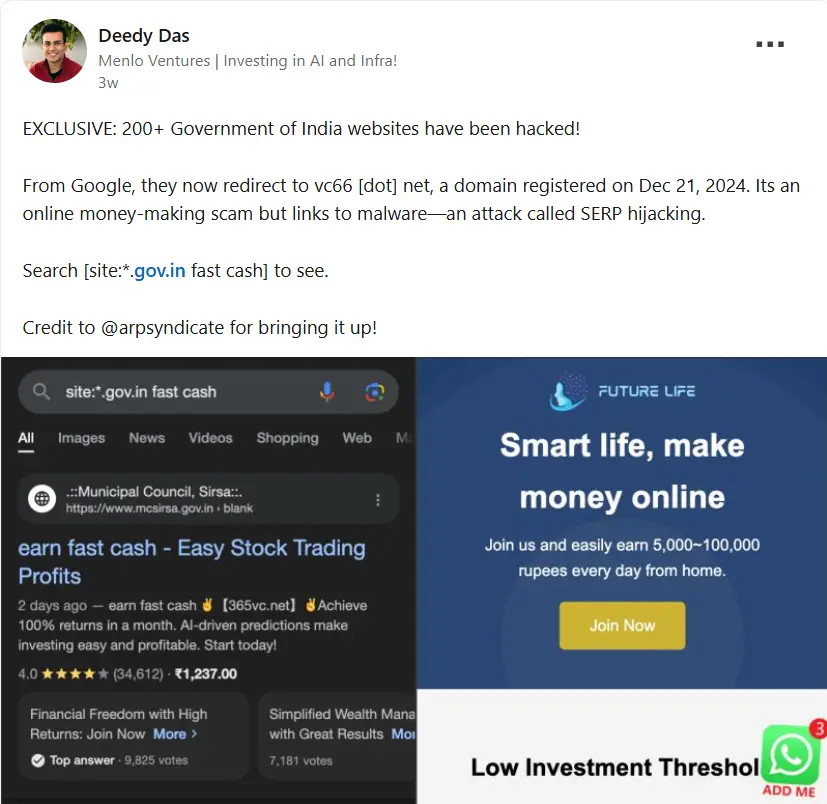
Linkedin Post
Researchers at CloudSEK have uncovered a large-scale Search Engine Poisoning (SEP) campaign targeting Indian government, educational, and financial websites. The attack, orchestrated by cybercriminals, manipulates search engine rankings to mislead users, redirecting them to rummy and investment-focused scam sites.
The report notes that over 150 Indian government portals (those using .gov.in and .ac.in domains) have been affected, amplifying concerns about cyber hygiene and security across critical sectors. “Indian Government websites, Educational Websites and well-known Financial brands have been affected in scale, by SEO Poisoning, leading to user traffic being redirected to sketchy websites promoting rummy, and other investment-focused games,” the CloudSEK report states.
Search Engine Poisoning (SEP) is a deceptive technique where cybercriminals manipulate search engine algorithms to rank fraudulent or harmful content higher in search results. Users searching for legitimate information unknowingly land on malicious sites, often leading to scams, phishing attempts, or malware infections.
CloudSEK researchers identified multiple black-hat SEO tactics used in this campaign, including:
- Referrer Header Manipulation – A technique where JavaScript injections alter the referrer headers to mislead search engines and users.
- Cloaking – Cybercriminals display different content to search engine crawlers and human users, making it difficult to detect fraudulent pages.
- Keyword Stuffing – Attackers embed trending keywords and financial brand names to improve search rankings.
- Backlinking Abuse – Fraudulent link farms artificially inflate the ranking of scam websites, making them appear more credible.
- Exploiting System Vulnerabilities – Threat actors exploit CMS vulnerabilities to inject malicious scripts and host deceptive content.
One of the most sophisticated aspects of this campaign is how users are redirected based on device type and user-agent. The CloudSEK report highlights how a malicious JavaScript snippet embedded in government websites determines whether a visitor should be redirected to a scam site.
The script:
- Retrieves the referrer URL to check if the visitor came from a search engine.
- Detects mobile users using predefined user-agent strings (e.g., “iPhone” and “Android”).
- Redirects them to rummy scam sites (such as yono-allslots[.]com, which further redirects to indorummy[.]net).
Researchers confirmed this redirection by tweaking browser settings using Google Developer Tools. They found that desktop users were instead served a 404 error page, reinforcing the presence of user-agent cloaking.
“The script was working as intended, and it goes on to demonstrate how stealthily threat actors are operating, in a way that more than meets the eye,” CloudSEK researchers stated.
Rummy has a massive following in India, with both casual players and high-stakes gamblers engaging in online platforms. Fraudsters leverage this popularity by luring victims with cash prizes and referral bonuses.
CloudSEK’s report warns that these games operate like Ponzi schemes, trapping users in a cycle of increasing bets and financial losses. The researchers draw parallels to investment scams, where victims are enticed to “upgrade” to VIP levels for higher rewards—only to be defrauded.
One of the key drivers behind the SEO poisoning campaign is black-hat backlinking. Researchers found that fraudulent rummy sites are extensively promoted via spam links on financial brand-related web pages.
One alarming discovery was that the scammers infiltrated Indian banking keywords by:
- Stuffing search results with loan and credit card-related terms to mislead users.
- Using government subdomains in keyword stuffing (e.g., Telangana state government pages were found promoting rummy games).
- Creating interlinked scam pages (a link farm) to manipulate search rankings.
CloudSEK researchers found that some Telegram groups and freelancer platforms like Fiverr are being used to buy and sell SEO manipulation services.
“A common Telegram handle was found to be linked within these websites for backlinking consultation. The handle has since been inactive,” CloudSEK researchers revealed.
The fraudulent rummy websites are backed by a large-scale infrastructure spread across multiple hosting services, including Cloudflare and Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Investigators identified 12 IP addresses associated with scam sites using keywords such as “rummy,” “bet,” and “vip.” Notably, these sites are hosted under Cloudflare’s AS13335 and Amazon’s AS16509, giving them a layer of anonymity and protection against direct takedown.
CloudSEK warns, “The presence of multiple A records in the same IP range indicates that the domains are using multiple IP addresses for load balancing, redundancy, or performance optimization.”
Interestingly, this phenomenon isn’t confined to India. Researchers also identified a similar campaign in Malaysia, where government websites were being used to promote online gambling and rummy platforms.
A LinkedIn post uncovered by CloudSEK researchers revealed that Malaysian authorities are dealing with an identical black-hat SEO infiltration, indicating a global pattern of abuse.
“It further goes on to establish the truth that insecure infrastructure will always be immune to unethical activities, if secure coding practices and failure to safeguard critical infrastructure is not followed. This is not an isolated incident,” CloudSEK stated.
For now, organizations must focus on strengthening their web security, ensuring file upload restrictions, and proactively monitoring SEO manipulations.
Related Posts:
- Security Alert: Hackers Can Access Google Accounts Without Passwords
- Threat Actors Exploit Fake Brand Collaborations to Target YouTube Channels
- Hacker forged Windows 11 upgrade website to trick users to download the virus
- SEO Poisoning: Unmasking the Malware Networks Behind Fake E-Commerce
- New Phishing Trend: Generic Pages Impersonate Any Brand