CVE-2024-5452: Critical PyTorch Lightning Vulnerability Exposes AI Models to Remote Hijacking
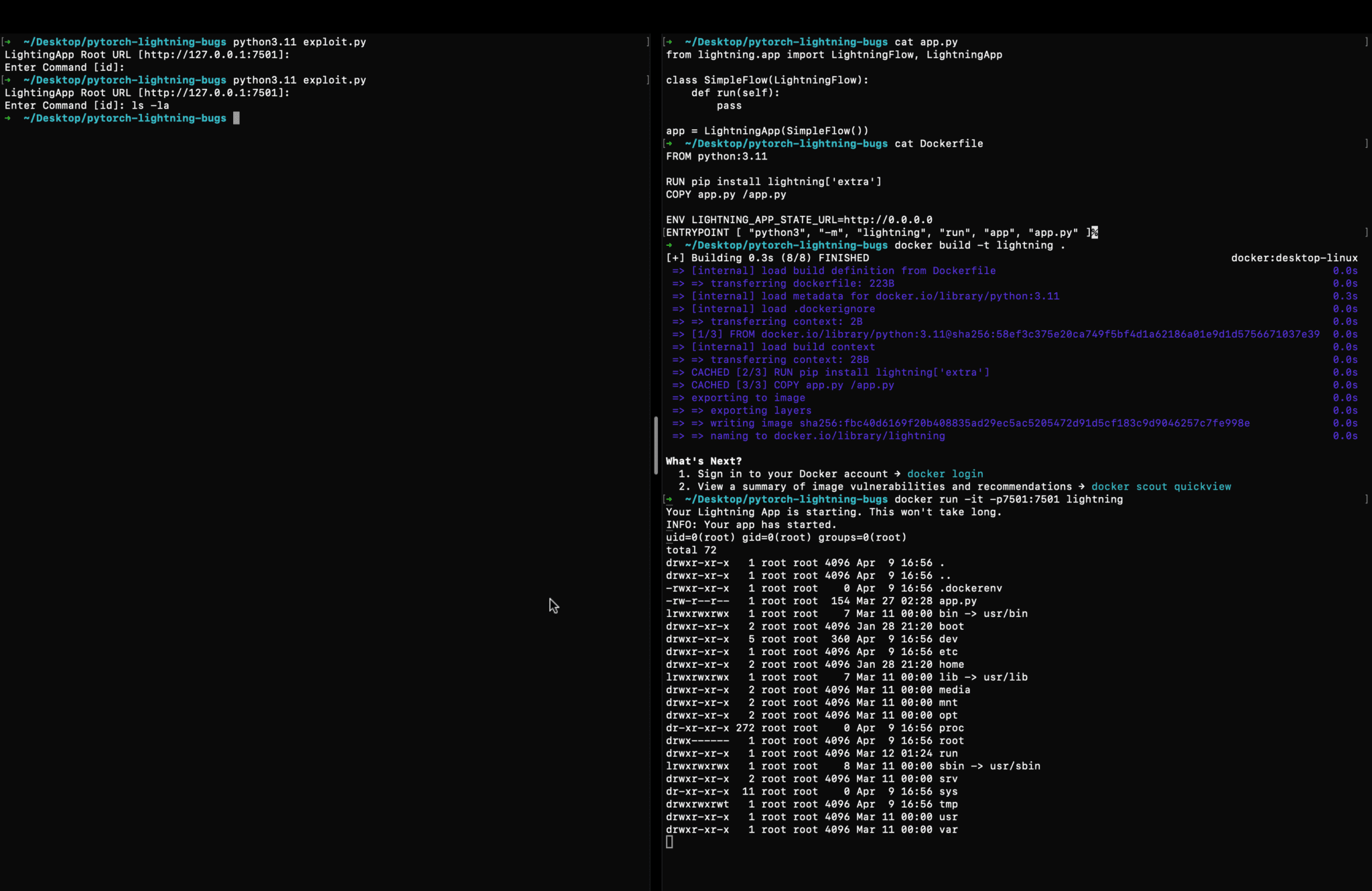
A severe remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability has been discovered in PyTorch Lightning, a widely-used framework for accelerating machine learning research and development. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-5452 (CVSS 9.8), enables attackers to remotely manipulate the entire application state, potentially leading to complete system takeover.
The flaw stems from improper handling of deserialized user input and the mismanagement of “dunder” (double underscore) attributes by the deepdiff library, which PyTorch Lightning employs to manage application state. A security researcher known as chilaxan identified the issue and published a proof-of-concept exploit code, raising alarms across the AI and machine learning community.
The implications of this vulnerability are profound. Attackers can manipulate the entire application state, including critical internal classes and attributes, leading to full remote code execution. This allows unauthorized individuals to execute arbitrary code on the server, potentially leading to data breaches, system compromise, and further network infiltration.
CVE-2024-5452 affects PyTorch Lightning version 2.2.1. Due to the framework’s popularity and its use in numerous research and production environments, the potential impact of the exploit is significant. Any self-hosted PyTorch Lightning application is vulnerable in its default configuration, as the endpoint responsible for processing user input is enabled by default.
Security experts strongly recommend that users immediately upgrade to a patched version of PyTorch Lightning if available, or disable the vulnerable endpoint as a temporary mitigation. Additionally, organizations utilizing PyTorch Lightning are urged to review their systems for any signs of compromise and monitor for suspicious activity.