CMSeeK v1.1.3 releases: Content Management Systems Detection and Exploitation suite
What is a CMS?
A content management system (CMS) manages the creation and modification of digital content. It typically supports multiple users in a collaborative environment. Some noteable examples are: WordPress, Joomla, Drupal etc.
Functions Of CMSeek:
- Basic CMS Detection of over 155 CMS
- Drupal version detection
- Advanced WordPress Scans
- Detects Version
- User Enumeration
- Plugins Enumeration
- Theme Enumeration
- Detects Users (3 Detection Methods)
- Looks for Version Vulnerabilities and much more!
- Advanced Joomla Scans
- Version detection
- Backup files finder
- Admin page finder
- Core vulnerability detection
- Directory listing check
- Config leak detection
- Various other checks
- Modular bruteforce system
- Use pre-made bruteforce modules or create your own and integrate with it
Changelog
- Added new CMS:
- Smartstore
- Solusquare Commerce Cloud
- Spree
- Brightspot CMS
- Amiro.CMS
- Weebly
- ekmPowershop
- GoDaddy Website Builder
- WHMCS
- Zen Cart
- OpenNemas CMS
- IPO CMS
- Version detection added for:
- Amiro.CMS
- GoDaddy Website Builder
- Added WordPress Bruteforce via XML-RPC
- improved logging for joomla scans
- improved logging for WordPress deep scan
- Switched to wpvulns.com for wordpress vulnerabilities
- Added
--light-scanargument - Added (
--only-cms,-o) argument
Installation
git clone https://github.com/Tuhinshubhra/CMSeeK cd CMSeeK python3 cmseek.py
Detection Methods:
CMSeek uses mainly 2 things for detection:
- HTTP Headers
- Page Source Code
Supported CMSs:
CMSeeK currently can detect 22 CMSs, you can find the list on cmss.py file which is present in the cmseekdb directory. All the cmss are stored in the following way:
Scan Result:
All of your scan results are stored in a json file named cms.json, you can find the logs inside the Result\<Target Site> directory, and as of the bruteforce results they’re stored in a txt file under the site’s result directory as well.
Here is an example of the json report log: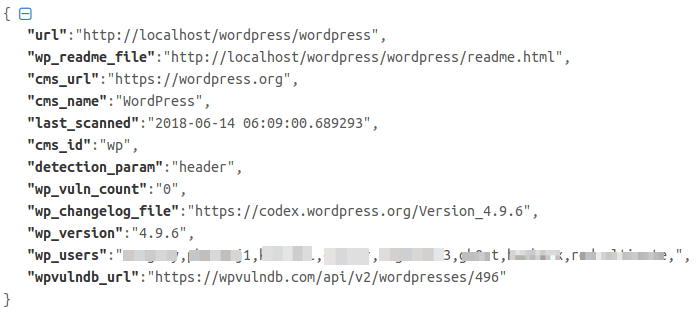
Bruteforce Modules:
It has a modular bruteforce system meaning you can add your custom made bruteforce modules to work with cmseek. A proper documentation for creating modules will be created shortly but in case you already figured out how to (pretty easy once you analyze the pre-made modules) all you need to do is this:
- Add a comment exactly like this # <Name Of The CMS> Bruteforce module. This will help CMSeeK to know the name of the CMS using regex
- Add another comment ### cmseekbruteforcemodule, this will help CMSeeK to know it is a module
- Copy and paste the module in the brutecms directory under CMSeeK’s directory
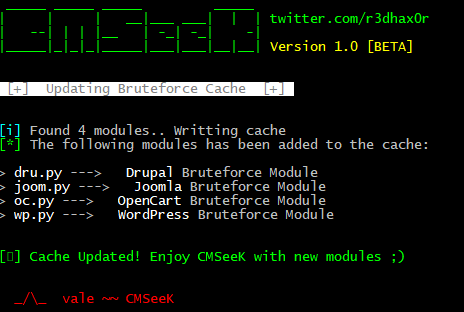
- Open CMSeeK and Rebuild Cache using U as the input in the first menu.
- If everything is done right you’ll see something like this (refer to screenshot below) and your module will be listed in a bruteforce menu the next time you open CMSeeK.

Main Menu
Scan Result
WordPress Scan Result
Disclaimer:
Usage of CMSeeK for testing or exploiting websites without prior mutual consistency can be considered as an illegal activity. It is the final user’s responsibility to obey all applicable local, state and federal laws. Authors assume no liability and are not responsible for any misuse or damage caused by this program.
Copyright (C) 2018 Tuhinshubhra
Source: https://github.com/Tuhinshubhra/