Researcher details MITM, RCE and LPE vulnerabilities in CyberGhost
CyberGhost, a leading VPN service provider, has recently faced security vulnerabilities that could potentially lead to local privilege escalation, remote code execution, and unauthorized control of users’ network traffic. CyberGhost offers its VPN services across multiple platforms, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
The Linux client of CyberGhost VPN operates by using user account credentials for logging into the management web panel, managing subscriptions, and downloading clients for specific platforms. Users can choose their preferred VPN server by defining criteria such as service type, country, city, and server type. When connecting to the VPN, the client requests a VPN configuration from the CyberGhost API and executes the locally installed VPN software using the downloaded configuration.
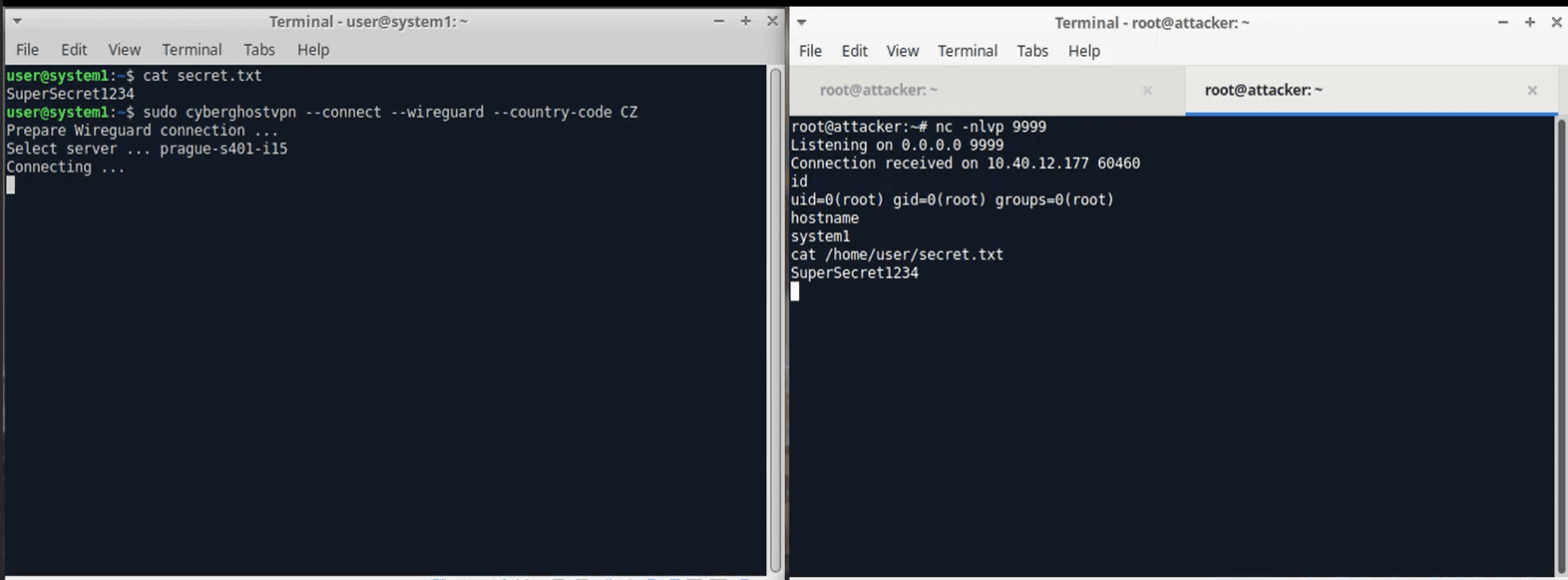
However, two vulnerabilities have been discovered, which, when combined, can lead to a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack and remote code execution (RCE). Firstly, the CyberGhost VPN client lacks certificate validation in one instance, which makes the client susceptible to trusting an illegitimate server impersonating the API. This vulnerability could potentially allow an attacker to route users’ entire network traffic through a malicious server, putting sensitive data at risk.

Secondly, a command injection vulnerability exists due to the lack of proper sanitization when parsing the response from the endpoint and generating a Wireguard configuration file. Although this would not typically pose a problem, it becomes an issue when combined with the first vulnerability, as a malicious API could return a command injection payload, which would then be executed on the user’s machine with root privileges, granting the attacker full control over the device.
Additionally, a local privilege escalation vulnerability has been discovered that could be exploited under non-standard configurations, allowing users to modify a file and inject their commands.
These vulnerabilities were found in the CyberGhostVPN Linux client version 1.3.5 and below. The company has since addressed these issues in version 1.4.1, which is available for download. However, the client lacks an auto-update feature, meaning users must manually update their software. If updating the client is not possible, users can mitigate the exploitation of MITM and RCE vulnerabilities by using the OpenVPN service type, for example, sudo cyberghostvpn –connect –openvpn –country-code CZ.





