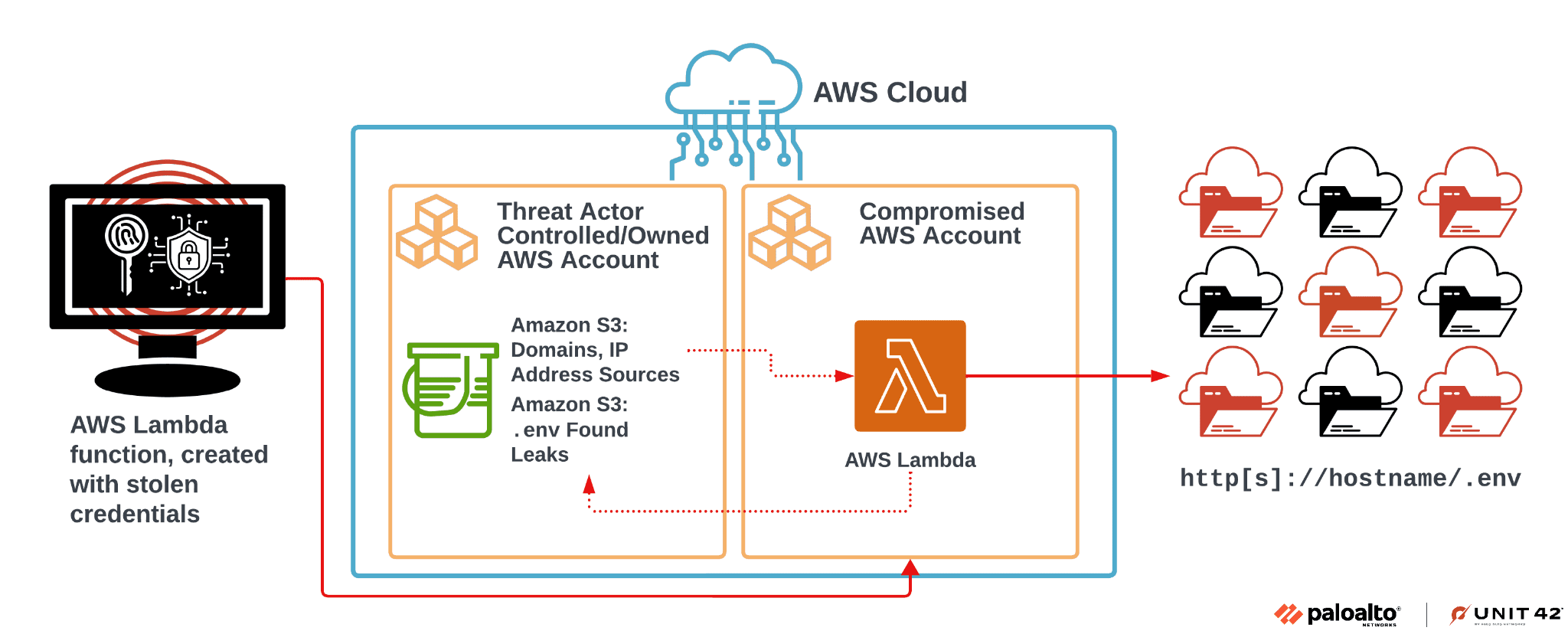
High-level example of the threat actor's operational architecture | Image: Unit 42
Palo Alto Networks has uncovered a large-scale ransomware campaign that has impacted over 100,000 domains. The perpetrators exploited misconfigured ENV files in AWS to gain access to data stored in the cloud and subsequently demanded ransom for the stolen information.
The attack was characterized by a high degree of automation and a deep understanding of cloud architecture. The primary user errors in cloud services that allowed data to be compromised included: a lack of protection for environment variables, the use of persistent credentials, and inadequate measures for privilege restriction.
By exploiting these vulnerabilities, the attackers gained access to victims’ cloud storage and demanded payment by placing ransom notes within the compromised environments. The data itself was not encrypted but simply extracted, enabling the attackers to blackmail the victims with the threat of data leaks.
The attack unfolded on Amazon Web Services (AWS) platforms, where the attackers established their infrastructure, scanning over 230 million unique targets in search of sensitive information. To evade security systems, they utilized the Tor network, VPNs, and VPS.
As a result of the attack, 110,000 domains were compromised, and over 90,000 unique variables were discovered in .env files. Among these, 7,000 were linked to cloud services, and 1,500 to social media accounts.
The success of the attack was largely due to configuration errors within the affected organizations, which inadvertently made the .env files publicly accessible. ENV files often contain access keys and other sensitive data, which allow attackers to gain initial access and escalate their privileges within the victims’ cloud environments.
An analysis of the attack revealed that the attackers used API requests to gather information about the AWS environment and services, including IAM, S3, and SES, to further expand their influence over the victims’ cloud infrastructures. They also attempted to escalate their privileges by creating new IAM roles with unrestricted access.
Organizations seeking to protect their cloud environments are advised to adhere to the principles of least privilege, use temporary credentials, and enable all possible event logging to monitor and detect suspicious activities. Enabling advanced Amazon security mechanisms, such as GuardDuty and CloudTrail, can also significantly enhance the protection of cloud resources.
Related Posts:
- Cybercriminals Evolve Social Engineering Tactics, Exploit CVE-2022-26923 in Sophisticated Campaign
- Iranian APT42 Ramps Up Phishing Campaigns Against Israel, U.S. Election Targets
- Tusk Campaign: Russian Cybercriminals Target Gaming & Crypto