Hackers are attempting to exploit a recently patched critical vulnerability (CVE-2023-6553) in the WordPress Backup Migration plugin that leads to remote code execution, in attacks that rely on publicly available proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code.
Rated a formidable 9.8 out of 10 in severity, CVE-2023-6553 is a vulnerability that opens the door to remote code execution. Discovered by the adept bug hunting team, Nex Team, and reported to Wordfence under a newly initiated bug bounty program, this security bug poses a significant threat to WordPress websites.
The vulnerability lies within the Backup Migration plugin, a tool designed to automate site backups to local storage or a Google Drive account. Specifically, it affects all plugin versions up to and including 1.3.6. Exploitation of this bug allows unauthenticated attackers to inject malicious PHP code through the `/includes/backup-heart.php` file, enabling them to execute arbitrary commands on the server hosting the WordPress site.

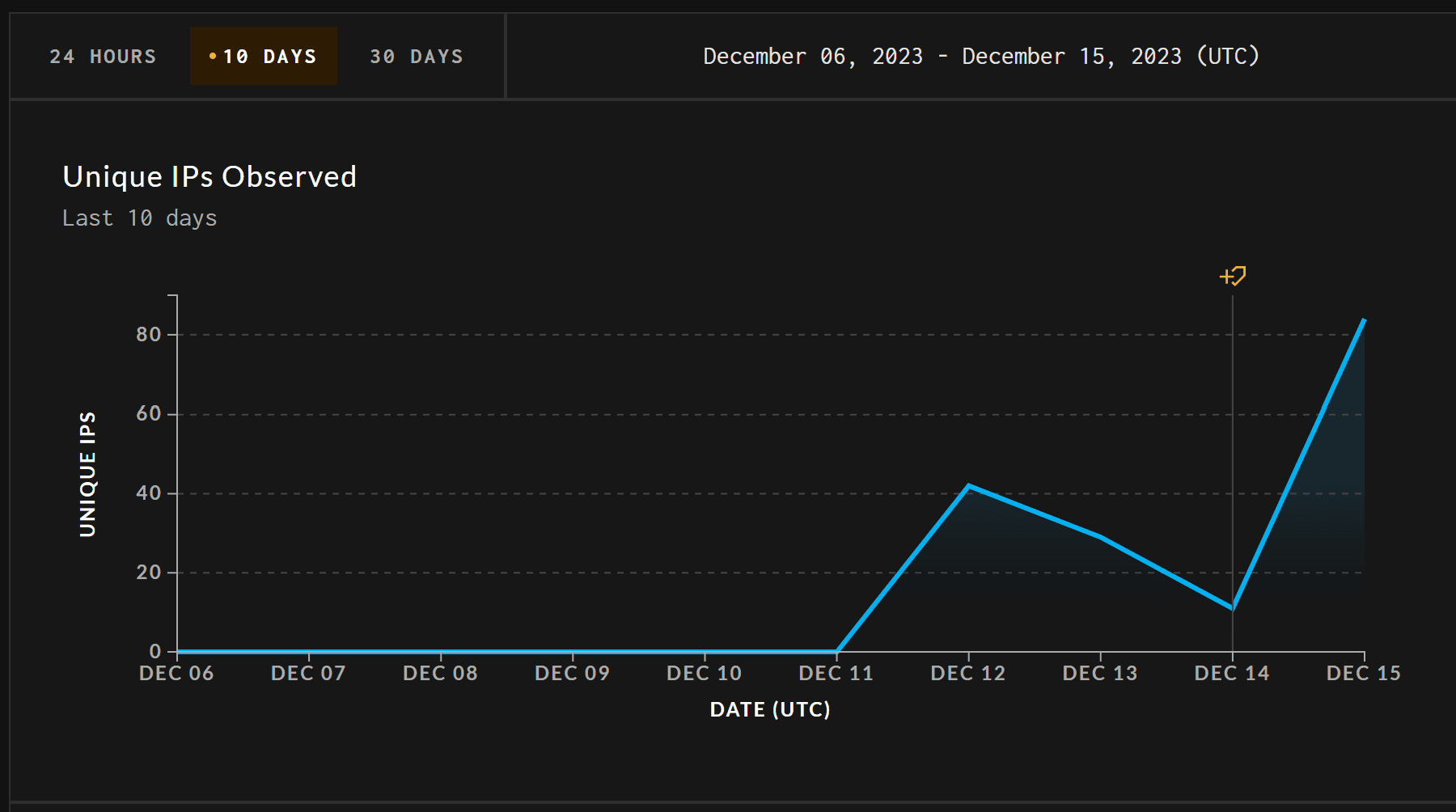
As per GreyNoise Intelligence, a cybersecurity firm, there have been observed attempts at exploiting this vulnerability. These efforts follow the public release of a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code, making the threat more imminent and real.
The CVE-2023-6553 vulnerability’s discovery and the subsequent publication of a technical write-up, coupled with the release of a PoC exploit code, have led to increased attention from threat actors. These developments have elevated the risk of exploitation attempts, making it imperative for website administrators to act swiftly.
For WordPress site administrators using the Backup Migration plugin, the following steps are crucial:
1. Immediate Update: Ensure that the plugin is updated to the latest version beyond 1.3.6, where the vulnerability has been patched.
2. Regular Monitoring: Keep a vigilant eye on website activities and logs to detect any unusual behavior.
3. Enhanced Security Measures: Implement additional security measures like firewalls, regular security audits, and the use of security plugins to fortify the website.