pyshell: Shellify Your HTTP Command Injection
PyShell – Shellify Your HTTP Command Injection!
Did firewall get you down? Are your reverse-shell connection attempts being filtered? Are you stuck working solely over HTTP / HTTPS? Then this just might be just the thing for you.
PyShell exists to make interacting with web-based command injection less painful. The goal is to make it feel as much like an interactive shell as possible. Commands are base-64 encoded to help deal with WAFs and are submitted as POST requests to be less visible in request logs.
Usage is python3 pyshell.py URL where URL points to a script which performs the command injection, something like this:
The server-side script should accept the following parameters:
cmd: the command to be run, base64 encodedopts: the options to provide to cmd, also base64 encoded[timeout]: optional, denotes the number of seconds to wait for a command
COOL FEATURES:
- Basic command history (up arrow / down arrow to navigate).
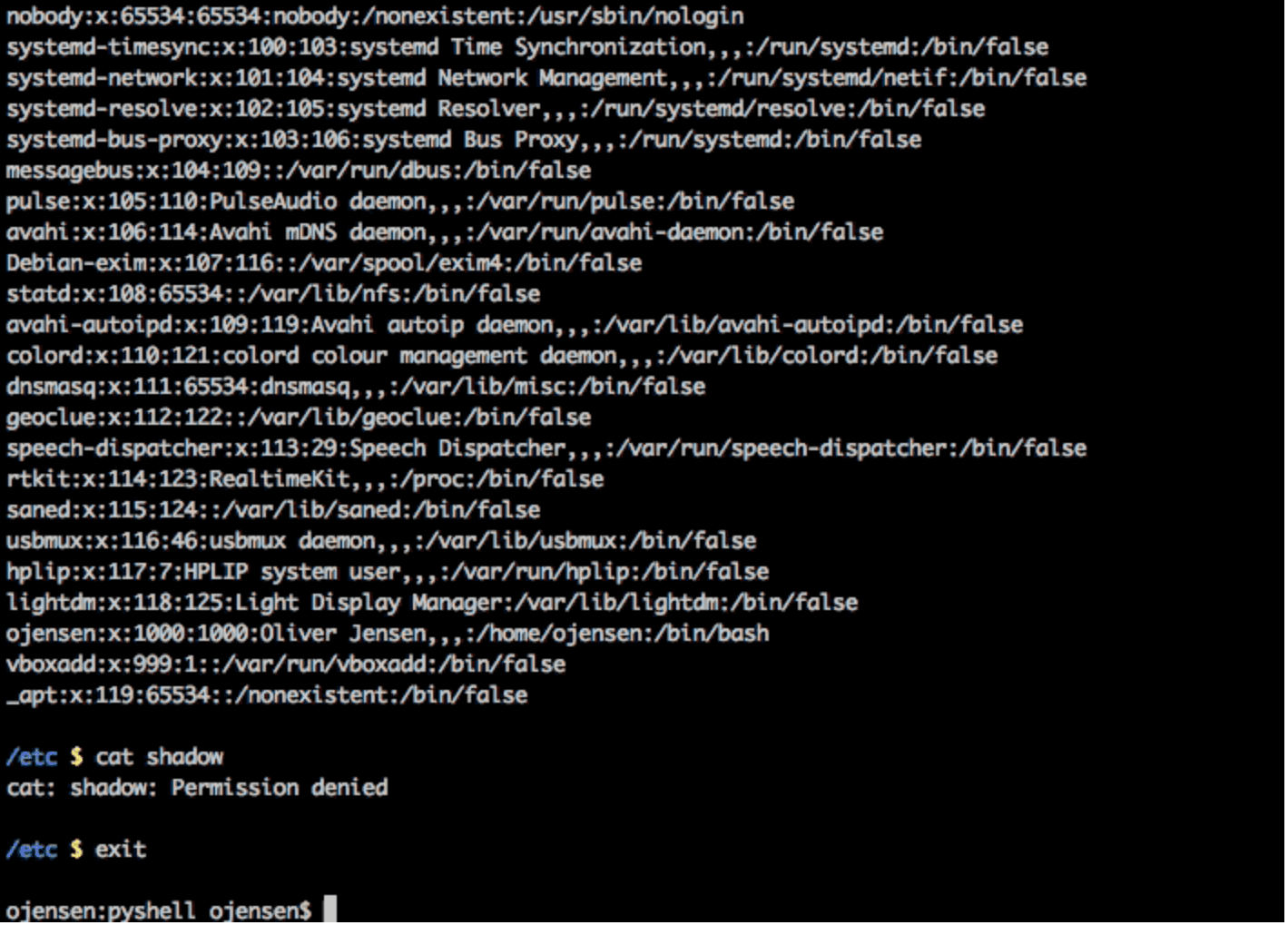
- Navigate directory tree with
cd [target]pseudo-command. - Exfiltrate files or folders via
get [target]pseudo-command. - Tab completion. (whoa!)
Download
git clone https://github.com/praetorian-inc/pyshell.git
USAGE DEMO:
MISC NOTES:
Note that you only get output when the command you run exits. Interactive commands are also unsupported, for reasons that should be obvious — although if you ever forget why while using PyShell, we’ll consider that a success!
To change the timeout parameter passed with each command, run settimeout n. It defaults to 20. Unless you handle the timeout parameter server side, it does exactly nothing.
Your command-history is located in ~/.pyshellhistory.
When exfiltrating data, a tgz file will be created in the downloads subdirectory (which will be created as needed). If you do not have permission to read a file, the file will simply be omitted in the downloaded archive.
KNOWN ISSUES:
- Trying to
cdinto a non-existent directory is not prevented