According to securityaffairs, CSE Cybsec’s malware experts found a large-scale malicious advertising campaign EvilTraffic, using tens of thousands of infected sites to attack. It is reported that hackers use some CMS vulnerabilities in this attack to upload and execute arbitrary PHP pages for generating revenue from advertisements.
The researchers said infected sites involved in malware EvilTraffic running various versions of the WordPress CMS, once the site was compromised, the attacker will upload a “zip” file containing all malicious files. Although the zip file has a different name for each infection, the files it contains always have the same structure when uncompressed. After the researchers analyzed, at present these documents have not been used.
Malicious files may be inserted into different versions of the same malware (“vomiu”, “blsnxw”, “yrpowe”, “hkfoeyw”, “aqkei”, “xbiret”, “slvkty”). This folder contains the following:
- a php file, called “lerbim.php”;
- a php file, that has the same name of the parent dir; it has initially “.suspected” extension and only in a second time, using “lerbim.php” file, it would be changed in “.php” file;
- two directories, called “wtuds” and “sotpie”, containing a series of files.
The figure below shows an example of this structure:
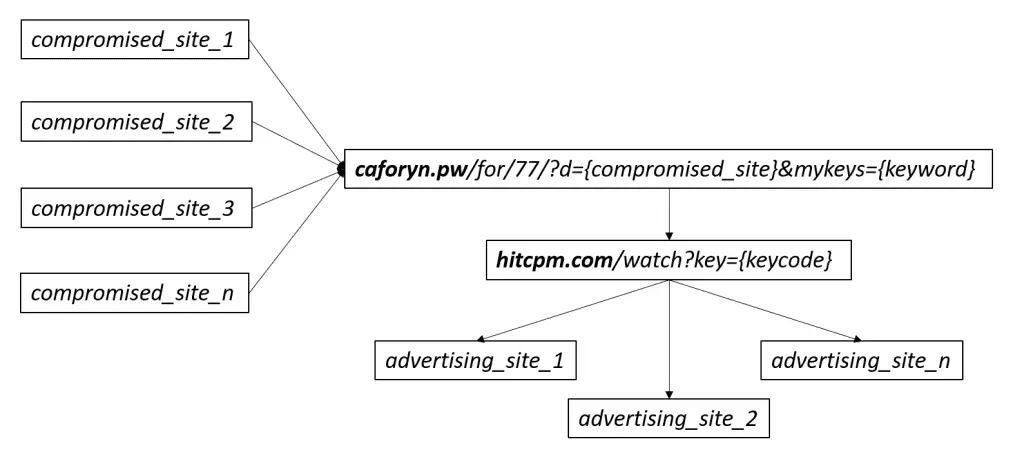
The main purpose of “malware” used in EvilTraffic activities is to trigger a redirect chain through at least two servers that generate ad traffic.
The file “{malw_name} .php” is at the core of any environment: if a user touches it through a web browser, it first redirects traffic to “caforyn.pw” and then redirects to “hitcpm.com” to act as Different websites register to the revenue chain dispatcher.
These sites can be used by attackers to provide business services in order to increase traffic to their customers, but this traffic is generated through illegal means of compromising the site. In addition, these sites can also provide fake pages to download fake things (such as toolbars, browser extensions or pseudo-antivirus) or steal sensitive data (ie, credit card information).
In order to improve the visibility of the site, the compromised site must have a good ranking on the search engine. Therefore, malware performs SEO poisoning by leveraging a glossary containing trending search terms.
Researchers at CSE CybSec ZLab have found about 18,100 infected sites. When researchers analyzed EvilTraffic’s malicious campaigns, they realized that infected sites used in the first few weeks were cleaned up in the last days. In just one week, the number of affected websites dropped from 350,000 to about 180,000.
According to Alexa Traffic Rank, hitcpm.com ranked 132nd in the world with about 0.2367% global internet users. Here are the traffic statistics related to hitcpm.com provided by hypestat.com:
Daily Unique Visitors 1,183,500 Monthly Unique Visitors 35,505,000 Pages per visit 1.41 Daily Pageviews 1,668,735
The analysis shows that traffic in October 2017 increased exponentially. At the moment, experts also find malware distributed through a variety of methods, such as:
- Attachment of junk mail
- Downloading freeware program via unreliable site
- Open torrent files and click on malicious links
- By playing online games
- By visiting compromised websites
The main purpose of malware is to hijack web browser settings such as DNS, settings, homepage, etc. in order to redirect traffic as much as possible to the scheduler site.
Source: SecurityAffairs