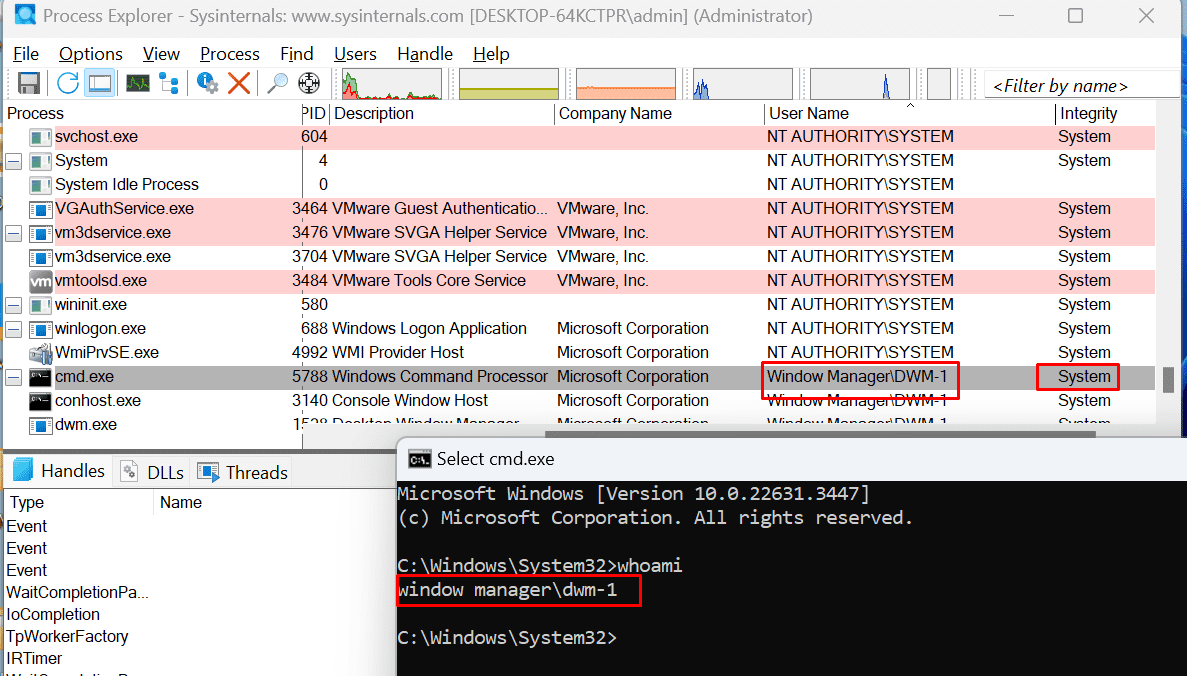
Security researchers published the technical details and a proof-of-concept exploit (PoC) code for a zero-day vulnerability in Windows, tracked as CVE-2024-30051, which could allow attackers to escalate their privileges to SYSTEM level. This critical flaw, rated 7.8 on the CVSS scale, is caused by a heap-based buffer overflow in the Desktop Window Manager (DWM) core library. Exploitation of this vulnerability can result in arbitrary code execution with system-level privileges, opening the door to potential malware attacks, including the deployment of payloads like QakBot.
The vulnerability stems from a size miscalculation error in the dwmcore.dll library, which is responsible for rendering Windows’ graphical user interface elements, including 3D transitions and glass window frames. Discovered by Kaspersky researchers, the flaw exists in the CCommandBuffer::Initialize method of the DWM library. This bug can be exploited by a local user to trigger a heap overflow, allowing them to execute arbitrary code with SYSTEM integrity.
An attacker can craft a DLL and load it into the DWM process, which will run with elevated privileges, enabling the attacker to take control of the system. The CVE-2024-30051 vulnerability affects various Windows versions, and the proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code has been made publicly available on GitHub, increasing the urgency for patching.
The exploit for CVE-2024-30051 involves a series of steps where the attacker performs a heap spray in the DWM process to manipulate memory. By releasing specific parts of the sprayed heap, a heap overflow is triggered in dwmcore.dll, leading to the execution of the attacker’s code. Once the exploit succeeds, the attacker can launch a command prompt or load malicious code with full SYSTEM privileges.
In real-world attacks, this vulnerability has been exploited to deliver malware such as QakBot, which is commonly used for credential theft and ransomware distribution. The ability to escalate privileges makes this flaw particularly dangerous, as it allows attackers to bypass many security controls and gain complete control over compromised systems.
Microsoft has patched CVE-2024-30051 in its May 2024 Patch Tuesday update. Users and system administrators are strongly encouraged to apply this patch immediately to prevent exploitation. Given the public availability of the PoC exploit code, unpatched systems are at a heightened risk of attack.
In addition to applying the patch, organizations should monitor their networks for any suspicious activity. Antivirus tools and endpoint detection solutions should be updated to recognize indicators of compromise associated with this vulnerability.
Related Posts:
- CVE-2024-30051: Windows Zero-Day Vulnerability Exploited to Deliver QakBot Malware
- Microsoft Patches Actively Exploited 0-Day Flaws (CVE-2024-30040 & CVE-2024-30051)
- Chrome 0-day Bug Under Active Attacks
- Apple backports fix for actively exploited 0-day to older macOS and iPhone/iPad devices