In an era where digital security is paramount, vigilance is our watchword. A recent vulnerability uncovered in Apache HTTP Server has shone a spotlight on the importance of keeping our systems updated and secure. This particular bug, designated CVE-2023-25690, has a severity level of 9.8, falling within the critical range on the CVSS score.
CVE-2023-25690 affects Apache HTTP Server versions 2.4.0 through 2.4.55. Specifically, it is an exploit that takes advantage of certain mod_proxy configurations, leading to the potential for an HTTP Request Smuggling attack. The presence of such a high-level vulnerability in widely used server software underlines the need for consistent scrutiny and swift response in addressing security threats.

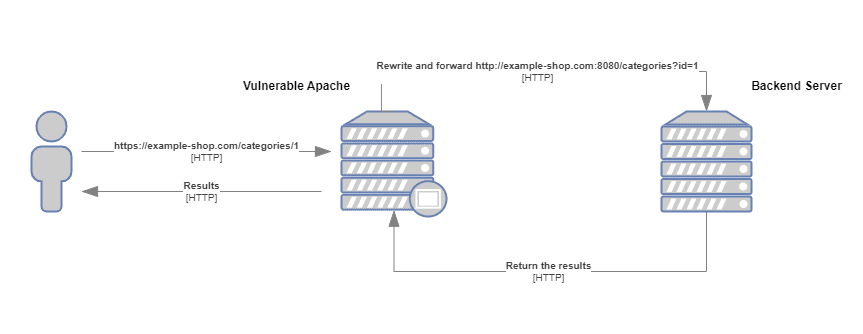
The root cause of this vulnerability lies in an error in mod_proxy when activated with a form of RewriteRule or ProxyPassMatch. As part of this fault, a non-specific pattern matches a portion of the user-supplied request-target data (URL) and is then reintroduced into the proxied request-target using variable substitution. The dire consequence of this action is the possibility of request splitting or smuggling.
Such a scenario poses a severe risk, as a remote attacker could exploit this vulnerability to circumvent access controls in the proxy server, thereby proxying unintended URLs to existing origin servers. Furthermore, this could lead to cache poisoning, a serious threat to data integrity and server security.
Security researcher DSkfunk, who brought this issue to light, not only shared a proof of concept (PoC) for the CVE-2023-25690 vulnerability but also published an in-depth write-up detailing the methods leveraged by the exploit. This contribution to the cybersecurity community serves as a valuable resource in understanding and mitigating the risk posed by this vulnerability.
“The impact of this vulnerability is that it allows attackers to target and access internal applications that are meant to be hidden by the reverse proxy, potentially leading to unauthorized access, data leakage, or further exploitation,” the researcher wrote.
The technical detail and PoC for the CVE-2023-25690 bug are available on Github.
For Apache HTTP Server users, the recommended course of action is an immediate update to version 2.4.56 at a minimum. It’s a small step to safeguard against a potentially large problem.