PoC Exploit Published for Fortra GoAnywhere MFT CVE-2024-0204 Vulnerability

A security researcher has published proof-of-concept (PoC) code targeting a recently patched critical CVE-2024-0204 vulnerability in the Fortra GoAnywhere MFT.
GoAnywhere MFT is a secure managed file transfer (MFT) solution that helps organizations automate, centralize, and secure their file transfers. However, this flaw (CVSS score of 9.8) is remotely exploitable, allowing an unauthorized user to create admin users via the product’s administration portal. Exploit code has now surfaced for this critical authentication bypass vulnerability, laying bare the potential for attackers to exploit unpatched systems by navigating through the administration portal to illicitly craft new admin users.

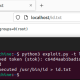
Administrative User Added | Image: Horizon3’s Attack Team
Interestingly, Fortra addressed the bug silently on December 7 with the rollout of GoAnywhere MFT 7.4.1. The public disclosure of this patch came significantly later. Before the fix, Fortra had dispatched private advisories to its clientele on December 4, advising them to fortify their MFT services against potential threats.
For administrators who find themselves in the precarious position of not being able to promptly upgrade to the latest version, Fortra recommends a couple of interim mitigation strategies:
- Deleting the InitialAccountSetup.xhtml File: This involves removing the specified file from the installation directory and restarting the services to eliminate the attack vector.
- Replacing the InitialAccountSetup.xhtml File: Alternatively, replacing this file with an empty file and restarting the services can also serve to neutralize the threat.
The severity of this vulnerability was further underscored by a publication from Horizon3’s Attack Team, which furnished a technical analysis alongside a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit. This PoC exploit leverages a path traversal issue at the heart of CVE-2024-0204, targeting the /InitialAccountSetup.xhtml endpoint. By accessing this endpoint, attackers can trigger the initial account setup screen— a feature that should be inaccessible post-setup— to establish a new administrator account.
“The easiest indicator of compromise that can be analyzed is for any new additions to the Admin Users group in the GoAnywhere administrator portal Users -> Admin Users section. If the attacker has left this user here you may be able to observe its last logon activity here to gauge an approximate date of compromise,” researcher Zach Hanley from Horizon3’s Attack Team said.