Image: Cofense
Phishing attacks continue to evolve in complexity, and the latest report from the Cofense Phishing Defense Center highlights a troubling trend: cybercriminals are increasingly using HR-related phishing tactics to trick employees into revealing sensitive credentials. The report reveals that attackers are leveraging fake emails disguised as official communications from Human Resources departments, targeting employees with a sense of urgency and authority.
In this recent campaign, attackers send emails that appear to come from the victim’s HR department, with subject lines such as “Important: Revised Employee Handbook”. These emails are crafted to look like legitimate corporate communications, with professional language and a formal tone. The messages urge employees to review a “revised employee handbook,” emphasizing the importance of compliance and often setting a tight deadline for action.
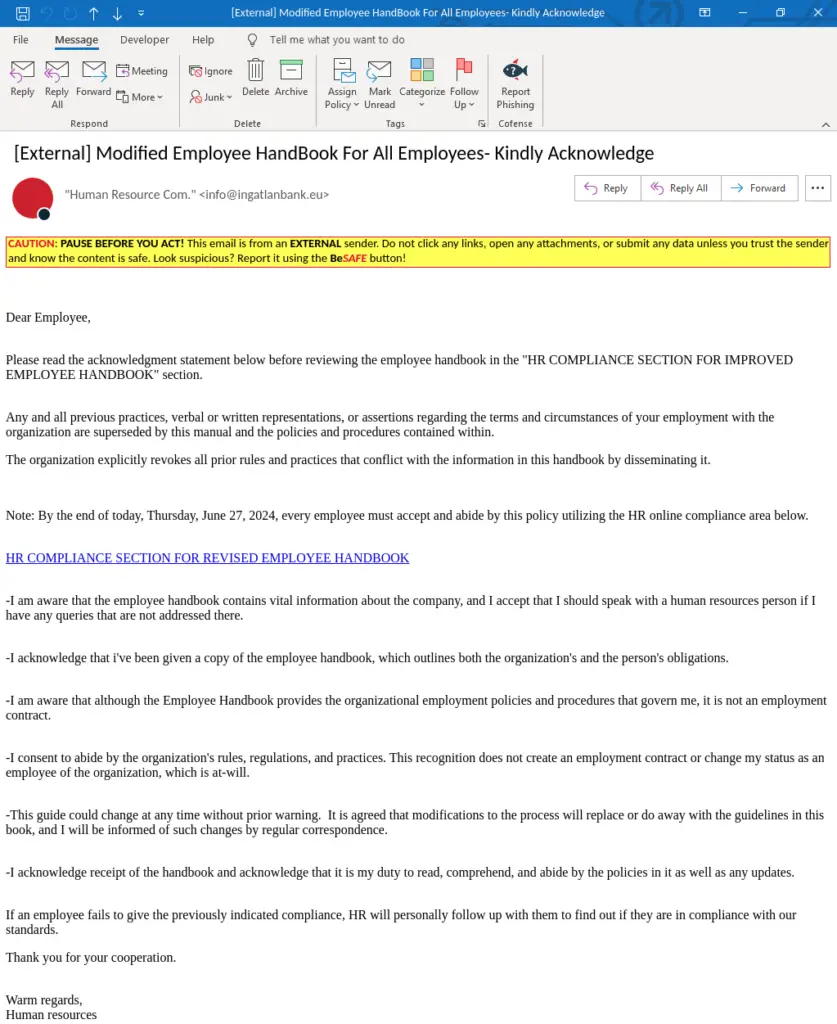
This creates a psychological sense of urgency, pushing recipients to act without fully questioning the legitimacy of the email. By using trusted internal channels like HR, threat actors increase the likelihood that employees will click on the embedded links without hesitation.
The emails contain a hyperlink labeled as the “HR Compliance Section for Revised Employee Handbook.” Upon clicking the link, victims are taken to a site that mimics a legitimate document hosting platform, with a clear “PROCEED” button. When the recipient clicks to proceed, they are redirected to a fake Microsoft login page—carefully designed to look identical to the genuine Office 365 login interface.
The goal of the phishing attack is clear: harvest the victim’s Microsoft credentials. After entering their company username and password, the victim sees an error message stating, “There was an unexpected internal error. Please try again.” This message is a ruse—while the victim believes there was a minor issue, the attackers have already captured their credentials.
To further mask the attack, the victim is then redirected to the company’s Single Sign-On (SSO) or Okta login page, making it appear as though the issue has been resolved.
This HR phishing campaign capitalizes on two key psychological elements: authority and urgency. By presenting the email as coming from HR, attackers tap into the authority employees associate with HR communications. Adding urgency, such as the need to review important documents by a set deadline, further pressures recipients to act without considering potential risks.
According to the Cofense report, this manipulation effectively overrides the natural skepticism employees might otherwise exhibit when handling unsolicited emails. The combination of professional language, trusted branding, and an urgent call to action makes this phishing tactic highly effective.
Related Posts:
- CVE-2024-36401 (CVSS 9.8): Critical GeoServer Flaw Under Active Attack, PoC Available
- Zyxel NAS Devices Under Attack: CVE-2024-29973 Exploitation Attempts by Mirai-Like Botnet
- VMware Patches Critical Vulnerability in Carbon Black App Control
- CVE-2024-39907 (CVSS 9.8): SQLi Flaw Exposes 1Panel Users to Remote Takeover, PoC Published