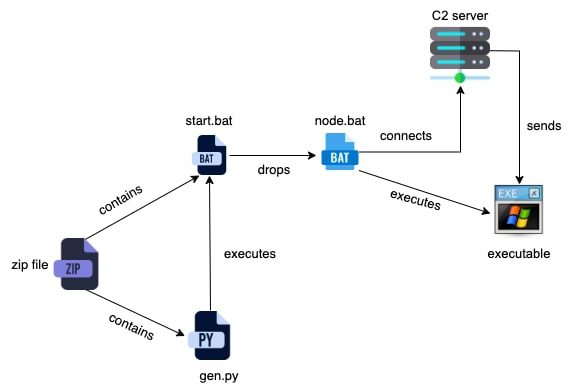
Infection chain | Image: Trellix Advanced Research Center
A new report from Trellix Advanced Research Center has exposed the inner workings of Celestial Stealer, a sophisticated Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) platform targeting developers, gamers, and cryptocurrency users. The JavaScript-based infostealer is disguised as seemingly legitimate applications, employing advanced obfuscation and anti-detection measures to extract sensitive data from compromised systems.
Celestial Stealer operates as a MaaS offering marketed on Telegram, with subscription plans available on a weekly, monthly, or lifetime basis. It is primarily designed for Windows 10 and 11 and is distributed either as an Electron application or a NodeJS single application. According to Trellix: “This stealer targets both Chromium and Gecko-based browsers, along with applications such as Steam, Telegram, and cryptocurrency wallets like Atomic and Exodus.”
The malware employs anti-analysis techniques, including checks for specific usernames and computer names, to evade detection. Its creators claim the stealer is “Fully Undetectable (FUD),” verified through submissions to VirusTotal.
Trellix identified several infection chains for Celestial Stealer:
- Discord Promotion Generator: A malicious tool disguised as a Discord utility executes the stealer by decoding and running a Base64-encoded payload.
- VR Chat NSFW Application: Promoted as a VR Chat enhancement tool, it entices victims to download a stealer-laden executable.
Once executed, the stealer connects to its command-and-control (C2) servers for payload delivery and data exfiltration.
Celestial Stealer exhibits a wide range of malicious functionalities:
- Data Theft: Extracts sensitive data such as cookies, passwords, autofill details, and credit card information from browsers and cryptocurrency wallets.
- Application Injection: Injects malicious payloads into popular applications like Discord and Exodus, intercepting user credentials and payment details.
- Persistence: Copies itself to the startup folder to ensure execution on system boot.
- Anti-Detection: Incorporates obfuscation techniques such as control-flow flattening, junk code insertion, and anti-sandbox checks.
Trellix explained: “The sample checks for the timestamp in various functions. If the system date is before or after a certain date, the executable will either terminate itself or start an infinite loop.”
The malware employs diverse data exfiltration methods, including:
- Leveraging Discord webhooks, Telegram bots, and file-sharing platforms like gofile.io for data transmission.
- Direct communication with C2 servers such as
admin.celestial-stealer[.]dev. - Updates in later samples replaced legitimate services with custom C2 infrastructure for greater control.
Celestial Stealer exemplifies the growing threat posed by MaaS platforms, blending technical sophistication with a commercialized distribution model. As Trellix emphasized: “Infostealers represent a serious risk to user security, capable of extracting sensitive data such as passwords, cookies, and more.”
For more details, see Trellix’s comprehensive analysis here.
Related Posts:
- Operation Celestial Force: A Persistent Multi-Component Threat Targeting Indian Entities
- OneDrive Users Targeted in Sophisticated Phishing and Downloader Campaign
- CVE-2024-5671 (CVSS 9.8) Exposes Trellix Intrusion Prevention System to Remote Attacks
- Malicious PyPI Packages Expose User Credentials
- Fickle Stealer: The New Rust-Based Malware Masquerading as GitHub Desktop