
Infection Chain
McAfee Labs has recently unveiled a sophisticated cyber threat known as DarkGate, which uses advanced tactics to exploit the AutoHotkey utility and evade Microsoft Defender SmartScreen. This discovery outlines a critical escalation in cyber attacks, showcasing the increasing capabilities of threat actors to infiltrate and manipulate systems. DarkGate, identified as a Remote Access Trojan (RAT), poses a formidable threat due to its array of functionalities including data theft, keylogging, and the execution of arbitrary commands on infected devices.
The Infection Chain: HTML and XLS Entry Points

DarkGate Remote Access Trojan initiates its infection through two primary vectors: an HTML file and an XLS file. Both vectors deploy identical shellcode and payloads, demonstrating a high level of sophistication in their approach.
HTML Vector:
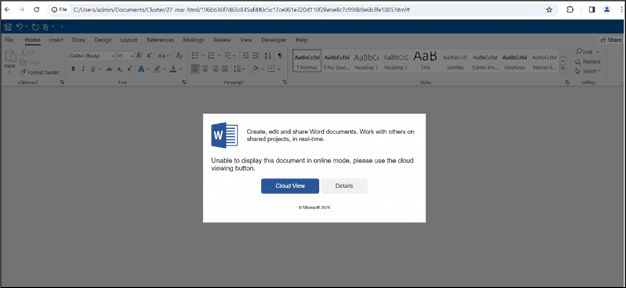
The HTML infection begins with a phishing page disguised as a Word document in a fake “Cloud View.” Unsuspecting users are lured into granting permissions which facilitate further malicious activities. The HTML page manipulates Windows Explorer’s title to display a seemingly legitimate “onedrive.live.com” address. This page leads to the execution of a .url file that triggers the download and automatic execution of a VBScript file, exploiting the CVE-2023-36025 vulnerability in Windows Defender SmartScreen to bypass security prompts.
XLS Vector:

Similarly, the XLS-based infection tricks users into enabling content under the guise of viewing the document correctly, which then executes a VBScript from a remote server. This script, like its HTML counterpart, proceeds to download and execute further malicious components, setting the stage for the DarkGate payload.
AutoHotkey: The Tool for Evasion and Execution
Central to the DarkGate infection chain is the use of AutoHotkey, a powerful scripting language for automating the Windows GUI. By downloading and executing AutoHotkey scripts, attackers can perform a variety of tasks undetected. These scripts are capable of reading, writing, and executing shellcode stored in seemingly benign text files. This allows DarkGate to inject malicious code directly into the memory, executing it without touching the disk and evading traditional antivirus detection.
Persistence and Network Exfiltration
DarkGate ensures its persistence on infected machines by creating a shortcut in the startup folder, which reinstalls the malware upon each reboot. This method is stealthy and ensures continued control over the compromised system. The network activity associated with DarkGate includes data exfiltration to a remote server, highlighting the threat’s capability to not only disrupt operations but also steal sensitive information.
Defense is a Multi-Layered Approach
This campaign is a stark reminder that even familiar tools can be used against us. It also underscores the importance of layered cybersecurity:
- Vigilance is Key: Be suspicious of unusual emails, unexpected attachments, and requests that seem out of the ordinary. Phishing tactics continue to evolve, so don’t let your guard down.
- Patching is Paramount: Install Windows updates and updates for other software promptly.
- Security Tools Matter: Reputable antivirus, endpoint protection, and robust email filtering can provide an extra line of defense.
- Employee Education: Regular training on identifying social engineering tactics is essential for all staff.