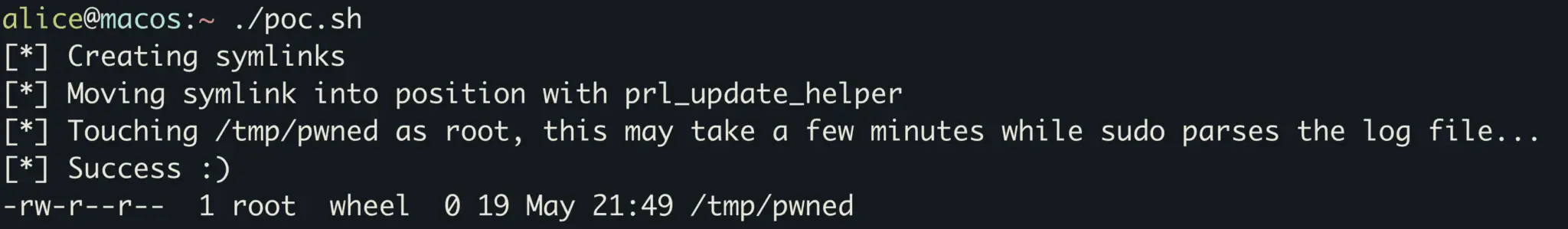
Proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code has been made available for a recently disclosed flaw, CVE-2023-50226 (CVSS 7.8), impacting Parallels Desktop.
At its core, CVE-2023-50226 is a privilege escalation vulnerability. It enables local attackers, those who already have access to the system with limited privileges, to gain elevated access and execute arbitrary code at the root level. This sort of vulnerability is particularly concerning because it can provide attackers with control over the entire system.
The flaw resides within the Updater service of Parallels Desktop. Attackers exploit this vulnerability by creating a symbolic link – a type of file that acts as a reference to another file or directory. Through this method, they can trick the service into moving arbitrary files, a classic example of exploiting file system operations for malicious gains.

What makes CVE-2023-50226 stand out is the availability of a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit. Published by the security researcher kn32 on GitHub, this PoC provides a practical demonstration of how the vulnerability can be exploited. While PoC exploits are invaluable for understanding and mitigating vulnerabilities, they also pose a risk as they can fall into the hands of malicious actors.
Recognizing the severity of this issue, Parallels swiftly released updates for affected versions. Versions 18.3.2 (53621) and 17.1.7 (51588), both released in July of the previous year, have patched this vulnerability, showcasing the company’s commitment to user security.
For users of Parallels Desktop, updating to the latest version is not just recommended, it’s essential for ensuring the security of their virtual environments.