Image: Horizon3Attack
Security researchers from the Horizon3 Attack Team have developed a CVE-2022-40684 PoC exploit code and planned to release it later this week.
Last week, Fortinet warned its customers of a security flaw affecting FortiGate firewalls and FortiProxy web proxies that could potentially allow an attacker to perform operations on the administrative interface via specially crafted HTTP or HTTPS requests.
The security bug tracked as CVE-2022-40684 (CVSS score: 9.6) is an authentication bypass on the administrative interface that allows an attacker to log into unpatched devices and perform operations on the administrative interface.
The flaw affects the following versions
- FortiOS version 7.2.0 through 7.2.1
- FortiOS version 7.0.0 through 7.0.6
- FortiProxy version 7.2.0
- FortiProxy version 7.0.0 through 7.0.6
- FortiSwitchManager version 7.2.0
- FortiSwitchManager version 7.0.0
Fortinet has been patched in FortiSwitchManager version 7.2.1, FortiProxy versions 7.0.7 and 7.2.1, and FortiOS versions 7.0.7 and 7.2.2. The company has recommended customers immediately update their products due to attackers being able to remotely exploit the vulnerability.
“Fortinet is aware of an instance where this vulnerability was exploited, and recommends immediately validating your systems against the following indicator of compromise in the device’s logs: user=”Local_Process_Access,” the company writes in the advisory. Fortinet has provided information on workarounds as follows to reduce the impact of the vulnerability:
- Disable HTTP/HTTPS administrative interface
- Limit IP addresses that can reach the administrative interface

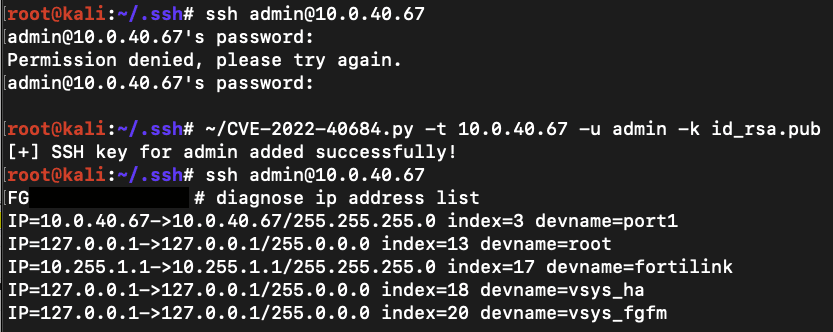
Today, Horizon3 Attack Team, which analyzed the patch that had fixed this vulnerability, announced that it is planning to release a blog and CVE-2022-40684 PoC code later this week.
Update: October 13th
The technical analysis and PoC are available on GitHub.