CloudImposer vulnerability flow
A critical vulnerability in Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Composer, discovered by security researchers at Tenable, could have enabled remote code execution on millions of servers, underscoring the ongoing threat of supply chain attacks in cloud environments. Dubbed “CloudImposer”, this flaw could have potentially exposed millions of Google Cloud Platform (GCP) servers to the devastating consequences of remote code execution, painting a stark picture of the risks inherent in even the most trusted cloud environments.
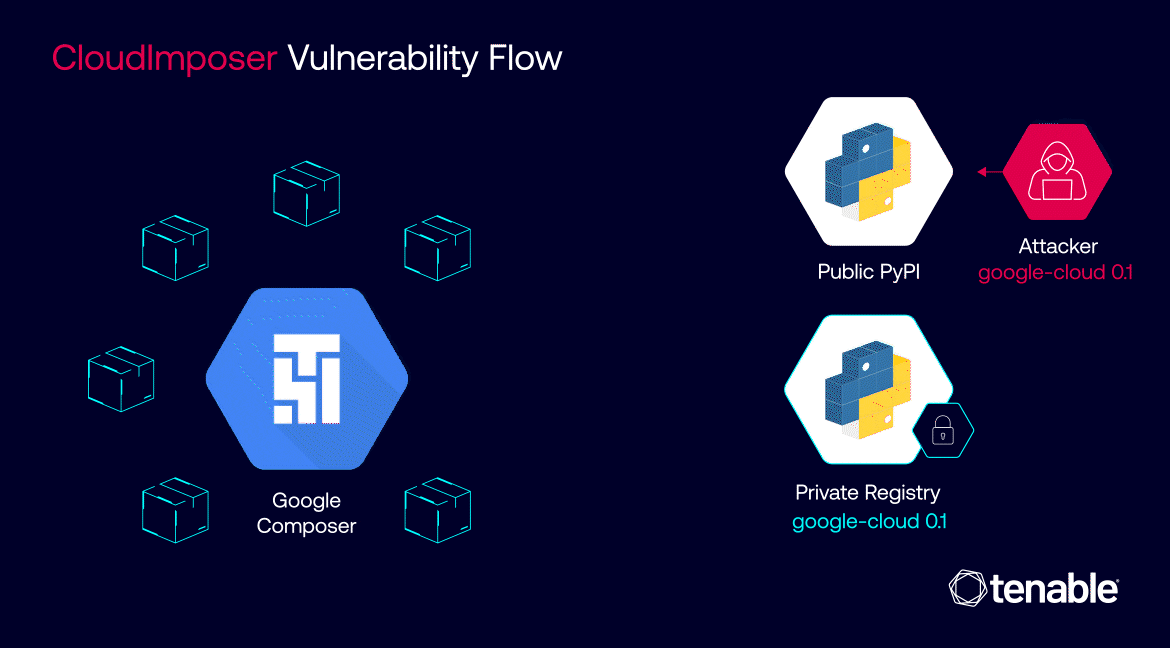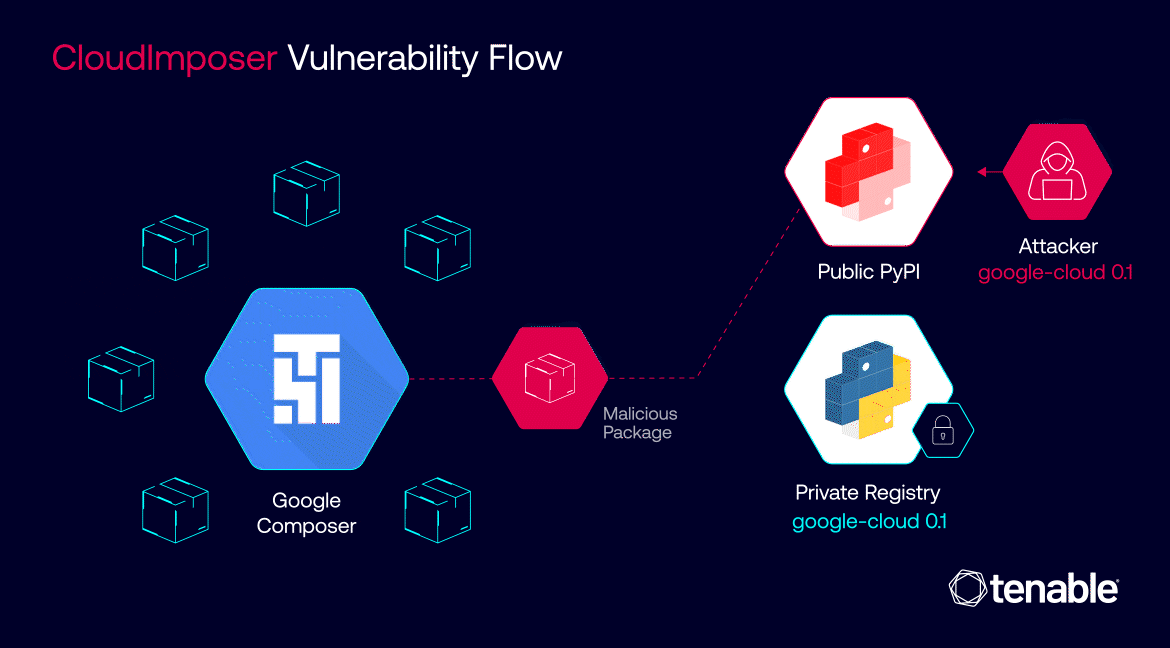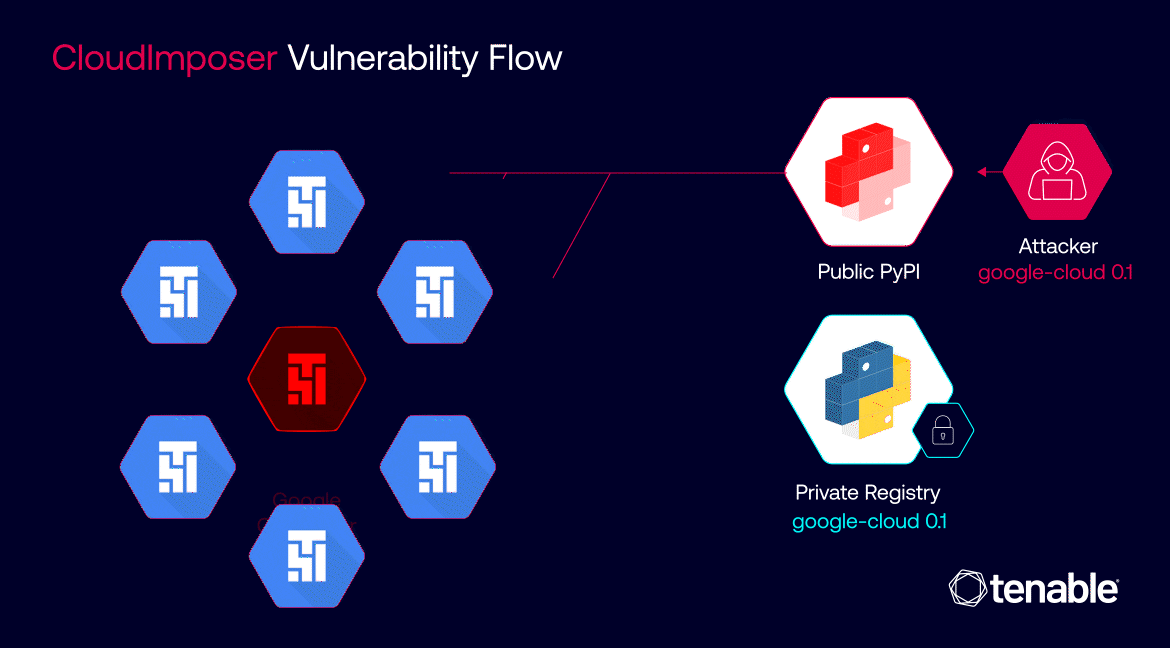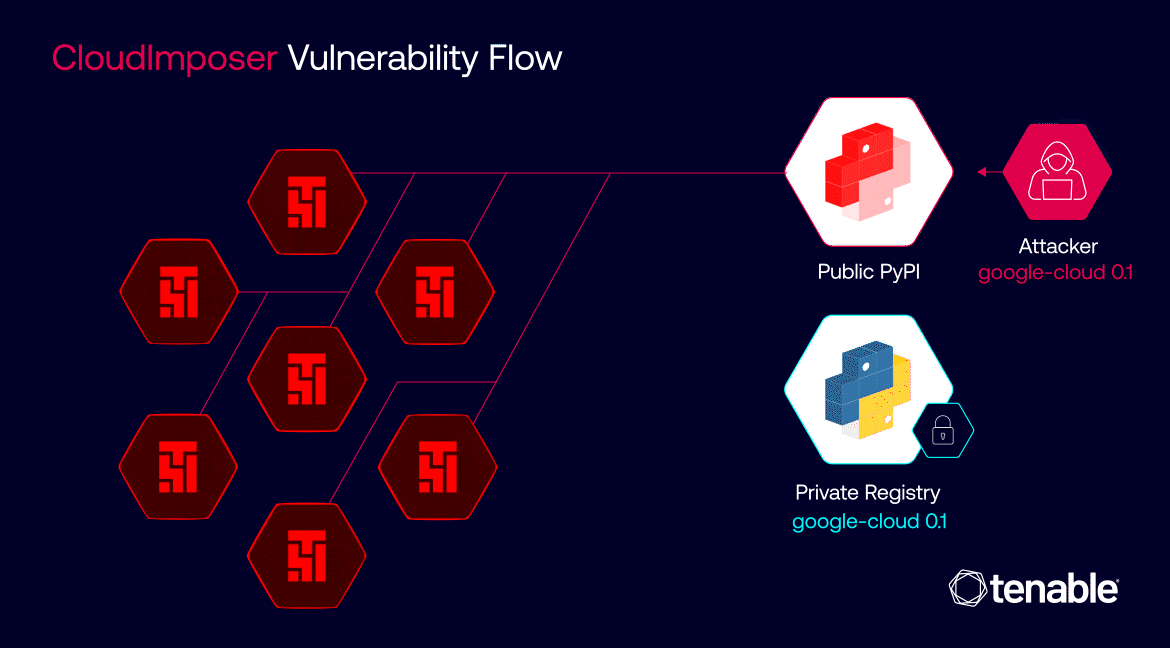
The vulnerability, which resided within the widely used GCP Composer service – a tool designed to streamline the orchestration of complex cloud workflows – exploited a cunning supply chain attack technique known as Dependency Confusion. By subtly manipulating the software supply chain, threat actors could have potentially injected malicious code into unsuspecting cloud workflows, wreaking havoc on organizations’ data and operations with surgical precision.
The inner workings of CloudImposer hinged on a clever deception. Attackers could intercept internal dependencies, essential software components pre-installed by Google on every GCP Composer instance. By uploading a counterfeit package to the public Python Package Index (PyPI) repository with a strategically chosen name – “google-cloud-datacatalog-lineage-producer-client” – they could trick GCP Composer into prioritizing the malicious package over the legitimate internal one.
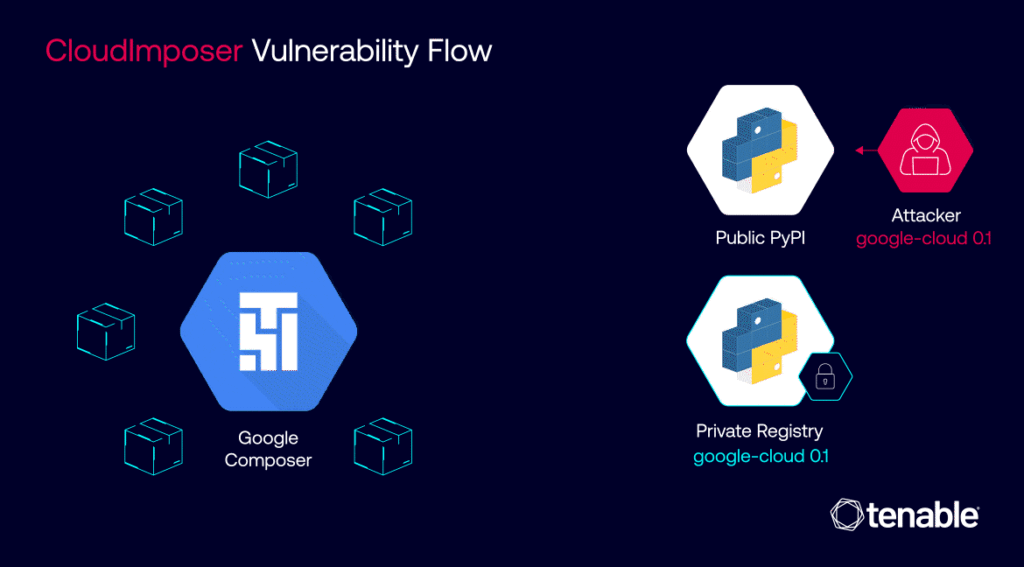
This insidious attack was made possible due to a confluence of factors. The use of the “pip install” command with the “–extra-index-url” argument inadvertently favored public repositories over private ones, creating an opening for the malicious package to infiltrate the system. Once installed, the package granted attackers the ability to execute arbitrary code with elevated privileges, effectively handing them the keys to the kingdom – sensitive credentials and, potentially, access to a wide array of Google Cloud services.
The ramifications of a successful CloudImposer attack could have been catastrophic. Given the widespread adoption of GCP Composer across diverse industries, the potential impact spanned from large-scale data breaches and service disruptions to significant financial losses for organizations of all sizes. The vulnerability underscored the fragility of cloud ecosystems and the urgent need for robust security measures to safeguard critical data and operations.
Fortunately, Tenable adhered to responsible disclosure practices, promptly informing Google of the vulnerability in January 2024. Google responded swiftly, releasing a patch in May to address the issue. The patch fortified GCP Composer by ensuring packages are exclusively downloaded from private repositories and by introducing checksum verification, an additional layer of protection against tampering. Google further advised developers to use the “–index-url” argument instead of “–extra-index-url” to mitigate the risk of future supply chain attacks.
Related Posts:
- Python Developers Targeted in Massive Supply Chain Attack; Over 170,000 Users Affected
- Google Cloud Services Disrupted in UK Due to Power Outage