According to securityaffairs February 12, researchers from CSE’s CybSec ZLAB lab analyzed a sample set of Pallas malware families used by the Lebanese APT espionage team Dark Caracal in hacking operations. The analysis pointed out that the malware was able to collect a large amount of sensitive data for the target application and send it to the C&C server via an encrypted URL that was decrypted at a run time.
Actually, Dark Caracal has been active since 2012, but until recently it was found to be a formidable threat in the online arena.
According to previous reports, a joint investigation by the Electronic Frontier Foundation Frontier Foundation and the security company Lookout found that the Dark Caracal APT, a surveillance and espionage organization associated with the Lebanese General Security Agency, stole large amounts of data from Android phones and Windows PCs around the world and recently hackers Dark Caracal spyware platform sold to some countries to monitor. According to the researchers, this espionage has spread malware that contains trojans through the manufacture of large numbers of fake Android applications and using social projects such as phishing email or fake social network information, which has involved 21 countries from the past 21 countries Journalists, military personnel, companies and other sensitive information (SMS, call history, archives, etc.).
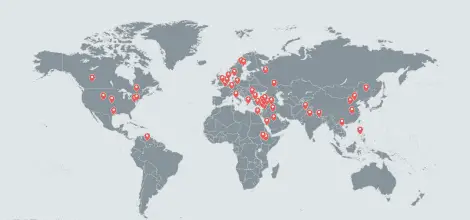
Dark Caracal Impact Area
Researchers said one of Dark Caracal’s most powerful advertising campaigns, which began in the first months of last year, uses a series of trojanized Android applications designed to steal sensitive data from victims’ mobile devices. It is reported that the Trojans injected into these applications are Pallas researchers have found.
So how do attackers step by step to steal data?
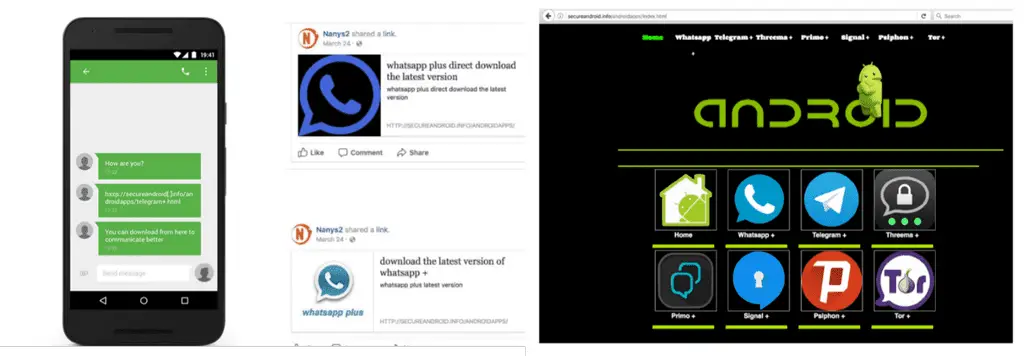
Attackers use “repackaging” technology to generate their malware samples by starting with a legitimate application and injecting malicious code before rebuilding the apk. In general, the target application belongs to a specific category, such as Whatsapp, Telegram, Primo), secure chat app (Signal, Threema), or software related to secure navigation (Orbot, Psiphon).
After the malware was made, attackers used social engineering techniques to trick victims into installing malware such as using SMS, Facebook messages, or Facebook posts to trick victimized users into downloading new and popular applications through a specific web address. Currently, these trojanized applications Are hosted on the same URL.

Pictured – Dark Caracal Repository – Malicious site
When a user’s device is infected, an attacker uses a malicious application to collect large amounts of data and send it to the C&C server through an encrypted URL that is decrypted at runtime.
The following is the specific function of the Trojan:
– read sms
– send text messages
– Record the call
– Read the call history
– Retrieve account and contact information
– Collect all stored media and send them to C2C
– Download and install additional malware
– Display a phishing window to attempt to steal credentials
– Retrieve a list of all devices connected to the same network
Read more
ZLAB Malware Analysis Report: Dark Caracal APT – The Pallas Family
Source: SecurityAffairs