A new AutoIT-compiled executable has been spotted in the wild targeting Gmail accounts, according to a recent analysis by the SonicWall Capture Labs threat research team. The malware, originally named “File.exe,” uses a variety of tactics to compromise user accounts, including reading clipboard data, capturing keystrokes, and potentially controlling keyboard and mouse events.
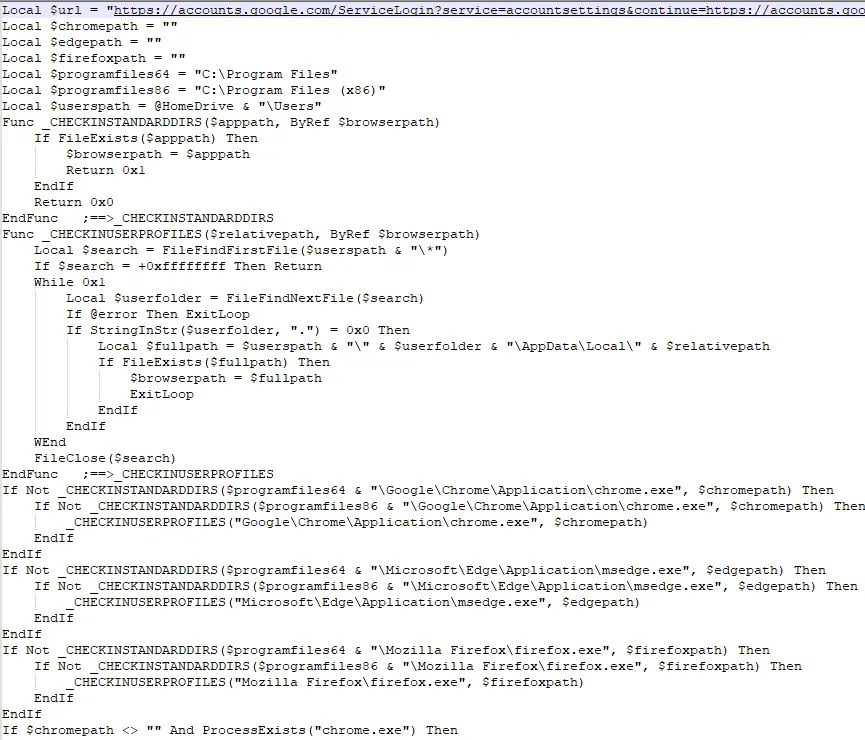
Once executed, MalAgent.AutoITBot attempts to open Gmail login pages using three of the most widely used web browsers: Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, and Mozilla Firefox. However, its threat extends far beyond just accessing email accounts.
The primary functionality of this bot revolves around data theft and system manipulation. It is equipped to capture keystrokes, read clipboard data, and even control keyboard and mouse inputs. These capabilities enable the malware to harvest sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and other confidential data entered by the user.
Moreover, MalAgent.AutoITBot has the potential to restart or shut down the infected system, run processes as different users, and block user input if it detects debugging tools. This anti-analysis feature complicates efforts to study the malware and devise countermeasures, making it a formidable adversary for cybersecurity professionals.
The SonicWall team utilized tools like Detect-It-Easy (DIE) and AutoITExtractor to analyze the malware’s behavior and script. The initial analysis revealed that the executable was heavily obfuscated, with multiple networking libraries imported under vague ordinal identifiers. This obfuscation makes it challenging to trace the malware’s exact operations and intentions.
Upon extracting the script, researchers discovered cleartext commands directing browsers to open Gmail login pages via accounts.google.com. However, the malware doesn’t stop there; it also includes generic login links for other popular social media platforms like Facebook and Reddit. This multi-target approach suggests that the bot is designed to harvest credentials from various online services, not just Gmail.
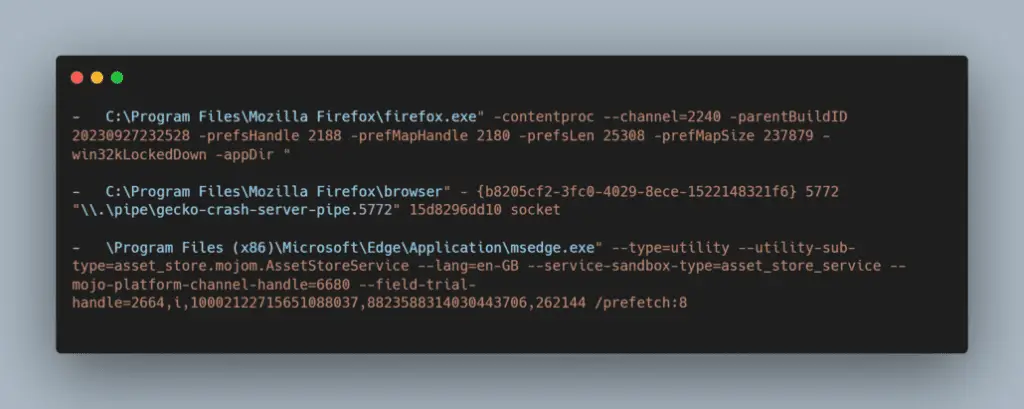
Interestingly, the malware employs a dynamic setup to determine the right environment for establishing a connection with a Command-and-Control (C2) server. If the socket setup fails, the malware calls the WSAGetLastError Windows API to troubleshoot the issue. Once successful, it triggers keylogging, screen capture, and file enumeration functions—though these activities were not observed during testing, indicating a possible failure to connect with the C2 server during analysis.
One of the more concerning aspects of MalAgent.AutoITBot has the ability to run multiple processes silently. For instance, when launching Firefox, the malware creates a hidden page while simultaneously attempting to establish a network socket. This stealthy behavior allows it to operate under the radar, making it difficult for users and traditional antivirus solutions to detect and mitigate the threat.
Given these capabilities, MalAgent.AutoITBot poses a severe risk to both individuals and organizations. Its potential to steal credentials and manipulate system functions underscores the importance of exercising caution when dealing with files of unknown origin.
Related Posts:
- Pidgin Users Beware! Malicious Plugin Discovered with Keylogger
- Cheana Stealer Targets VPN Users Across Windows, Linux, and macOS in Sophisticated Phishing Campaign