A new critical-severity security vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-22120, has been discovered in Zabbix, the popular open-source IT infrastructure monitoring tool. With a CVSS score of 9.1, this time-based SQL injection flaw poses a significant risk to systems running affected versions of Zabbix, potentially allowing attackers to escalate privileges and even achieve remote code execution (RCE).

Zabbix is widely used to monitor various components of IT infrastructure, including networks, servers, virtual machines, and cloud services. By collecting and displaying essential metrics, Zabbix enables administrators to track the performance and health of their systems. However, the recent discovery of a critical vulnerability in its server audit log function underscores the importance of maintaining robust security practices.
The vulnerability resides in the Zabbix server’s audit logging mechanism. When the server executes commands for configured scripts, it logs the actions in an “Audit Log.” Unfortunately, the clientip field within this log is not properly sanitized, opening the door for a time-based blind SQL injection attack.
The flaw was pinpointed in the audit.c file, specifically within the zbx_auditlog_global_script function.
Since the clientip field is controlled by the attacker and not sanitized, malicious SQL queries can be injected into this field. This type of SQL injection can only be exploited using time-based methods, but it is potent enough to extract sensitive data from the database and escalate user privileges to admin levels. In certain scenarios, this SQL injection could even lead to remote code execution (RCE).
The vulnerability was discovered and reported by security researcher Maxim Tyukov, also known as mf0cuz, through the HackerOne bug bounty platform. Tyukov provided technical details and a proof-of-concept (PoC) to demonstrate the exploitability of the flaw, emphasizing the urgency of addressing this security gap.
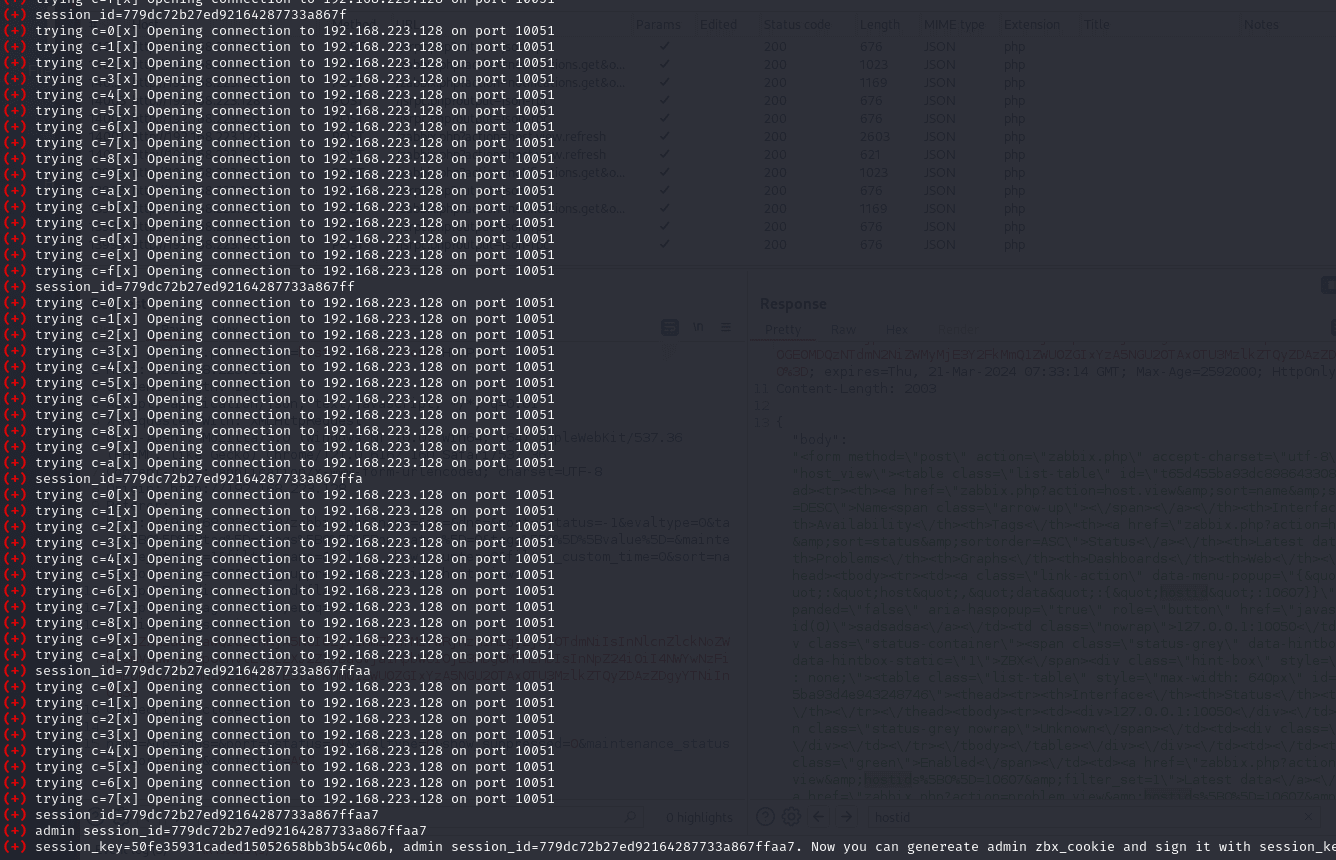
The potential impact of CVE-2024-22120 is substantial. Exploiting this vulnerability allows attackers to dump any values from the database, including sensitive information. Moreover, privilege escalation from a regular user to an admin can significantly compromise the security and integrity of the monitored IT infrastructure. In extreme cases, successful exploitation can lead to remote code execution, further endangering the targeted systems.
All Zabbix versions from 6.0.0 to 6.4.12 and 7.0.0alpha1 to 7.0.0beta1 are vulnerable to this SQL injection attack. Organizations using any of these versions should take immediate action to mitigate the risk.
The Zabbix team has released patches to address the vulnerability in versions 6.0.28rc1, 6.4.13rc1, and 7.0.0beta2. All Zabbix users must upgrade to these patched versions as soon as possible. Additional security measures, such as web application firewalls (WAFs) and intrusion detection systems (IDS), can also help protect against this type of attack.