A security researcher has published details and proof-of-concept (PoC) code for a Microsoft Windows Sysmon vulnerability that could be exploited to gain elevated privileges on the system.
Tracked as CVE-2022-41120 (CVSS score of 7.8), the security defect was identified and reported in June, with a patch available in the Patch Tuesday in November.
“An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could gain administrator privileges,” Microsoft wrote in its advisory.
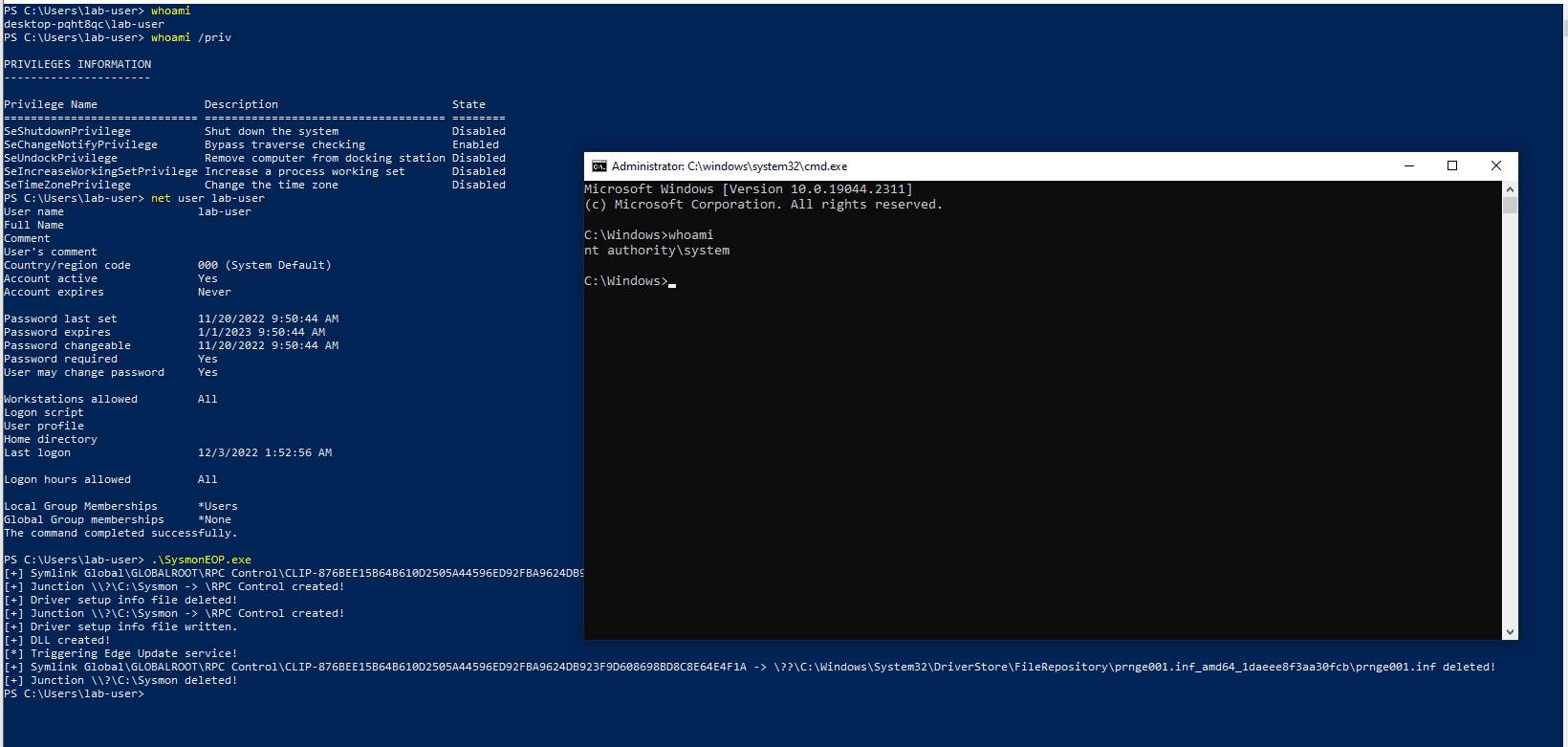
Wh04m1001 has made public a PoC code for CVE-2022-41120 that allows an attacker to achieve elevation from local user to SYSTEM admin.

“Vulnerability is in code responsible for ClipboardChange event that can be reached through RPC. Local users can send data to RPC server which will then be written in C:\Sysmon directory (default ArchiveDirectory) and deleted afterwards. In version before 14.11 Sysmon would not check if directory was created by low privilege user or if it’s a junction which can be abused to perform arbitrary file delete/write (kinda limited as you can only write strings) in context of NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM user,” researcher wrote.
By executing a specially-crafted program, an authenticated attacker could exploit this vulnerability to execute arbitrary code with higher privileges.
Wh04m1001 believed that Sysmon versions 12.0 – 14.12 are vulnerable as the ClipboardChange event was introduced in version 12.0.
CVE-2022-41120 PoC exploit is available on Github. In light of the release of the PoC, users that use vulnerable Windows versions are recommended to prioritize the patches to mitigate exploitation attempts.
“If you are using vulnerable version and cannot update you can create ArchiveDirectory (C:\Sysmon by default) and set permissions that will only allow access to NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM account,” the researcher added.