WebBorer
WebBorer is a directory-enumeration tool written in Go and targeting CLI usage.
This project was formerly named ‘GoBuster’, but that had a namespace collision with OJ Reeves’ excellent tool (which was released about the same time as I was preparing this for release).
Features
- Highly portable — requires no runtime once compiled.
- No GUI required.
- Supports Socks 4, 4a, and 5 proxies.
- Supports excluding entire subpaths.
- Capable of parsing returned HTML for additional directories to parse.
- Highly scalable — Go’s parallel model allows for many workers at once.
How webborer works
WebBorer has a number of components. In general, each one runs in a goroutine and they communicate amongst each other with channels.
After settings are loaded, the initial URLs are passed into the workqueue. The workqueue is an unbounded queue implemented with an input channel, an output channel, and a singly-linked-list to allow it to continue to grow. The workqueue also maintains a count of work to be done and work that has been done.
The workqueue empties into the expander. The expander uses the wordlist and possible variations on the URL to produce many candidate URLs. It reports the expansion back to the workqueue for counting but passes the URLs on to the filter.
The filter ensures that URLs are not processed more than once, and also processes URLs against any specified blacklists to ensure that they are not accessed inappropriately.
The workers take work from the filter stage and make the HTTP request to check if the page exists, size, type, etc. There are usually several of these in parallel because they basically block on network traffic. They also invoke auxiliary workers on the returned content: currently, this is only the HTMLWorker to parse the page for links in HTML content.
Finally, the worker may dispatch results the result manager which will write the results to the appropriate output.
Install
go get github.com/Matir/webborer
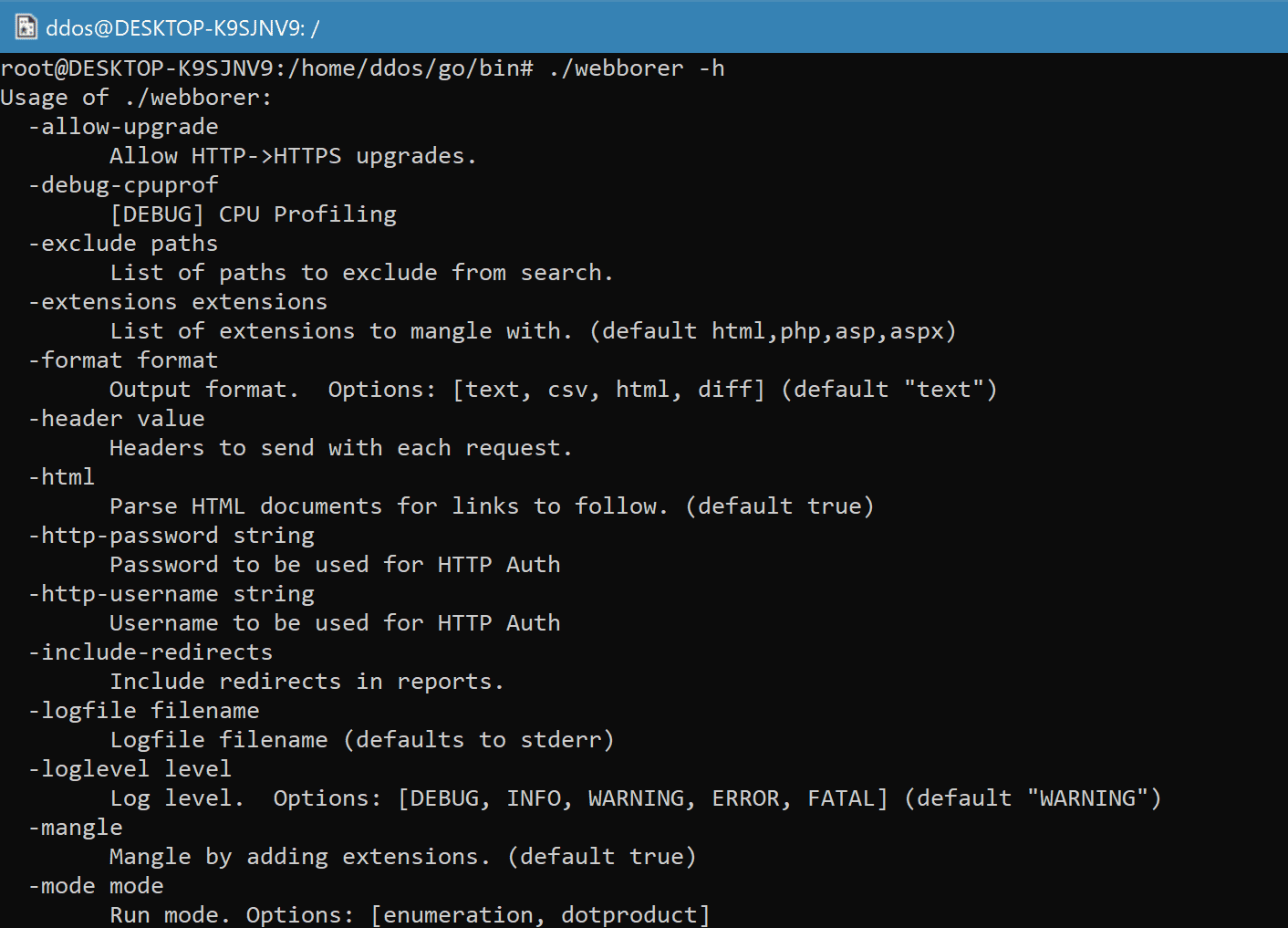
Use

Source: https://github.com/Matir/