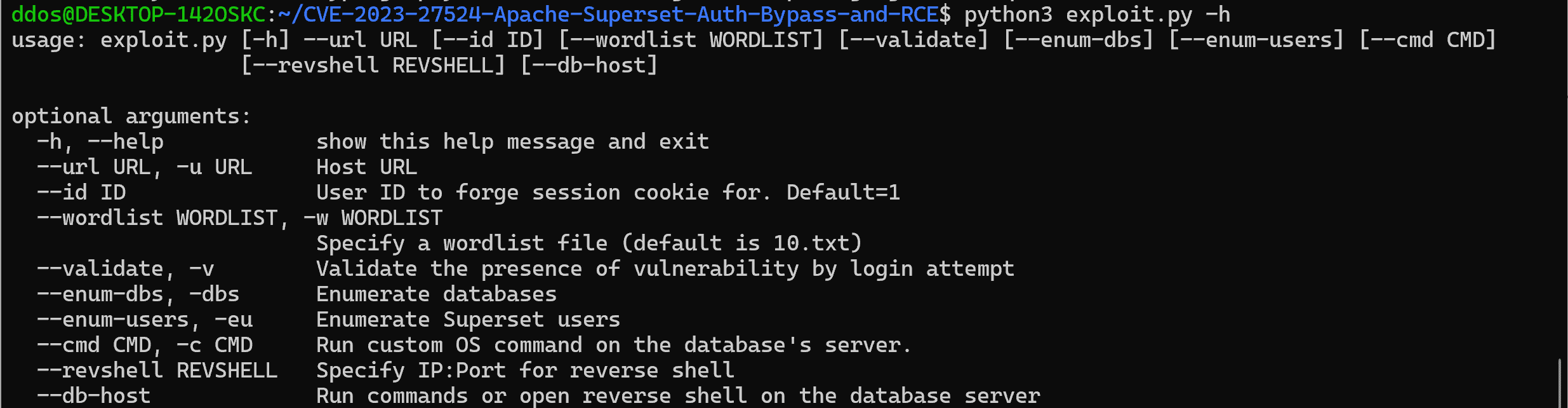
For those well-versed in cyber weaponry, a tool named flask-unsign can be employed to exploit this vulnerability. With it, attackers can create counterfeit cookies and, consequently, achieve unfettered administrator access. This exposes connected databases to unauthorized access and arbitrary SQL command execution.
If administrators have been diligent enough to replace the default key with one beyond the attacker’s knowledge, the looming threat dissipates. And in a commendable gesture of solidarity, the security firm Horizon3 has published a script on GitHub, enabling Apache Superset admins to assess their system’s vulnerability.
But the revelations don’t end there. A security researcher, Jakabakos, has shed light on the specifics of the CVE-2023-27524 flaw and even provided a proof-of-concept (PoC), accentuating its potential for remote code execution.

In Jakabakos’ words: “The root cause lies in the predictable Flask Secret Key set during installation, affecting a significant number of exposed Apache Superset instances. Despite some mitigation efforts, this vulnerability remains a pivotal concern for those yet to update their configurations.”
For users navigating the stormy waters of this vulnerability, Horizon3 offers a beacon of guidance:
1. Examine Defaults: This includes the Flask SECRET_KEY, Superset admin credentials, and database credentials. A provided script can help ascertain vulnerability to CVE-2023-27524.
2. Update: Ensure you’re running the latest version, Superset 2.1.1.
3. Avoid Root Credentials: When linking Superset to databases, avoid using top-level credentials.
4. Purge the Example Database: It’s safer without it.
5. Reassess Accessibility: If you’re exposing Superset online, ponder the necessity of it. Using a VPN or keeping it offline might be a safer bet.
Given that the PoC exploit code for CVE-2023-27524 is openly accessible on GitHub, it’s crucial for organizations to promptly detect and bolster their cyber defenses to safeguard against potential RCE threats.





