Overview of the downloader’s behavior | Soure: JPCERT/CC
In August 2024, JPCERT/CC confirmed a targeted attack against a Japanese organization, believed to be the work of the threat group APT-C-60. This advanced campaign utilized legitimate services like Google Drive, Bitbucket, and StatCounter to deliver and control malware, showcasing a calculated approach to evading detection while compromising systems.
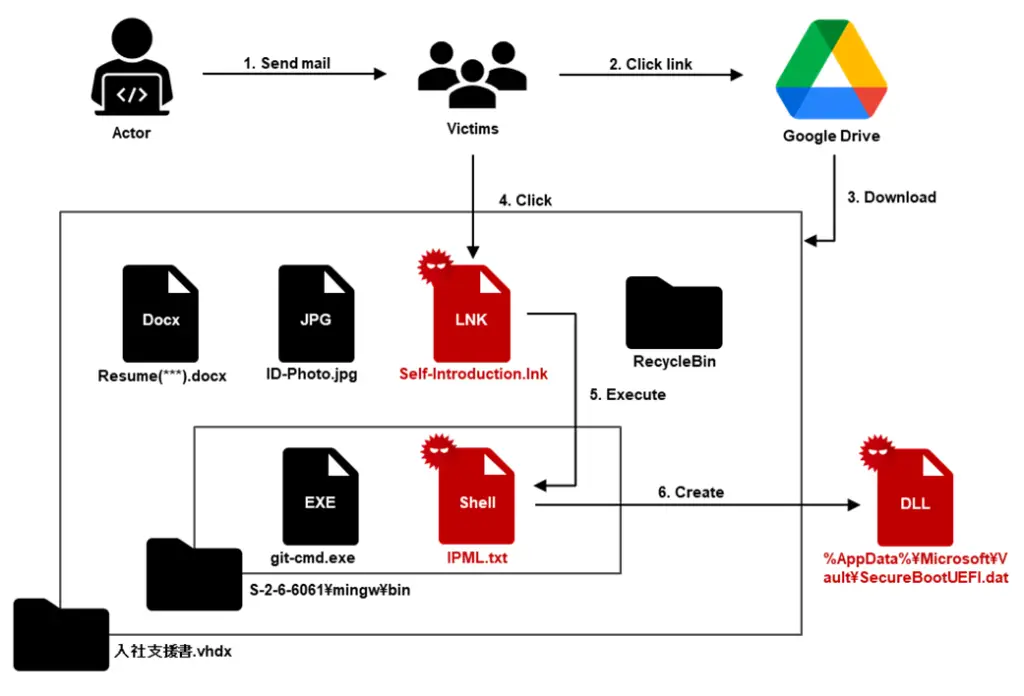
The attack began with a targeted phishing email disguised as a job application, which directed the recipient to download a file from a Google Drive link. The downloaded file, in VHDX format, contained malicious LNK files and decoy documents. When executed, the LNK file, named Self-Introduction.lnk, leveraged the legitimate git.exe to execute a malicious script.
“The LNK file Self-Introduction.lnk executes IPML.txt using the legitimate executable file git.exe,” JPCERT/CC reported. This process created a downloader named SecureBootUEFI.dat, which was made persistent through COM hijacking by registering its path in the system’s COM interface.
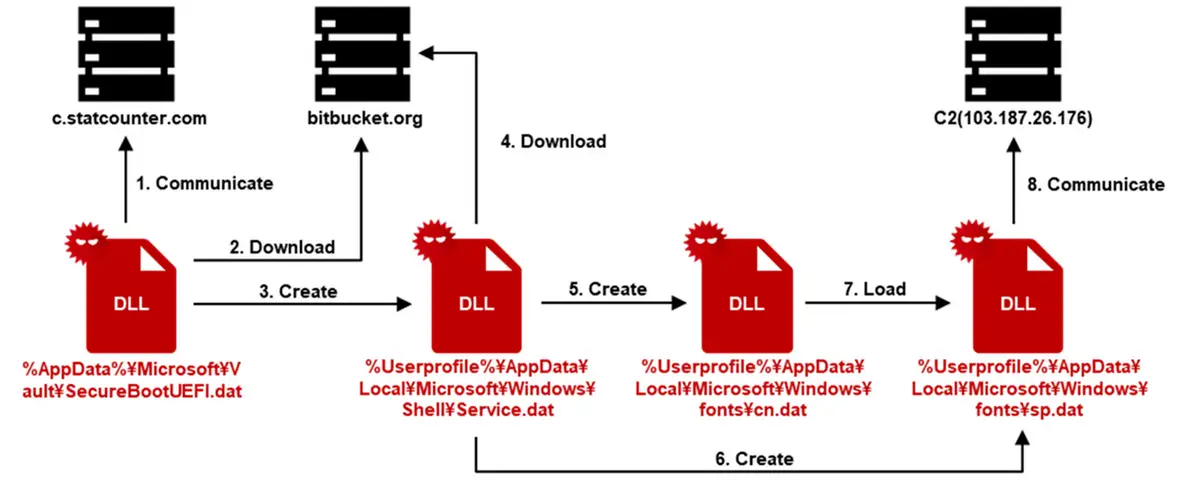
The malware accessed StatCounter as its first point of communication, gathering information about infected devices. It then uploaded its downloader to Bitbucket, where subsequent payloads were hosted. The use of legitimate platforms not only masked the attack’s intent but also complicated detection efforts.
“SecureBootUEFI.dat accesses Bitbucket using the URL path containing the encoded string included in the referrer, downloads Service.dat, decodes it using an XOR key, and executes it,” the report detailed. Additional payloads downloaded from Bitbucket were encoded and stored on the infected system, ensuring persistence through COM hijacking.
The malware’s backdoor component, identified as SpyGrace v3.1.6, exhibited advanced capabilities, including:
- Network connectivity checks.
- Execution of files in sensitive directories.
- Use of encryption keys (RC4 and AES) for secure communication with command-and-control (C2) servers.
The backdoor leveraged legitimate services to maintain stealth, eroding confidence in widely used platforms like StatCounter and Bitbucket.
“This attack needs careful attention because it exploits legitimate services such as Bitbucket and StatCounter, and also because it targets East Asian countries including Japan,” JPCERT/CC concluded.
Related Posts:
- AsyncRAT Malware Campaign Exploits Bitbucket to Deliver Multi-Stage Attack
- Bitbucket Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
- Urgent GitLab Update Patches Account Takeover Flaw, Other High-Severity Bugs
- Atlassian Bitbucket Data Center and Server RCE Vulnerability