Image: Tonmoy Jitu
macOS users, beware. A new, fully undetected (FUD) version of the AMOS Stealer is out in the wild — bypassing detection, evading virtual machines, and exfiltrating personal data with surgical precision. Security researcher Tonmoy Jitu took a deep dive into this stealthy threat, dissecting how it evades macOS defenses and steals credentials, crypto wallets, and more.
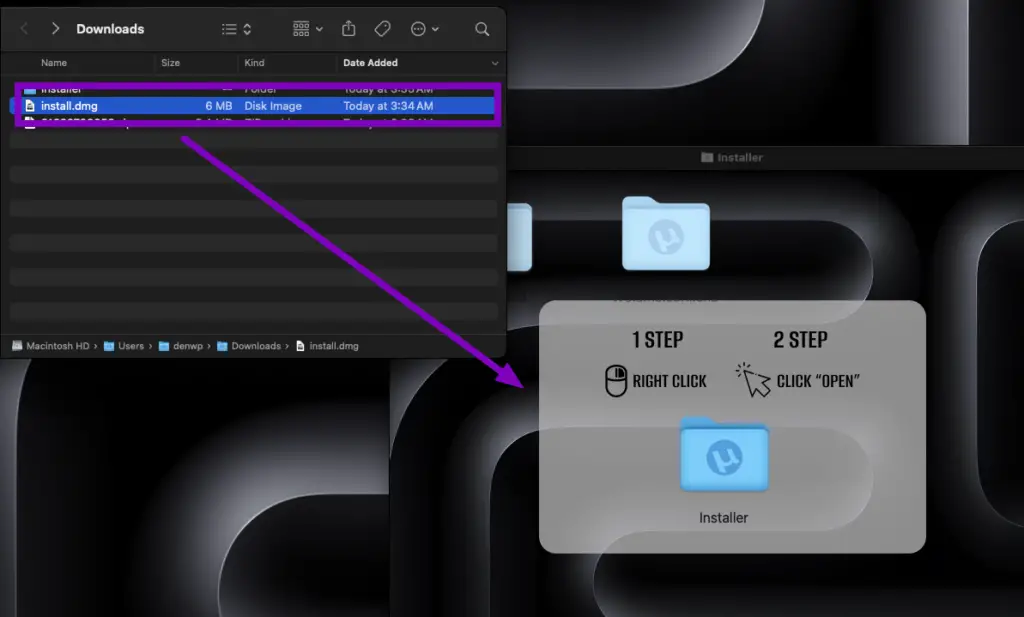
The malware is distributed via a DMG file named Installer_v2.7.8.dmg, leveraging a clever trick to bypass macOS Gatekeeper. Victims are instructed to right-click and select “Open” — a maneuver that sidesteps Apple’s verification mechanism.
“This technique is commonly used on macOS to bypass Gatekeeper… preventing unverified apps from running unless explicitly allowed by the user.”
The binary itself is a Mach-O universal binary, targeting both Intel (x86_64) and Apple Silicon (arm64) Macs, and signed with a valid code signature — adding an extra layer of legitimacy.
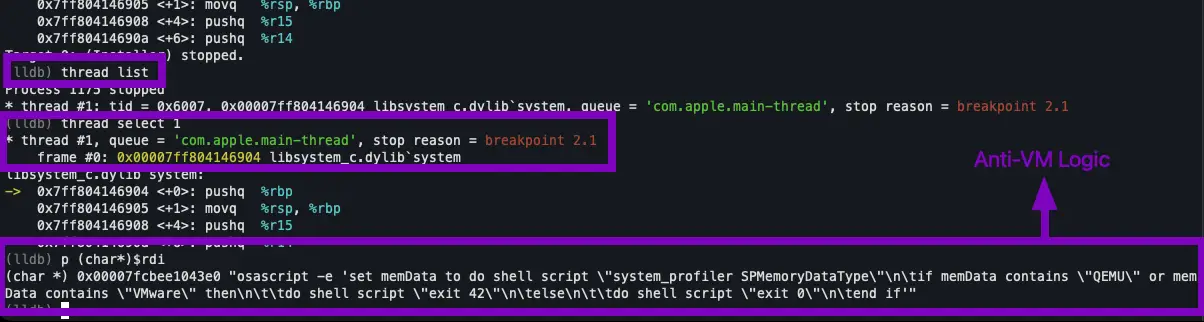
On March 11, 2025, the sample was fully undetected across 61 antivirus engines.
“The below sample screenshot… confirms the FUD status and shows no security vendors flagged it as malicious, with a community score of 0/61.”
Strings inside the binary appeared as random blobs — an early indication that the real payload was encrypted or encoded.
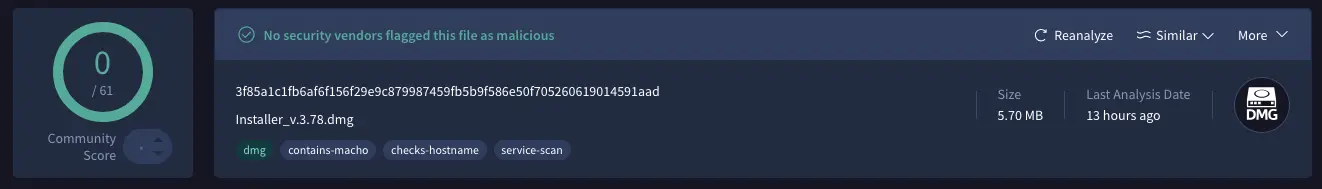
AMOS includes anti-VM logic to evade sandboxes. Jitu bypassed this using LLDB, setting breakpoints on functions like pthread_create, sysctl, and system to neutralize its checks.
“This malware remained undetected… thanks to a single anti-VM command that halts execution on QEMU and VMware virtual machines.”
A key osascript command was discovered that checks for QEMU or VMware:
Jitu patched the return value to trick the binary into thinking it’s running on real hardware, allowing the malware to continue and reveal its malicious intent.
After stepping through the logic, the true osascript payload was dumped using a custom LLDB Python script. The payload performs several key functions:
Stealth
-
Hides its Terminal execution.
-
Kills the Terminal app post-execution using pkill.
File Collection
-
Grabs .txt, .pdf, .docx, .wallet, .key files from user folders.
-
Targets browser data (cookies, logins, extensions) from:
-
Chrome, Brave, Edge, Opera, Firefox.
-
-
Extracts desktop cryptocurrency wallet data (e.g., Electrum).
-
Steals Telegram session files.
Password Theft
-
Attempts to retrieve Chrome’s master password
-
Prompts users with a fake macOS dialog pretending to be from “System Preferences.”
Exfiltration
-
Archives stolen files into /tmp/out.zip.
-
Uploads via curl to: hxxp[://]95[.]164[.]53[.]3/contact
“It leverages AppleScript to perform a variety of malicious tasks, including stealing browser data, cryptocurrency wallet information, and personal files.”
Related Posts:
- Atomic Stealer Malware Returns in New Disguises, Targets Mac Users’ Sensitive Data
- New Mac Stealer “AMOS” Poses as Loom Screen Recorder, Targets Crypto Wallets
- 10,000 WordPress Websites Compromised to Deliver macOS and Windows Malware
- The Rise of Mac Malware: 2024 Threat Report Reveals Alarming Trends
- FakeSG Campaign, Akira Ransomware, AMOS Stealer: Kaspersky Uncovers Malware Variety