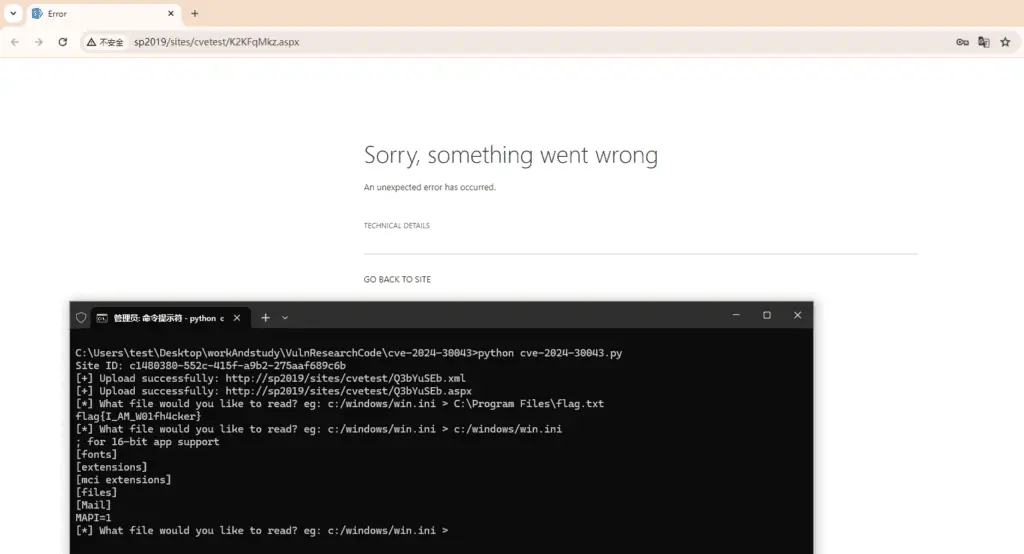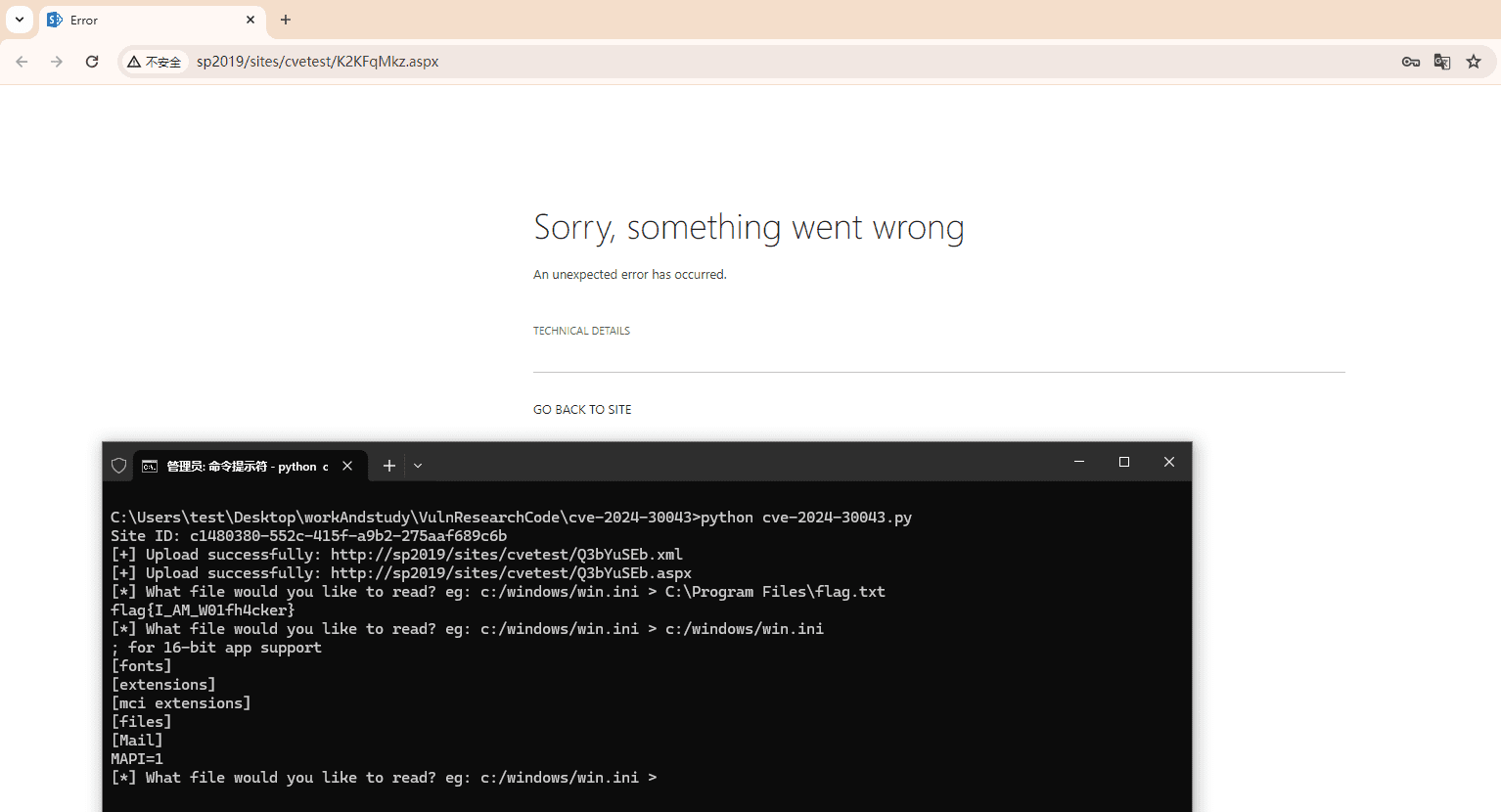
A security researcher has published a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code targeting a recent important severity vulnerability (CVE-2024-30043) in Microsoft SharePoint Server. Rated with a CVSS score of 6.5, this vulnerability exposes sensitive information and potentially opens doors to more severe security threats. The flaw, found in the BaseXmlDataSource class, involves improper restrictions on XML External Entity (XXE) references, allowing attackers to manipulate XML documents to access unauthorized data.
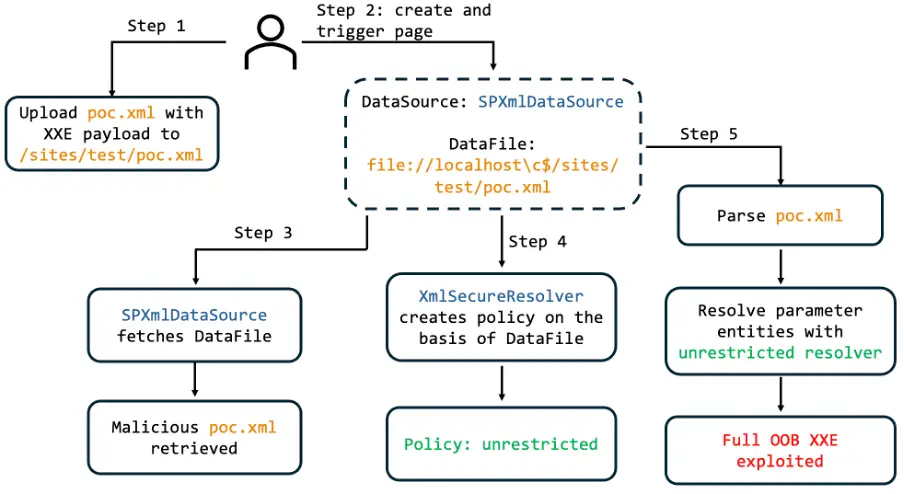
The CVE-2024-30043 vulnerability exists in the Microsoft SharePoint Server due to the improper handling of XML External Entity (XXE) references within the BaseXmlDataSource class. By exploiting this flaw, remote attackers can craft documents that cause the XML parser to access external URIs and embed their contents into the XML document for further processing. This can lead to the disclosure of sensitive information and other malicious activities:
- Sensitive Information: Attackers could exploit this vulnerability to gain unauthorized access to confidential documents and data stored on SharePoint servers.
- Server-Side Request Forgery: SSRF attacks could allow attackers to trick the server into making requests to internal or external systems, potentially leading to further compromise.
- NTLM Relay Attacks: NTLM relaying could enable attackers to escalate their privileges and gain access to additional systems within the network.
The vulnerability was discovered by Piotr Bazydlo (@chudypb) of Trend Micro Zero Day Initiative. His detailed technical analysis provided the foundation for understanding and addressing this flaw.
W01fh4cker, a well-known security researcher, developed a proof-of-concept exploit code to demonstrate how the CVE-2024-30043 vulnerability could be exploited. The exploit code effectively highlights the risks and potential damage this vulnerability can cause if left unpatched.