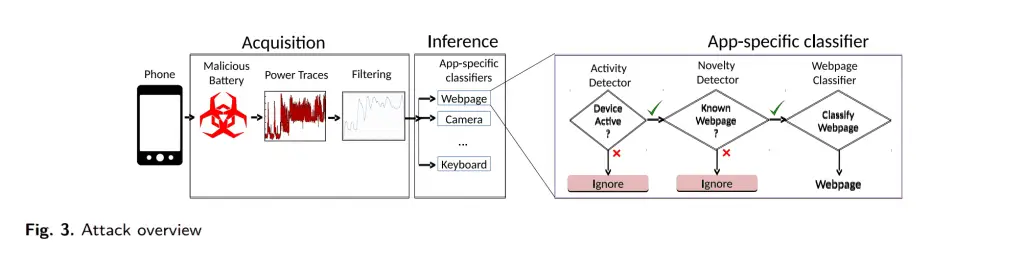
Recent researchers from the University of Texas in Austin, the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, and the Israel Institute of Technology have confirmed that the use of a particular cell phone battery can obtain sensitive information within a smartphone. The principle of utility is to continually detect the consumption of the battery, including the power consumption of the GPU chip and memory in the mobile phone, and the main reason is that the power consumption of the CPU and the touch screen leaks the most mobile phone information.

To enhance the accuracy of the information obtained, the attacker entice the user to input specific characters through the touchscreen, and the user can restore the user’s browsing records, call information and photos on the mobile phone. To obtain this information is also very simple, only need to continue to send bitstream through the background of the mobile phone browser can be obtained.
The keystroke accuracy of the touchscreen is 36%, and the attacker can also search for the password input by the user. In the experiment, the attacker can also restore the site URL of the user’s previous visit, with an accuracy of 65%. The success rate of monitoring calls is up to 100%. There is also a very high accuracy of the monitoring of the camera operation of the mobile phone. In addition to the tracking of the photographing operation, other data can obtain through flash and ambient light conditions.
The above operation premise is that the special cell phone battery is replaced in advance, or the battery installed at the factory of the cell phone already has this function. Considering the slow and low accuracy of data obtained through this method, it is currently not a trend to spread. However, the idea of this attack method is very novel. It uses the traces of the mobile phone hardware rather than the installation of specific malicious software and has low-cost features. In one case, the attacker peddled low-priced batteries online and claimed that it could extend the warranty period of the cell. This way, users were encouraged to purchase the battery.
The Battery Status API interface was used for data acquisition. This interface was previously removed from their browsers by Mozilla and Apple, but it still exists in the Chrome browser. This interface has three parameters: battery full charge and discharge time, battery power, charge status. Researchers indicated that the charge status parameter is usually 0 or 1 to show whether it is charging or not. It is often used to obtain data under wireless charging status.
When the phone is wirelessly charged, the battery charging status parameter is activated by the wireless charging dock. The attacker can simulate the battery charging current generated inside the phone battery to change the battery charging status and continuously send the binary bit stream. Of course, the attacker needs the user to open a specific website on the mobile phone in advance to receive the data information sent by the battery charging status parameter interface. Since this process is two-way communication, the attacker can also set the cell to ensure that the user has previously visited a particular website.
The complete charging or non-charging detection transmission process takes 3.9 seconds, and it takes 1.6 seconds to return to the non-charging state so that 0.1-0.5 bits of data can acquire per second. This type of attack requires too much bedding, such as the operation of replacing the battery of a mobile phone. Therefore, the attacker will generally combine with other attack methods. Although it is unlikely, it is still a significant security reminder.