
In a recent investigation, Aqua Nautilus uncovered alarming security vulnerabilities within the Prometheus ecosystem. Their research highlights critical flaws spanning information disclosure, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, and remote code execution risks, potentially affecting over 336,000 Prometheus servers and exporters exposed to the internet.
Prometheus, an open-source monitoring and alerting toolkit, has become indispensable in modern IT environments. However, its flexible architecture and modular components often lead to misconfigurations. Aqua Nautilus notes: “Exposed Prometheus servers or exporters, often lacking proper authentication, allowed attackers to easily gather sensitive information, such as credentials and API keys.”
The report identifies three major areas of concern:
- Information Disclosure: Publicly accessible Prometheus endpoints allow attackers to extract sensitive data. As Aqua Nautilus explains: “When Prometheus servers or exporters are connected to the public internet without authentication, they introduce a significant risk.” This includes revealing secrets like subdomains, Docker registries, and even internal API keys.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Vulnerability: Misconfigured debugging endpoints, such as
/debug/pprof, are an open door for attackers. Aqua Nautilus demonstrated how these endpoints could be exploited to “force the server to perform intensive profiling operations, consuming excessive CPU and memory resources.” Such attacks can lead to system crashes in Kubernetes pods or even render entire hosts inaccessible. - Remote Code Execution via RepoJacking: This supply chain attack allows malicious actors to hijack abandoned GitHub repositories for Prometheus exporters. The report warns: “Unsuspecting users following the documentation could unknowingly clone and deploy this malicious exporter, leading to remote code execution on their systems.”
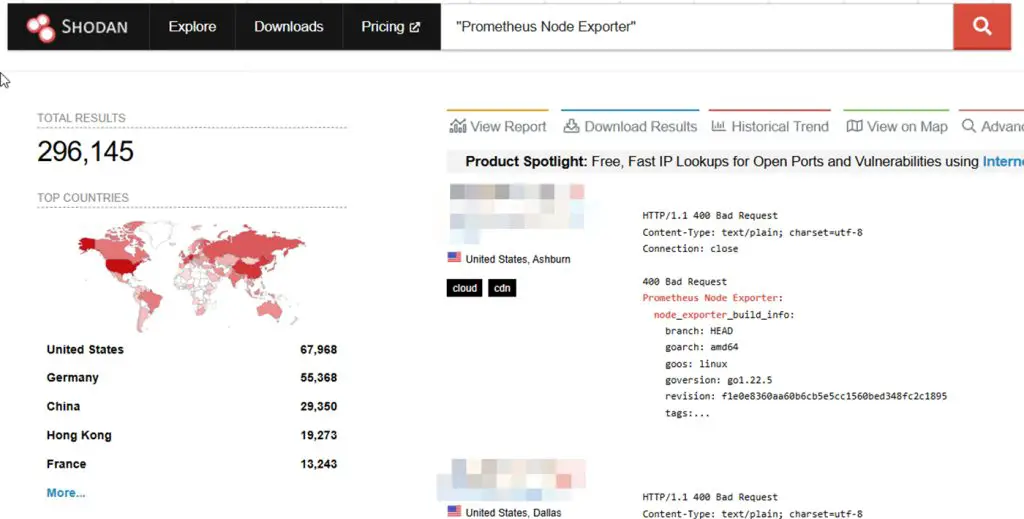
Using Shodan, Aqua Nautilus discovered over 296,000 internet-facing exporters and 40,000 Prometheus servers. This widespread exposure amplifies the risk to organizations, making them prime targets for cyberattacks.
One notable case involved an unauthenticated Prometheus instance associated with Skoda, a major European car manufacturer. Aqua Nautilus reported: “In addition to exposing Docker registries and images linked to Skoda, this Prometheus server also revealed subdomains and paths of Skoda through the kube_ingress_path metrics.” Skoda’s security team mitigated the risk by blocking public access to the instance.
Aqua Nautilus emphasizes the urgent need for better practices in securing Prometheus deployments. They conclude: “Exposing Prometheus components without authentication introduces significant security risks.”
Related Posts:
- Authentication Bypass in Open-Source Prometheus Project
- 35 Million Devices Vulnerable: Matrix DDoS Campaign Highlights Growing IoT Threat