In the realm of telecommunication, a new vulnerability, CVE-2023-51443, has emerged, casting a shadow over FreeSWITCH, an open-source communication framework integral to many of the world’s telephony infrastructures. Maintained by SignalWire, FreeSWITCH is crucial for deploying telecom solutions in the cloud, with over 5,000 businesses globally depending on it daily.
CVE-2023-51443, with a CVSS score of 7.5, exposes FreeSWITCH to potential Denial of Service (DoS) attacks during the delicate handshake phase of DTLS protocol, used in SRTP for media setup. This vulnerability is triggered by a race condition, allowing continuous attacks that disrupt new DTLS-SRTP encrypted calls.

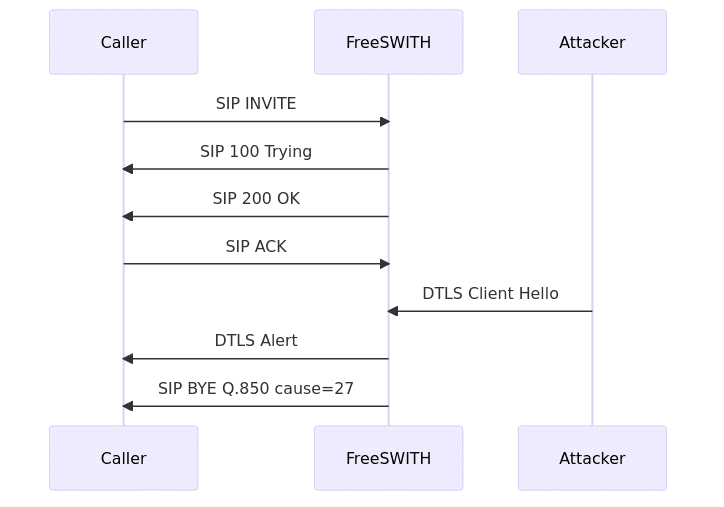
Discovered by a security researcher from Enable Security, the flaw lies in the handling of DTLS ClientHello messages. When a ClientHello message with an invalid CipherSuite is sent to FreeSWITCH, it creates a DTLS error, leading to the media session and subsequent SIP signaling level being torn down. This vulnerability was confirmed in FreeSWITCH version 1.10.10.
“When handling DTLS-SRTP for media setup, FreeSWITCH is susceptible to Denial of Service due to a race condition in the hello handshake phase of the DTLS protocol. This attack can be done continuously, thus denying new DTLS-SRTP encrypted calls during the attack,” read the security advisory.
Hackers exploit this flaw by sending a ClientHello DTLS message with an invalid CipherSuite to the FreeSWITCH server. This triggers a DTLS error, leading to the breakdown of the media session and subsequent signaling level teardown.
The impact of this vulnerability is significant, threatening massive DoS on servers relying on DTLS-SRTP for calls. With versions up to 1.10.10 affected, upgrading to version 1.10.11 or later, which includes a security fix, is strongly recommended. This fix involves dropping packets from unvalidated addresses, enhancing the resilience of FreeSWITCH against such exploits.