
sncscan
Tool for analyzing SAP Secure Network Communications (SNC).

Background: SNC system parameters
SNC Basics
SAP protocols, such as DIAG or RFC, do not provide high security themselves. To increase security and ensure Authentication, Integrity, and Encryption, the use of SNC (Secure Network Communications) is required. SNC protects the data communication paths between various client and server components of the SAP system that use the RFC, DIAG, or router protocol by applying known cryptographic algorithms to the data in order to increase its security. There are three different levels of data protection, that can be applied to an SNC-secured connection:
- Authentication only: Verifies the identity of the communication partners
- Integrity protection: Protection against manipulation of the data
- Confidentiality protection: Encrypts the transmitted messages
SNC Parameter
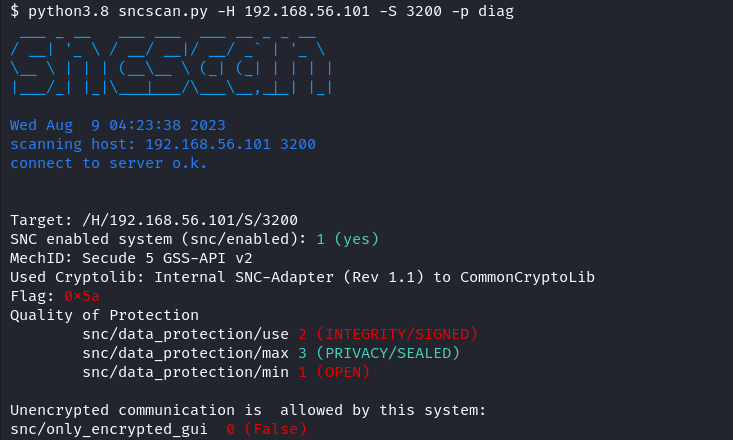
Each SAP system can be configured with SNC parameters for communication security. The level of the SNC connection is determined by the Quality of Protection parameters:
- snc/data_protection/min: Minimum security level required for SNC connections.
- snc/data_protection/max: highest security level, initiated by the SAP system
- snc/data_protection/use: default security level, initiated from the SAP system
Additional SNC parameters can be used for further system-specific configuration options, including the snc/only_encrypted_gui parameter, which ensures that encrypted SAPGUI connections are enforced.
Reading out SNC Parameters
As long as a SAP System is addressed that is capable of sending SNC messages, it also responds to valid SNC requests, regardless of which IP, port, and CN were specified for SNC. This response contains the requirements that the SAP system has for the SNC connection, which can then be used to obtain the SNC parameters. This can be used to find out whether an SAP system has SNC enabled and, if so, which SNC parameters have been set.
Install & Use
Copyright (C) 2023 usdAG