tlspretense: framework for testing SSL/TLS client certificate validation
TLSPretense — SSL/TLS Client Testing Framework
TLSPretense provides a test framework for testing SSL certificate validation. It generates a set of certificates containing specific flaws, and it presents the certificates to a client that has been configured to trust a CA used by TLSPretense. The test framework then configures its system’s firewall to redirect and intercept network traffic so that the test runner can present its certificate to the client. To speed up testing, the test runner starts the next test as soon as the current test finishes.
The test framework must be run on a Unix-like OS that contains a supported firewall, but the program being tested can run on any device whose network traffic can be routed through the system hosting the test framework. Currently, it supports Netfilter (Linux), ipfw (Mac OS X 10.6, *BSD), and PF on Mac OS X Lion.
How It Works
TLSPretense requires the TLS client software to be configured to trust a CA that TLPretense controls. That way “good” certificates created by TLSPretense will be accepted by the client.
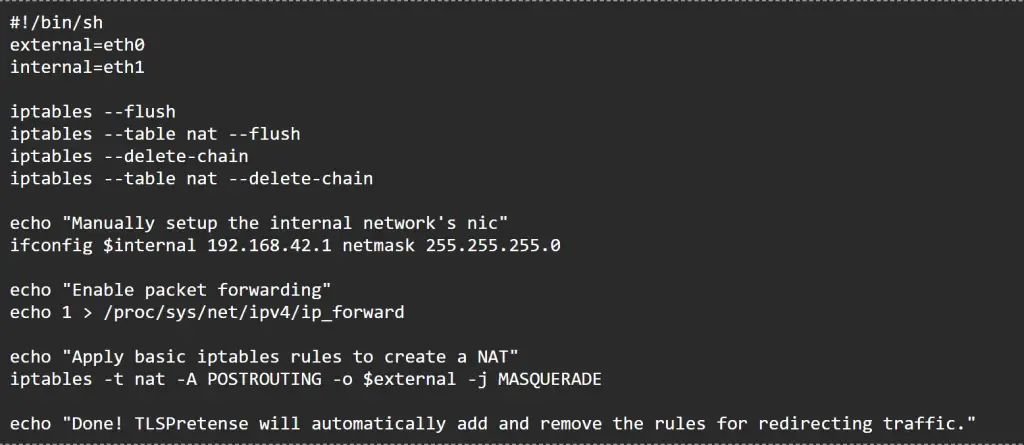
Once the system hosting the test runner has been configured to be a gateway for the network traffic of the client being tested, it will add a firewall rule to redirect network traffic to a test listener. The test listener checks to see whether the client is trying to connect to a predefined host. If the client is connecting to the desired host, then the test listener presents a test certificate chain to the client. The test runner then determines whether the test passes or fails based on whether the client completes the TLS handshake or not.
The test harness was designed to anticipate working with a client that may connect to more than one host. The config.yml file specifies a hostname that should be used for the actual test — all other intercepted SSL connections are essentially ignored (although they currently have their certificate re-signed by the goodca in order to make interception easier).
Copyright (c) 2012 iSEC Partners





