SourcePoint v3.2 releases: polymorphic C2 profile generator for Cobalt Strike C2s
SourcePoint
SourcePoint is a polymorphic C2 profile generator for Cobalt Strike C2s, written in Go. SourcePoint allows unique C2 profiles to be generated on the fly that helps reduce our Indicators of Compromise (“IoCs”) and allows the operator to spin up complex profiles with minimal effort. This was done by extensively reviewing Articles as well as Patch Notes to identify key functions and modifiable features. SourcePoint was designed with the intent of addressing the issue of how to make our C2 activity harder to detect, focusing on moving away from malicious IoCs to suspicious ones. The goal here is that it is harder to detect our C2 if our IoCs are not malicious in nature and require additional research to discover the suspicious nature. SourcePoint contains numerous different configurable options to choose from to modify your profile (in most cases if left blank SourcePoint will randomly choose them for you). The generated profiles modify all aspects of your C2. The goal of this project is to not only aid in circumventing detection-based controls but also help blend C2 traffic and activity into the environment, making said activity hard to detect.
Important
SourcePoint primarily automates the build process of a profile. It’s very important to know all the features modified in these profiles. Knowing these features can really help increase your success.
Options
While there are a lot of settings and features described in the help function of SourcePoint, there are numerous important features baked into each profile that are important to be familiar with. These features are:
Global Options
This part of your profile modifies how the beacon operators. Some of the features used to modify the behaviour are:
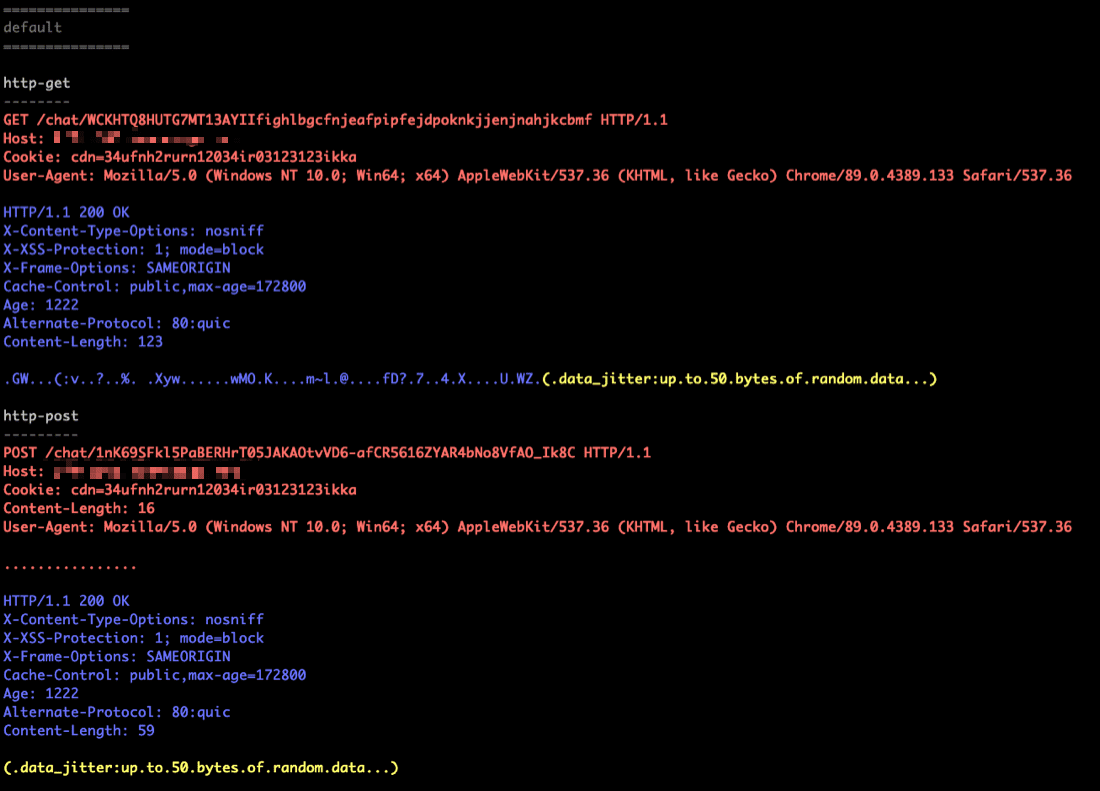
- Host Stage – Allows the team server to host staged shellcode for HTTP, HTTPS, DNS. If this is enabled, anyone sending a GET request with a specific value such has
/9ZXqcan pull the shellcode as well - Sleep – The length of time that a beacon calls back home
- Jitter – Appends a percentage to the beacon call home time
- Useragent – The useragent string used when communicating HTTP and HTTPS traffic. Using the appropriate useragent string can help blend into the environment
- Data Jitter – Adds a random-length string to all GET and POST requests to ensure incoming requests are not the same length
- SMB Frame Header – Adds a header value to the SMB beacon messages
- Pipename – Sets the name of the SMB pipe the beacons is going to use for communication
- Pipename Stager – Sets the name of the SMB stager for the beacons
- TCP Frame Header – Adds a header value to the TCP beacon messages
- SSH Banner – The SSH banner used
- SSH Pipename – The name used for the SSH banner
Stage
This part of your profile controls how beacon is loaded into memory and edit the content of the beacon DLL. Some of the features used to modify the behaviour are:
- Obfuscate – Obfuscates the import table of the reflective DLL
- Stomppe – Asks the payload to stomp MZ, PE and, e_lfanen values after loading
- Clean up – Tells the beacon to free up memory assoicated with the refelctive DLL that initalized it
- UseRWX – Ensures shellcode does not use Read, Write Execute permissions
- Smart Inject – Uses embedded function pointer hints to bootstrap the beacon agent without walking kernel32 EAT
- Sleep Mask – TCP and SMB beacons will obfuscate themselves at rest while they wait for the connection to be established
- PE Header – Changes the characteristics of your beacon Reflective DLL to look like something else in memory
- Transformation – Transform beacon’s Reflective DLL stage by removing or adding strings to the .rdata section
Process-Inject
This part of your profile controls how the beacon shapes injected content and controls process injection behavior. Some of the features used to modify the behaviour are:
- Allocator – Determines how the beacon’s Reflective loader allocates memory
- Minimum Allocation – Minimum amount of memory to request for injected content
- Userwx – Ensures shellcode does not use Read, Write Execute permissions (The alternative is RW)
- Startrwx – Use Read, Write Execute as initial permissions for injected content (The alternative is RW)
- Transformer – Adds a block of padding content injected by the beacon
- Execute – This section determines how to execute the injected code
Post-Exec
This part of your profile controls how the beacon handles post-exploitation modules and commands. Some of the features used to modify the behaviour are:
- Spawnto – Determines the default temporary process beacon will spawn for its post-exploitation command and options
- Obfuscate – Obfuscates the import table of the reflective DLL
- Smart Inject – Pass key function pointers from beacon to its child jobs
- AMSI disable – Disable AMSI for powerpick, execute-assembly, and psinject (Certain EDRs can detect this best avoid using these tools)
- Keylogger – Determines how the keystroker logging API use to capture keystrokes
Profiles
Currently, SourcePoint provides you with 6 baked in options for HTTP/HTTPS traffic profiles, based on existing profiles. Of these 6, 4 of them are influenced by and based on:
- Microsoft Window’s Update Communication
- Slack’s Message Communication
- Gotomeeting’s Active Meeting Communication
- Microsoft Outlook’s Email Communication
2 of the profile options (5 and 6) are designed specifically for:
- Cloudfront.net
- AzureEdge.net
The last option (7) is designed to input a custom profile. This option is designed to allow an operator to utilize a completely custom traffic profile. There are many cases where a completely unique traffic profile will yield high success rather than one of these. This also allows operators to still utilize SourcePoint’s malleability features with their go-to or favorite traffic profile. As this allows for unique profiles it’s important to ensure you tweak and adjust the profile for SourcePoint to work. At a minimum:
- Replace – header “Host” “acme.com”; with header “Host” “{{.Variables.Host}}”;
- Replace – /pathtolegitpage/ under the GET field with {{.Variables.HTTP_GET_URI}}
- Replace – /pathtolegitpage/ under the POST field with {{.Variables.HTTP_POST_URI}}
To do so, use the following options -CustomURI and -ProfilePath along with -Profile 7. While developing a profile, it’s highly recommended to use the native ./c2lint to verify everything is working.
Changelog v3.2
Bug Fix
- Fixed issue with one of the Magic_MZ options
- Fixed syscall_method printout display
- Fixed Post-Ex PE name generation array
Install & Use
Copyright (c) 2021 Tylous