Dr. Mordechai Guri, head of the research and development team at Ben Gurion University in Israel, since presenting various methods for stealing data from hermetic computers, has now released a new study called “BeatCoin”, about how to steal the cryptocurrency wallet private key installed on the cold storage device.

BeatCoin is not a new hacking technique. Instead, it is an experiment. The researchers demonstrated all previously discovered out-of-band communication methods that can be used to steal cryptocurrency wallet private keys on cold storage devices.
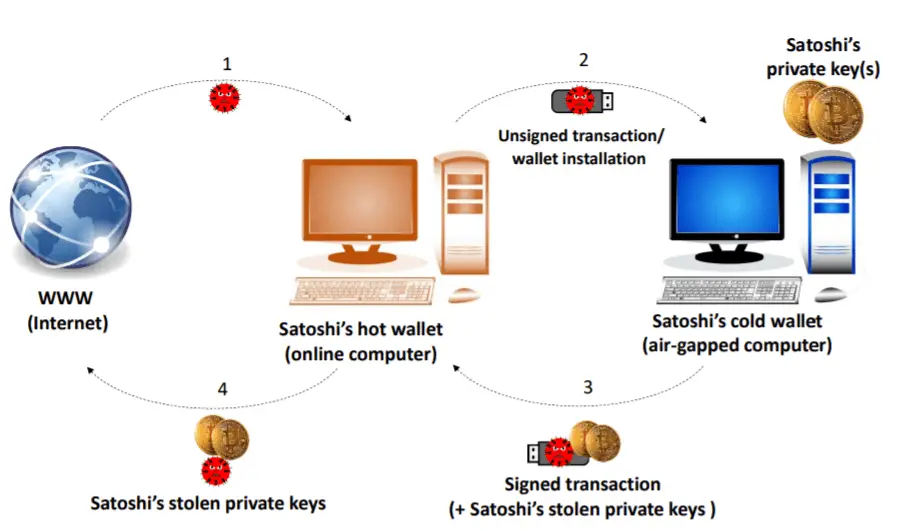
Cold storage: The cryptocurrency protection is called cold storage in a wallet on a device that is completely off-line. Due to the different security risks of online digital wallets, some people prefer to keep the private key offline.
Air-gap computers are hard-to-penetrate computers that are isolated from the Internet, local networks, and Bluetooth and are therefore considered the most secure devices.
For the BeatCoin experiment, Dr. Guri deployed malware on an air-gap computer running the Bitcoin wallet application, then executed each attack vector one by one, and transmitted wallet keys to nearby devices through covert channels.
“In the adversarial attack model, the attacker infiltrates the offline wallet, infecting it with malicious code.The malware can be pre-installed or pushed in during the initial installation of the wallet, or it can infect the system when removable media (e.g., USB flash drive) is inserted into the wallet’s computer in order to sign a transaction. These attack vectors have repeatedly been proven feasible in the last decade.” the paper [ PDF ] writes.
Currently, according to the Guri, AirHopper, MOSQUITO, and Ultrasonic techniques are the fastest ways to transfer 256-bit private keys to remote receivers, while the Diskfiltration and Fansmitter methods take minutes.
Guri shared two videos to further explain the research:
The first shows the leakage of a private key from an air-gap computer, which can use ultrasound to transmit data to a nearby smartphone in a matter of seconds. In the second video, researchers used a RadIoT attack to transmit the private key stored on the Raspberry Pi device to a nearby smartphone, which is a radio signal leaked from hermetic Internet of Things (IoT) and embedded devices.
“The radio signals – generated from various buses and general-purpose input/output (GPIO) pins of the embedded devices – can be modulated with binary data. In this case, the transmissions can be received by an AM or FM receiver located nearby the device.”
In a new study released earlier this month, Guri’s team also demonstrated how hackers exploit the power fluctuations in the current flow “propagating through the power line” to hide highly sensitive data from air-gap computers.
Source: Thehackernews