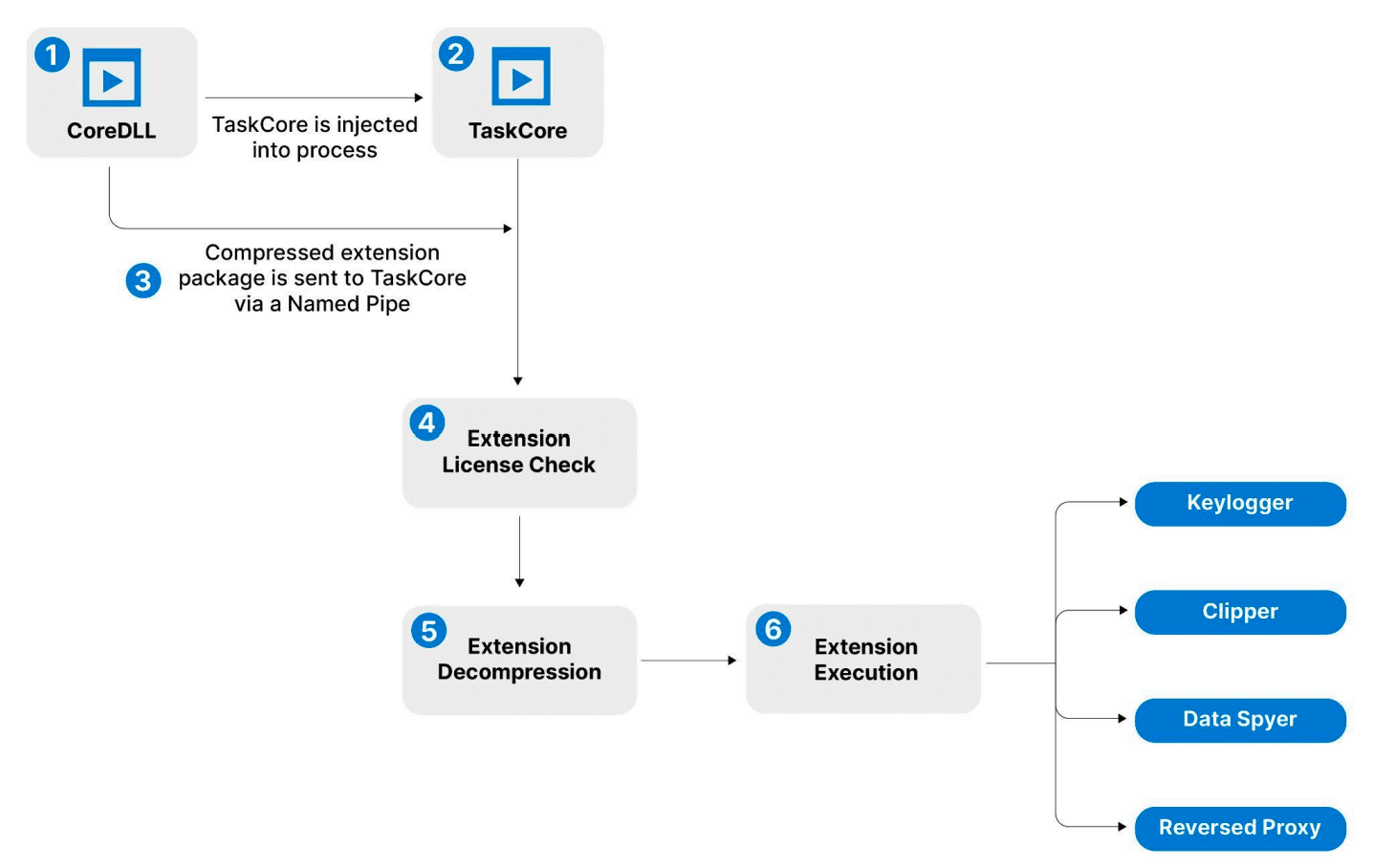
Rhadamanthys extension loading (Source: Recorded Future)
The relentless evolution of malware continues with the latest iteration of Rhadamanthys Stealer, version 0.7.0, which incorporates cutting-edge AI-powered features. Released in mid-2024, this version showcases how artificial intelligence (AI) is being weaponized to enhance data theft capabilities, particularly through the integration of Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology. This addition enables Rhadamanthys to automatically extract cryptocurrency seed phrases from images, representing a significant leap in the malware’s ability to target and compromise sensitive financial information.
Rhadamanthys, first detected in 2022, continues to evolve with rapid releases. The malware targets organizations across North and South America, with its versatility and advanced features making it a popular choice on underground forums. Priced at just $250 for 30 days of access, it remains an accessible option for cybercriminals seeking to exploit vulnerable systems.
While Rhadamanthys has been banned on prominent underground forums for targeting Russian and former USSR entities, the developer behind the malware, known as “kingcrete2022,” continues to advertise new versions through private channels, including TOX and Telegram.
Insikt Group’s latest report highlights the introduction of AI-powered OCR capabilities, which allow Rhadamanthys to scan and analyze images for cryptocurrency wallet seed phrases. By incorporating this advanced technology, cybercriminals can now automate the extraction of sensitive data from images stored on compromised systems, streamlining the process of targeting and exploiting financial accounts. This feature is a stark reminder of how AI can be misused to escalate the impact of malware attacks.
The implementation of the OCR functionality occurs in two stages: first, images are scanned and flagged on the infected system. Then, once the images are exfiltrated to Rhadamanthys’ command-and-control (C2) server, AI algorithms are deployed to extract seed phrases, which can then be used to drain cryptocurrency wallets. The report notes that this development is particularly alarming given the increasing use of images and screenshots for securely storing sensitive information, such as passwords and recovery phrases.
In addition to AI-powered OCR, Rhadamanthys v0.7.0 includes several new features designed to enhance its ability to evade detection. Notably, the malware now allows threat actors to execute Microsoft Software Installer (MSI) files, which are less likely to be flagged as malicious by traditional security systems. MSI files, commonly used for legitimate software installations, provide an effective means for attackers to bypass security measures and establish a foothold on targeted systems.
Moreover, Rhadamanthys version 0.7.0 employs a new technique involving mutex creation, which acts as a kill switch to prevent the malware from re-executing on the same system. By creating known Rhadamanthys mutexes on non-infected machines, organizations can prevent future infections from running, providing a potential defensive measure against this evolving threat.
Related Posts:
- New Cyber Threat: RHADAMANTHYS Infostealer Targets Israel
- Hackers Target System Admins with Fake PuTTY Website, Deploy Rhadamanthys Stealer
- Rhadamanthys Stealer: MaaS Malware Hits Oil & Gas
- TA547 Targets Germany with Rhadamanthys, Suspected AI-Generated Code