The urgency of the situation escalated when proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code for a zero-day CVE-2024-21893 vulnerability became publicly accessible, raising the stakes for potential malicious exploitation. This flaw, along with CVE-2024-21887, could enable attackers to execute code remotely without authentication, emphasizing the critical need for immediate updates to safeguard against potential breaches.
CVE-2024-21893, a server-side request forgery vulnerability in the SAML component of Ivanti Connect Secure, Ivanti Policy Secure, and Ivanti Neurons for ZTA has raised alarms in the cybersecurity world. This vulnerability, present in versions 9.x and 22.x, allows attackers to gain access to restricted resources without authentication – a nightmare scenario for network administrators.
Ivanti’s response to the vulnerability was swift. As part of their ongoing investigation, they discovered new vulnerabilities that impact all supported versions of their software. While there is no evidence of customers being affected by CVE-2024-21888, CVE-2024-21893 has already affected a small number of users, prompting Ivanti to issue a critical warning.
“We have no evidence of any customers being impacted by CVE-2024-21888 at this time. We are only aware of a small number of customers who have been impacted by CVE-2024-21893 at this time.”
“It is critical that you immediately take action to ensure you are fully protected,” Ivanti warned.

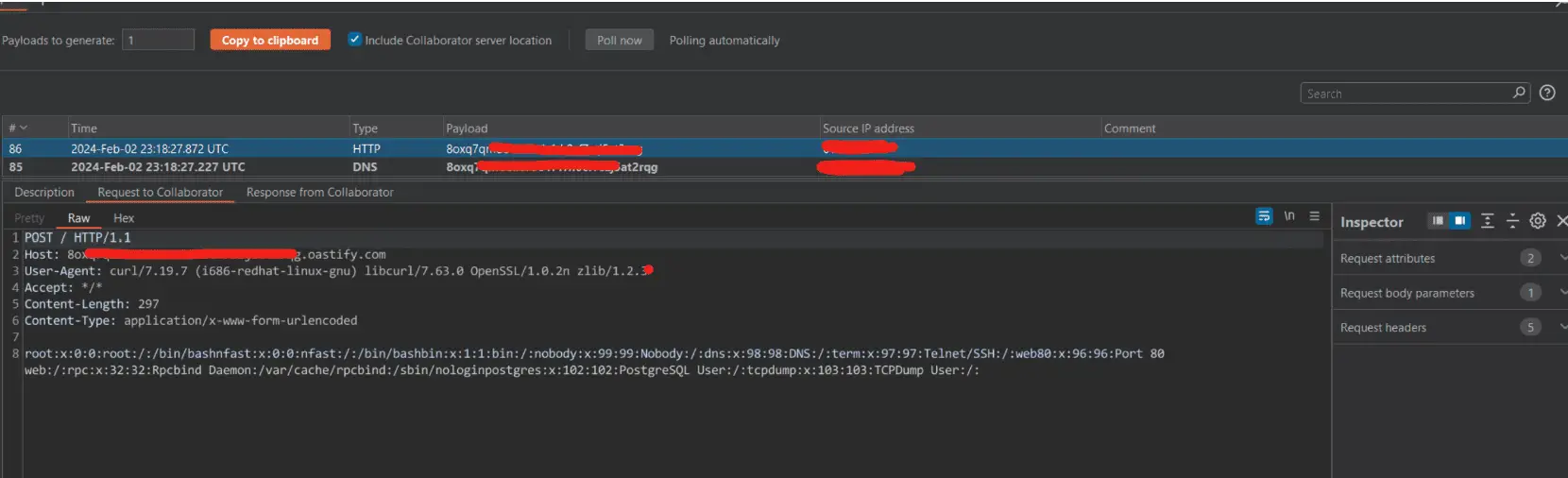
Within days after Ivantin announced patches for this and several other vulnerabilities, Rapid7 published a technical writeup on CVE-2024-21893.
“To trigger the SSRF vulnerability, we provide an XML SOAP envelope. Inside the SOAP envelope is a signature that will be processed by xmltooling. The signature contains a KeyInfo element that has a child RetrievalMethod element. The RetrievalMethod element has an attribute called URI. This attribute allows us to specify an arbitrary URI that the function XMLToolingFIPS.XMLObject.Signature will use to request a remote resource via a HTTP GET request, thus giving an attacker an SSRF exploit primitive,” the researcher wrote.
What makes this vulnerability particularly concerning is the rapid pace at which events unfolded. Shortly after Ivanti announced patches for this and other vulnerabilities, PoC (Proof-of-Concept) code targeting CVE-2024-21893 emerged on GitHub.

The PoC code not only exposes CVE-2024-21893 but also enables attackers to chain it with CVE-2024-21887, allowing for unauthenticated remote code execution. This combination of vulnerabilities could spell disaster for unprepared networks.
To combat these threats, Ivanti has released security patches for affected ZTA and Connect Secure versions. For devices awaiting patches, the company has provided mitigation instructions, emphasizing the importance of immediate action.