Researcher details 5 zero-day flaws in Qualcomm chipsets & ARM Mali GPU
The blog title”Deep Dive: Qualcomm MSM & ARM Mali Kernel 0-day Exploit Attacks of October 2023″ by Zero Day Engineering Insights, authored by Alisa Esage, delves into five kernel vulnerabilities in Qualcomm chipsets and ARM Mali GPU reported between October and December 2023. These vulnerabilities, exploited “in the wild,” have not had their exploit details publicly disclosed. The analysis is based on security patches and general information about the vulnerabilities, to clarify the practical impact of exploitation and inform offensive research trends. The document provides a comprehensive technical analysis, referencing Qualcomm Security Bulletins and ARM Security Center, to understand the nature and impact of these vulnerabilities in depth.

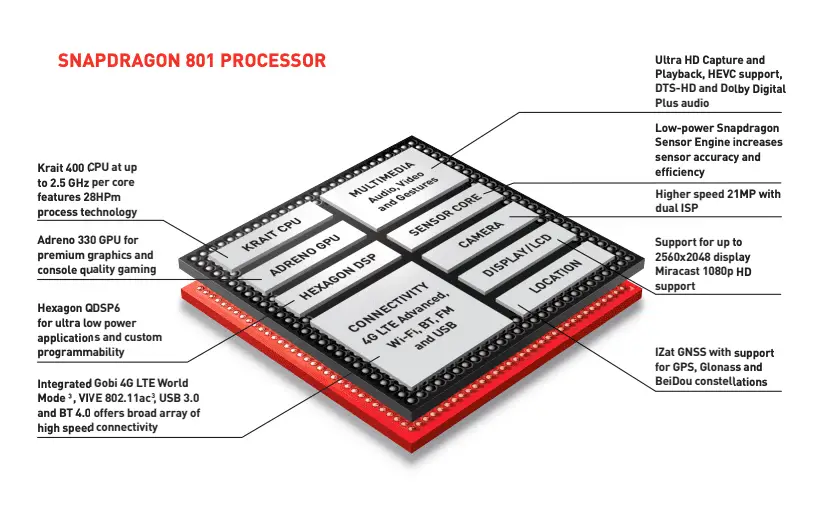
Source: Snapdragon 801 Processor Product Brief (Qualcomm)
Smartphones and devices powered by Qualcomm and ARM Mali GPUs form the backbone of modern digital communication. Qualcomm’s custom version of the Linux Kernel, known as MSM, which primarily houses these vulnerabilities, is an intricate web of specialized code supporting a range of microdevices on SoC. ARM Mali, a GPU core design licensed to industry partners, is equally ubiquitous, powering a wide range of devices. The vulnerabilities discovered within these systems hold significant implications due to their widespread use.
The vulnerabilities in question were added to the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog and include the following:
1. CVE-2023-33063: A use-after-free issue in aDSP FastRPC DMA Memory Management in Qualcomm’s MSM kernel, leading to potential memory corruption during a remote call from HLOS to DSP.
2. CVE-2023-33106: This vulnerability involves unsanitized input in Adreno GPU KGSL IOCTL, which could result in memory corruption while submitting a large list of sync points in an AUX command.
3. CVE-2023-33107: Here, an integer overflow in KGSL IOMMU SVM memory management can lead to memory corruption in the Graphics Linux kernel during IOCTL call.
4. CVE-2022-22071: A use-after-free in aDSP driver memory management within the Automotive OS Platform Android, potentially leading to exploitation when process shell memory is freed.
5. CVE-2023-4211: A vulnerability in ARM Mali’s GPU Kernel Driver, allowing improper GPU memory processing operations.
These vulnerabilities, particularly concerning memory management and processing logic, create avenues for attackers to execute arbitrary code with elevated privileges. They underscore a critical challenge in protecting the intricate layers of modern computing architectures. The exploitation of these vulnerabilities could lead to elevated privileges, persistence on the device, or more powerful arbitrary code execution, affecting a significant portion of Android devices.
In response to these vulnerabilities, patches have been introduced by Qualcomm and ARM, highlighting the ongoing battle between maintaining cutting-edge technological capabilities and ensuring the security of these systems. The complexity of modern SoCs, coupled with the sophisticated nature of these vulnerabilities, necessitates a heightened level of awareness and proactivity from users, developers, and security professionals.




